Recommended
PDF
Storytelling For The Web: Integrate Storytelling in your Design Process
PDF
2024 Trend Updates: What Really Works In SEO & Content Marketing
PPTX
Calcium as a Regulatory and Signalling ion
PPT
Calcium channels –physiology and Therapeutics uses..
PPTX
Calcium in Neuronal Homeostasis
PPTX
PDF
Calcium entry channels in non excitable cells 1st Edition Juliusz Ashot Kozak
PPTX
ASSESSMENT OF ABNORMALITIES IN AUTONOMIC FUNCTION IN PATIENTS.pptx
PPTX
Introduction to Geriatric Nursing,Theory
PPTX
WHEN NOT TO DO TENDOACHILLES TENOTOMY.pptx
PPTX
BENIGN BREAST DISEASES BBD/ Fibroadenoma, Fibrocystic Diseases/ ANDI.pptx
PPTX
Tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis
PDF
The Doctor's Balance Sheet By Dr Kanhu Charan Patro
PPTX
Sample Acceptance-Rejection-Criteria in lab
PPTX
CTEV [ clubfoot] DR ARUN LAL ,DR MOHAMED ASHRAF travancore medical college k...
PDF
ARCHES OF FOOT -Prof.Dr.N.Mugunthan. KMMC Medical College & Hospitals.pdf
PPTX
TRIGEMINAL NERVE trigeminal nuclei .pptx
PPTX
PRODUCTION OF ANTIBIOTICS e.g (Penicillin)
PDF
Seminario biología molecula - EBV-miR-BART5-3p
PPTX
OXFORD TECHNIQUE ,Zinovieff OXFORD TECHNIQUE
PPTX
ATA_2025_DTC_MCh_Detailed_Presentation.pptx
PDF
A beginner-friendly introduction to gym training
PPTX
Preformulation Studies for new Pharmaceutical substances
PPTX
Hormones classification, mechanism and role.pptx
PPTX
FEBRUARY 2026 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
PPTX
Dental plaque dental plaque periodontology.pptx
PPTX
“Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) with Pleural Effusion – Clinical Case Pre...
PDF
Artículo Biomol Interaction between ZMIZ2 and AR promotes prostate cancer pro...
PDF
Artificial Intelligence, Data and Competition – SCHREPEL – June 2024 OECD dis...
PDF
How to Leverage AI to Boost Employee Wellness - Lydia Di Francesco - SocialHR...
More Related Content
PDF
Storytelling For The Web: Integrate Storytelling in your Design Process
PDF
2024 Trend Updates: What Really Works In SEO & Content Marketing
PPTX
Calcium as a Regulatory and Signalling ion
PPT
Calcium channels –physiology and Therapeutics uses..
PPTX
Calcium in Neuronal Homeostasis
PPTX
PDF
Calcium entry channels in non excitable cells 1st Edition Juliusz Ashot Kozak
PPTX
ASSESSMENT OF ABNORMALITIES IN AUTONOMIC FUNCTION IN PATIENTS.pptx
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Introduction to Geriatric Nursing,Theory
PPTX
WHEN NOT TO DO TENDOACHILLES TENOTOMY.pptx
PPTX
BENIGN BREAST DISEASES BBD/ Fibroadenoma, Fibrocystic Diseases/ ANDI.pptx
PPTX
Tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis tonsillitis
PDF
The Doctor's Balance Sheet By Dr Kanhu Charan Patro
PPTX
Sample Acceptance-Rejection-Criteria in lab
PPTX
CTEV [ clubfoot] DR ARUN LAL ,DR MOHAMED ASHRAF travancore medical college k...
