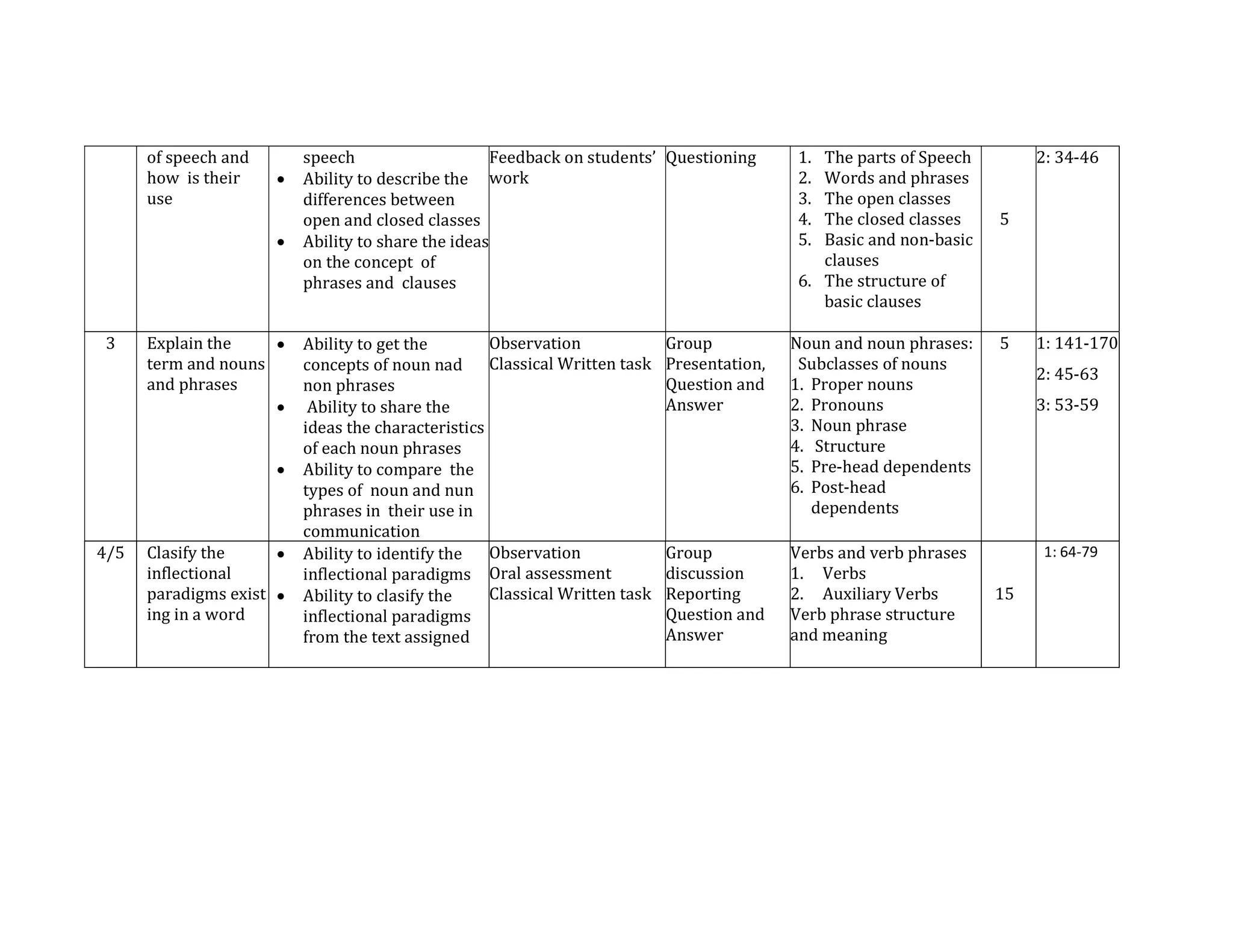
