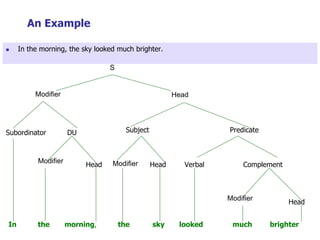
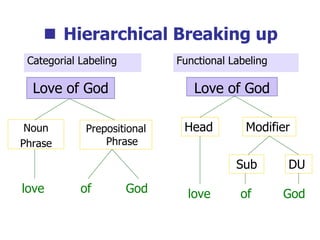
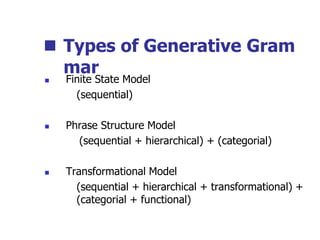
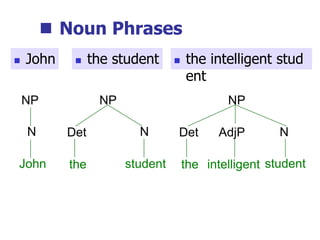
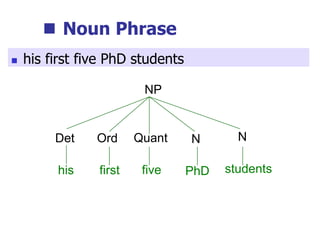
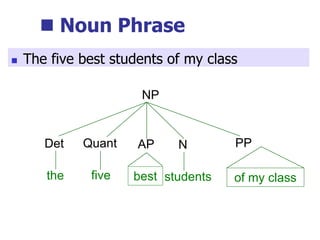
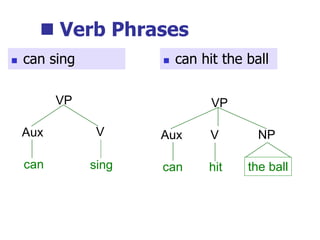
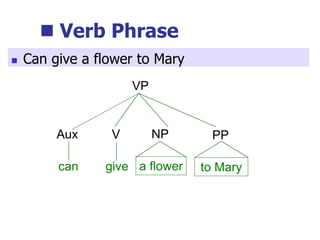
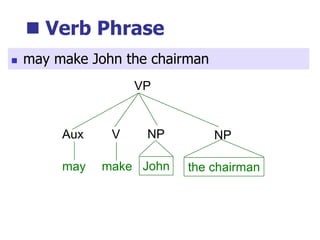
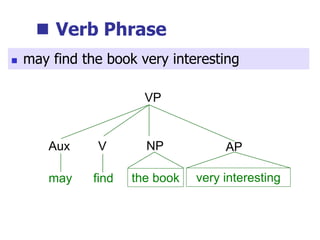
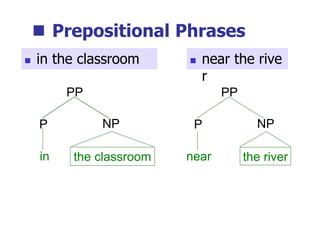
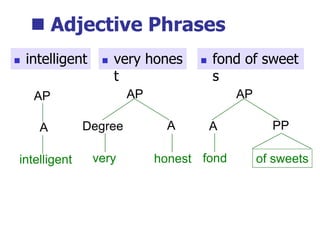
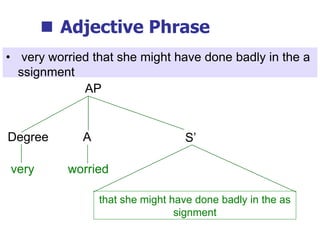
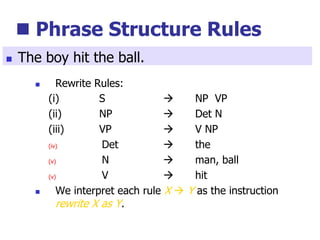
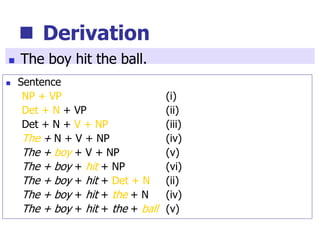
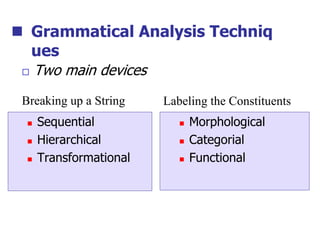
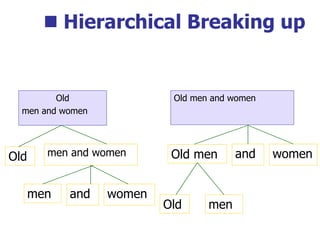
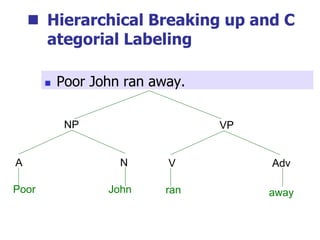
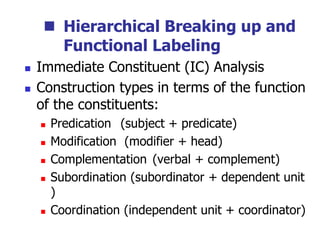
This document provides an overview of syntax and grammatical analysis techniques. It defines syntax as the set of rules that generates sentences in a language. There are various techniques for analyzing syntax grammatically, including sequential breaking up of sentences, hierarchical phrase structure trees, and labeling of constituents categorically and functionally. Phrase structure grammar is introduced as a model consisting of a vocabulary, terminal symbols, a start symbol, and phrase structure rules. Examples of noun phrases, verb phrases, prepositional phrases, and adjective phrases are given and analyzed using phrase structure trees.








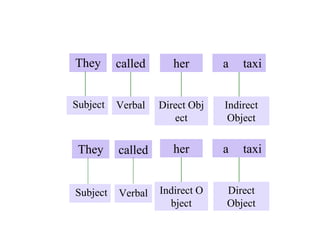
![ Predication
[Birds]subject [fly]predicate
S
Predicate
Subject
Birds fly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxpresentation01-230830103942-60032f99/85/Syntax-presentation-01-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![ Modification
[A]modifier [flower]head
John [slept]head [in the room]modifier
S
Predicate
Subject
John Head Modifier
slept In the room](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxpresentation01-230830103942-60032f99/85/Syntax-presentation-01-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![ Complementation
He [saw]verbal [a lake]complement
S
Predicate
Subject
He Verbal Complement
saw a lake](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxpresentation01-230830103942-60032f99/85/Syntax-presentation-01-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![ Subordination
John slept [in]subordinator [the room]dependent unit
S
Predicate
Subject
John Head Modifier
slept
the room
Subordinator Dependent Unit
in](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxpresentation01-230830103942-60032f99/85/Syntax-presentation-01-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![ Coordination
[John came in time] independent unit [but]coordinator [Mary was not r
eady] independent unit
S
Coordinator
Independent Unit
John came in time but Mary was not ready
Independent Unit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/syntaxpresentation01-230830103942-60032f99/85/Syntax-presentation-01-pptx-18-320.jpg)