PDF
ARCHES OF FOOT -Prof.Dr.N.Mugunthan. KMMC Medical College & Hospitals.pdf
PPTX
TRIGEMINAL NERVE trigeminal nuclei .pptx
PPTX
PRODUCTION OF ANTIBIOTICS e.g (Penicillin)
PDF
Seminario biología molecula - EBV-miR-BART5-3p
PPTX
OXFORD TECHNIQUE ,Zinovieff OXFORD TECHNIQUE
PPTX
ATA_2025_DTC_MCh_Detailed_Presentation.pptx
PDF
A beginner-friendly introduction to gym training
PPTX
Preformulation Studies for new Pharmaceutical substances
PPTX
Hormones classification, mechanism and role.pptx
PPTX
FEBRUARY 2026 ONCOLOGY CARTOONS BY DR KANHU CHARAN PATRO
PPTX
Dental plaque dental plaque periodontology.pptx
PPTX
“Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) with Pleural Effusion – Clinical Case Pre...
PDF
Artículo Biomol Interaction between ZMIZ2 and AR promotes prostate cancer pro...
Featured
PDF
Artificial Intelligence, Data and Competition – SCHREPEL – June 2024 OECD dis...
PDF
How to Leverage AI to Boost Employee Wellness - Lydia Di Francesco - SocialHR...
PDF
2024 State of Marketing Report – by Hubspot
PDF
Everything You Need To Know About ChatGPT
PDF
Product Design Trends in 2024 | Teenage Engineerings
PDF
How Race, Age and Gender Shape Attitudes Towards Mental Health
PDF
AI Trends in Creative Operations 2024 by Artwork Flow.pdf
PDF
PDF
PEPSICO Presentation to CAGNY Conference Feb 2024
PDF
Content Methodology: A Best Practices Report (Webinar)
PPTX
How to Prepare For a Successful Job Search for 2024
PDF
Social Media Marketing Trends 2024 // The Global Indie Insights
PDF
Trends In Paid Search: Navigating The Digital Landscape In 2024
PDF
5 Public speaking tips from TED - Visualized summary
PDF
ChatGPT and the Future of Work - Clark Boyd
PDF
Getting into the tech field. what next
PDF
Google's Just Not That Into You: Understanding Core Updates & Search Intent
PDF
How to have difficult conversations
PDF
Introduction to Data Science
PDF
Time Management & Productivity - Best Practices
T-Type_Calcium_Channels.pptx calcium ion c 1. 2. 3. Key Features
• - Low voltage activation (-70 mV to -40 mV)
• - Rapid and transient inactivation
• - Low conductance
• - Expressed in neurons, cardiac cells, and
smooth muscle
• - Involved in pacemaking and rhythmic activity
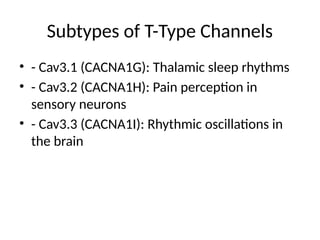
4. Subtypes of T-Type Channels
• - Cav3.1 (CACNA1G): Thalamic sleep rhythms
• - Cav3.2 (CACNA1H): Pain perception in
sensory neurons
• - Cav3.3 (CACNA1I): Rhythmic oscillations in
the brain
5. Functions
• - Contributes to burst firing in neurons
• - Regulates cardiac pacemaking
• - Modulates hormone secretion
• - Controls smooth muscle tone
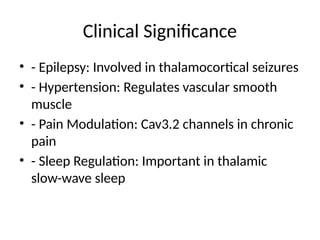
6. Clinical Significance
• - Epilepsy: Involved in thalamocortical seizures
• - Hypertension: Regulates vascular smooth
muscle
• - Pain Modulation: Cav3.2 channels in chronic
pain
• - Sleep Regulation: Important in thalamic
slow-wave sleep
7. Treatment & Blockers
• - Ethosuximide: Used for absence seizures
• - T-type channel blockers: Potential targets for
pain and hypertension treatment
8. Conclusion
• T-type calcium channels play a crucial role in
neuronal activity, cardiac function, and disease
pathology. Understanding their function can
help develop targeted therapies.