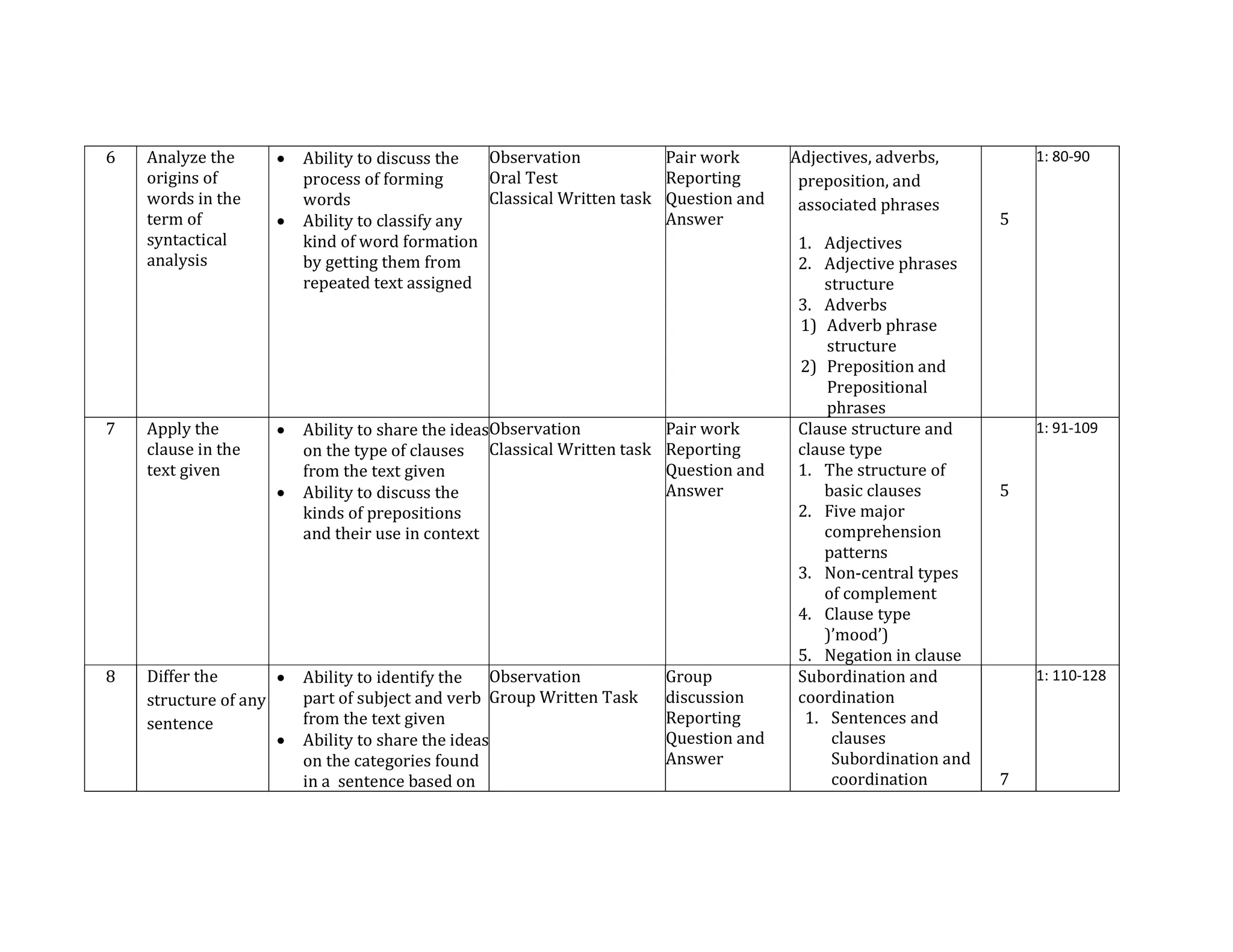
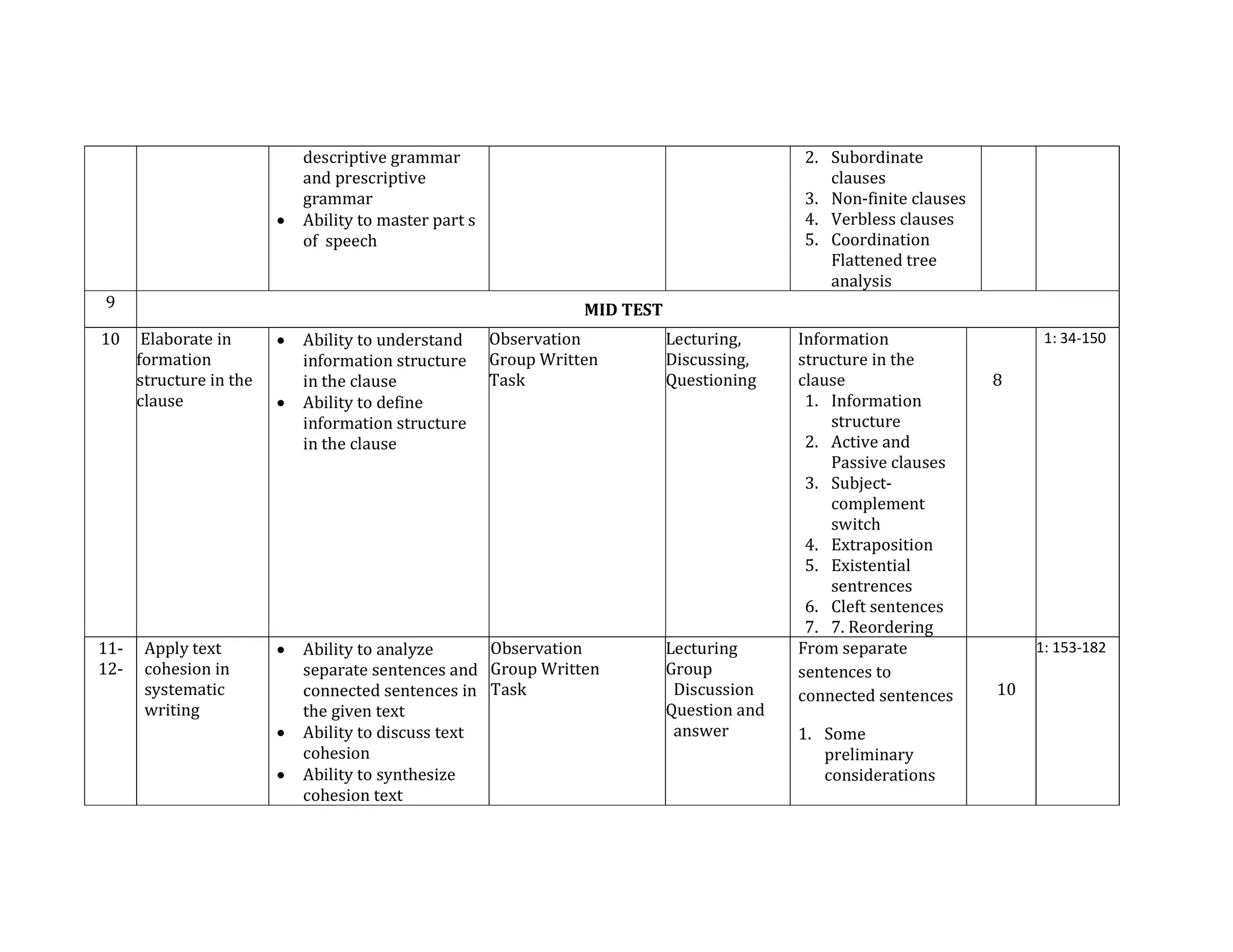
