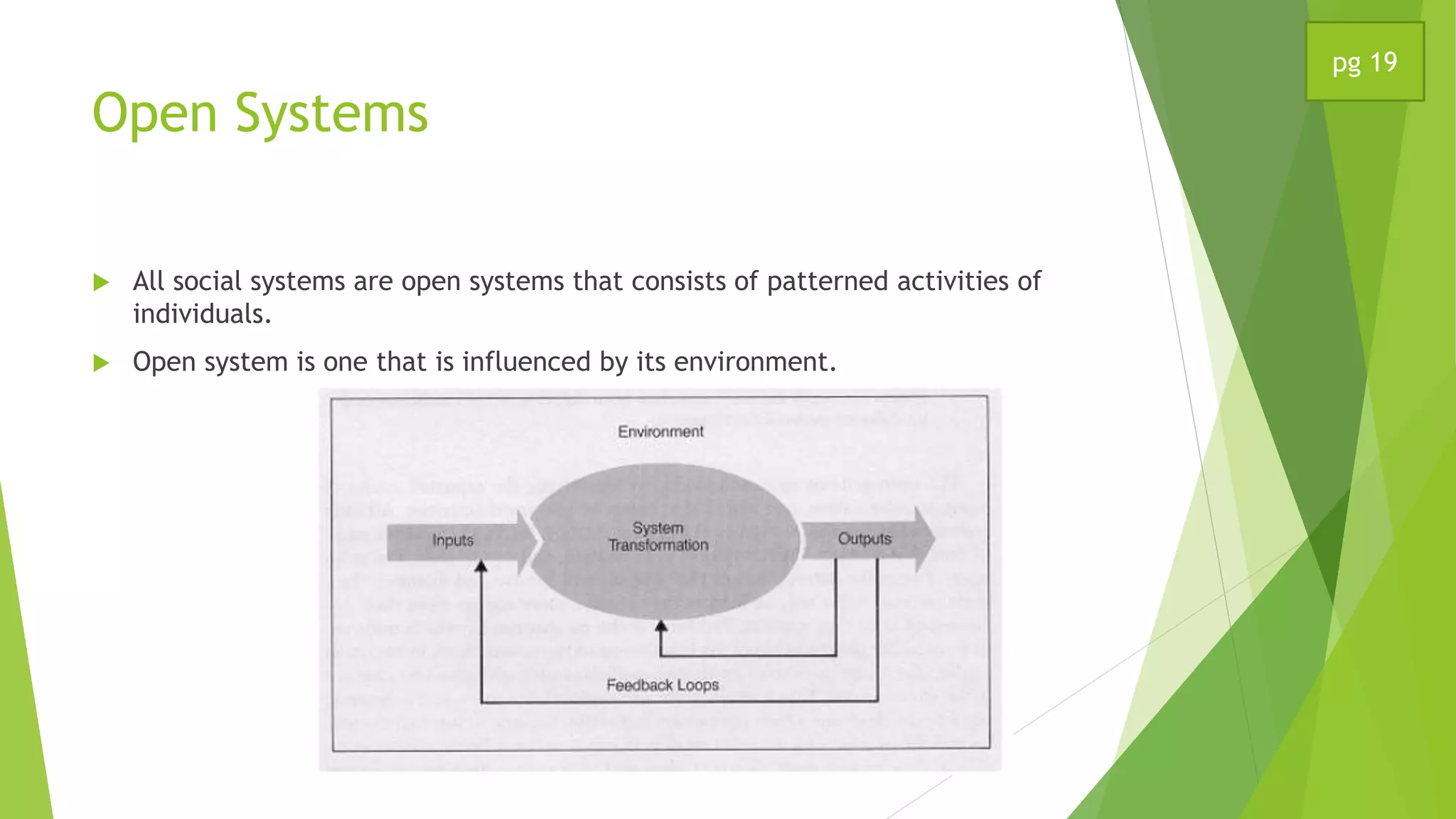
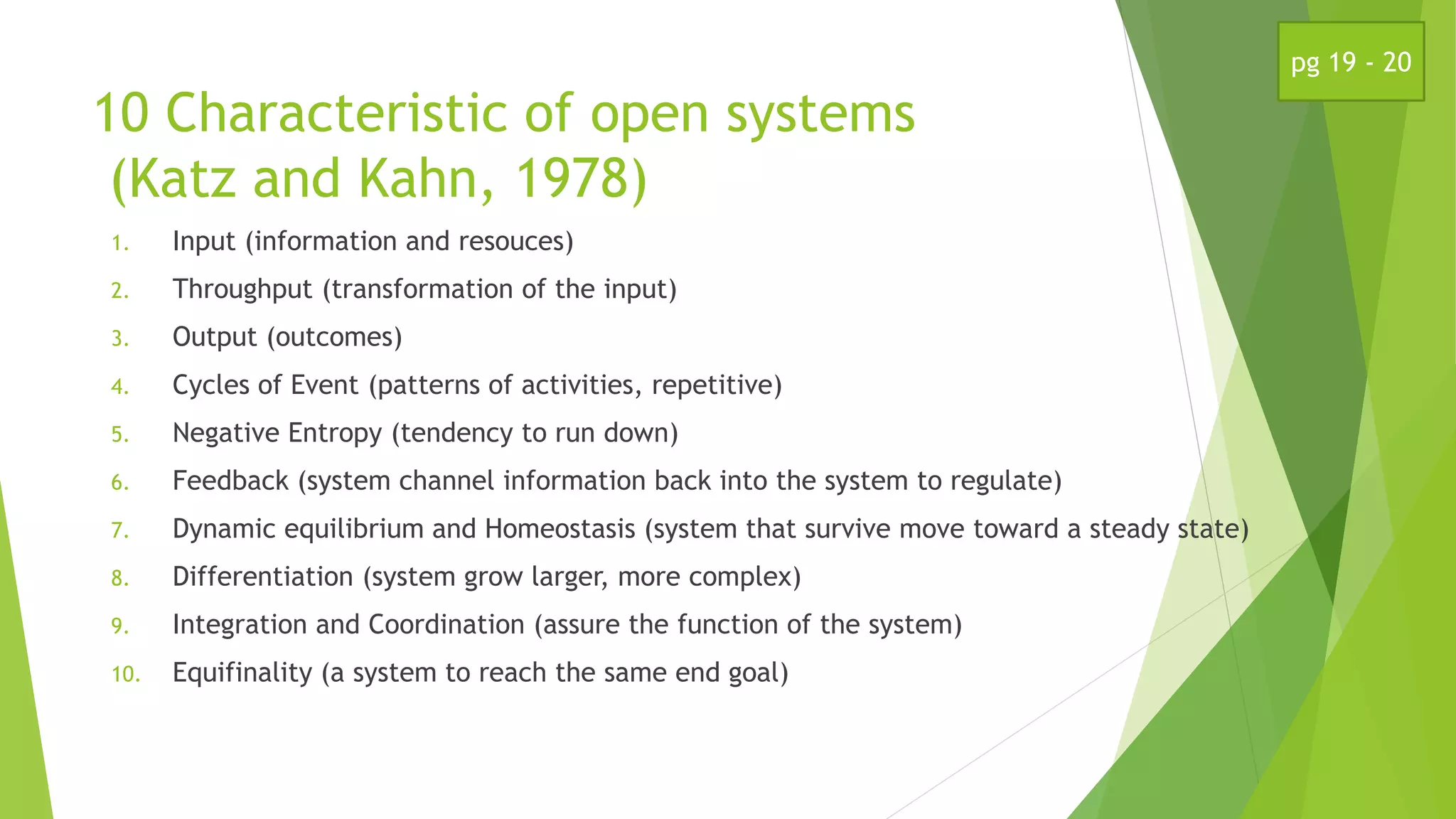
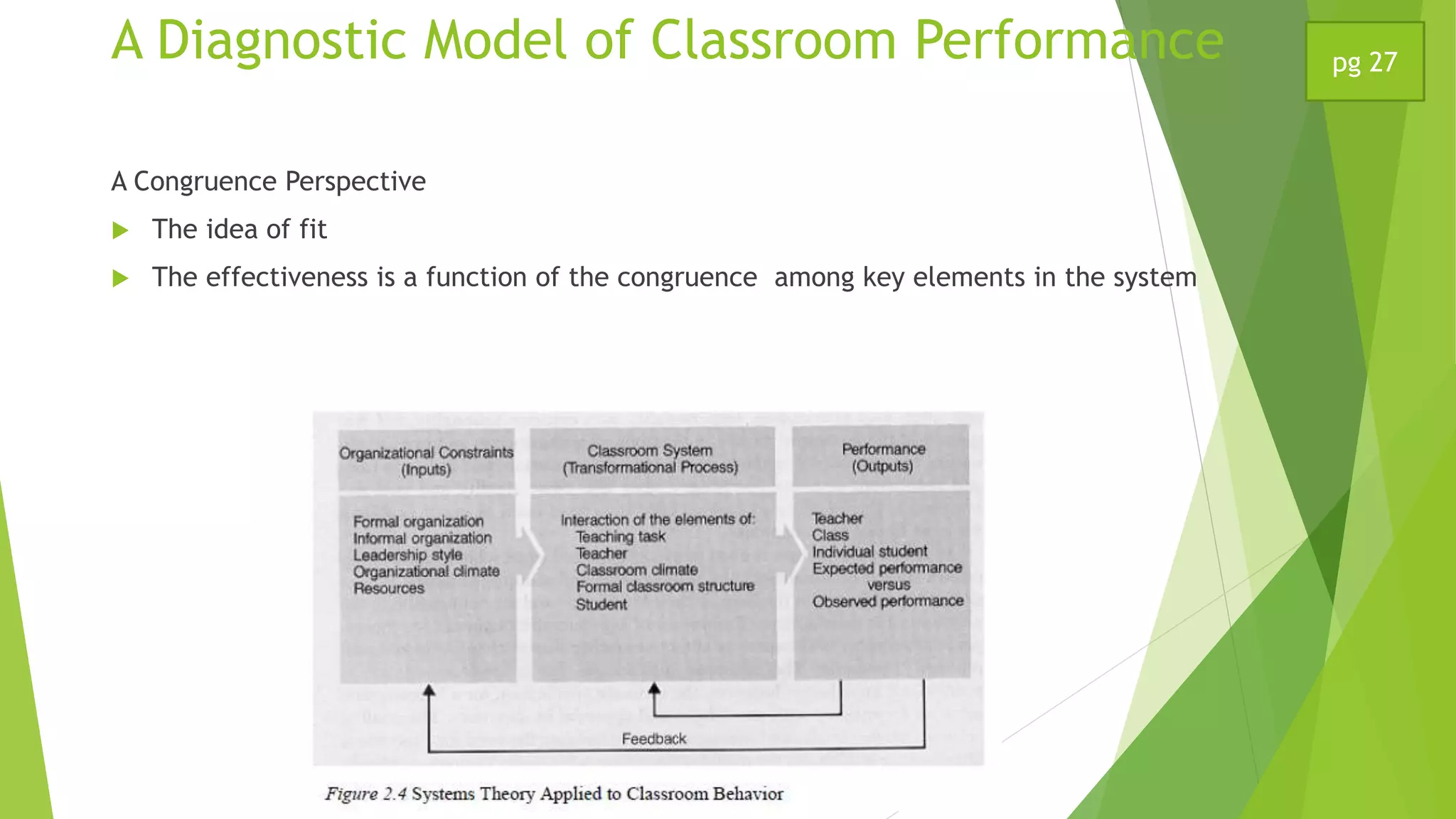
This document discusses a systems model of classroom performance. It describes a school as a social system influenced by bureaucratic expectations, informal norms, and individual needs. An open systems model is presented, with inputs like leadership and resources, a transformational process in the classroom, and outputs like student and teacher performance. Congruence among these elements is key to effectiveness. An example is given applying this model to the film "Lean on Me".