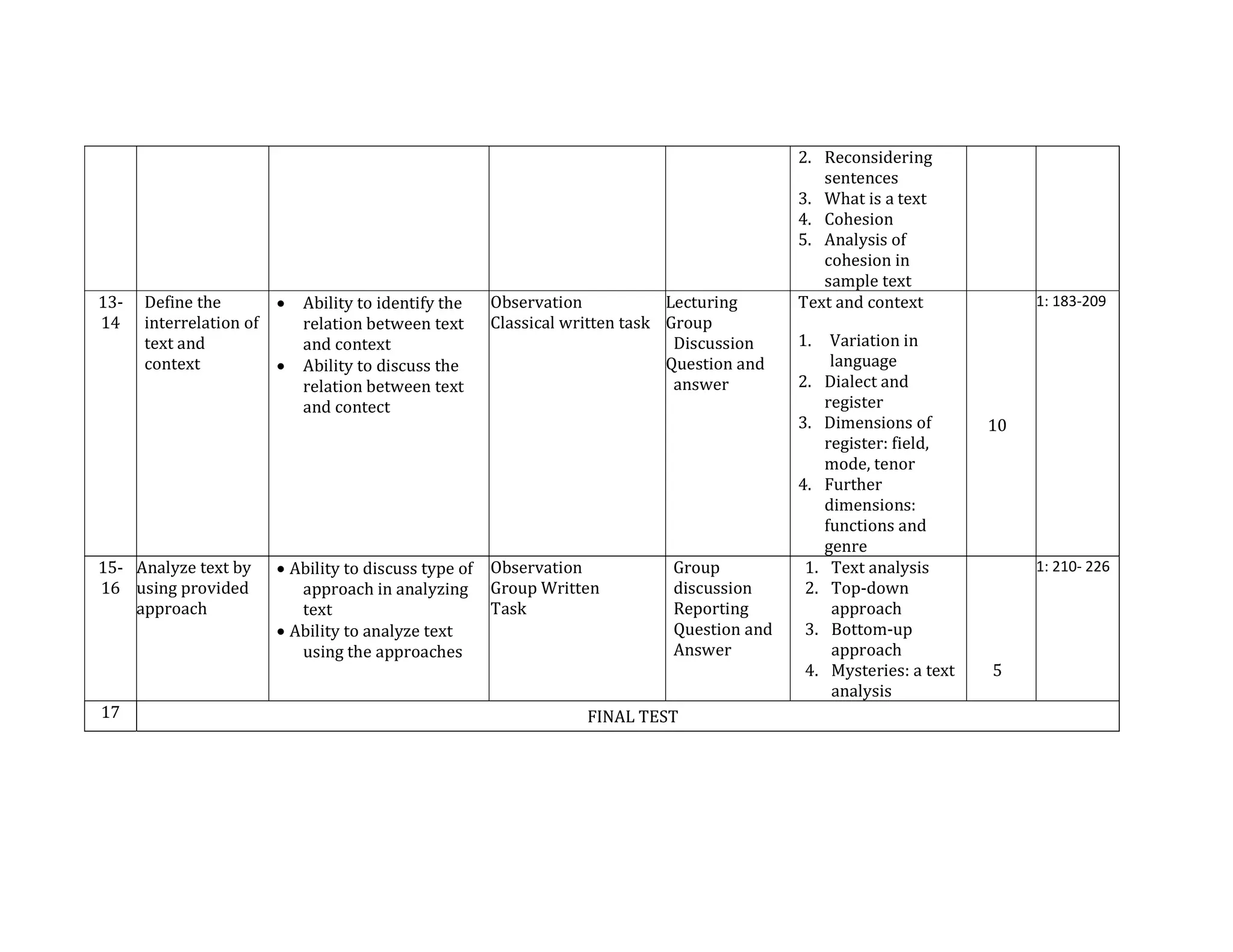
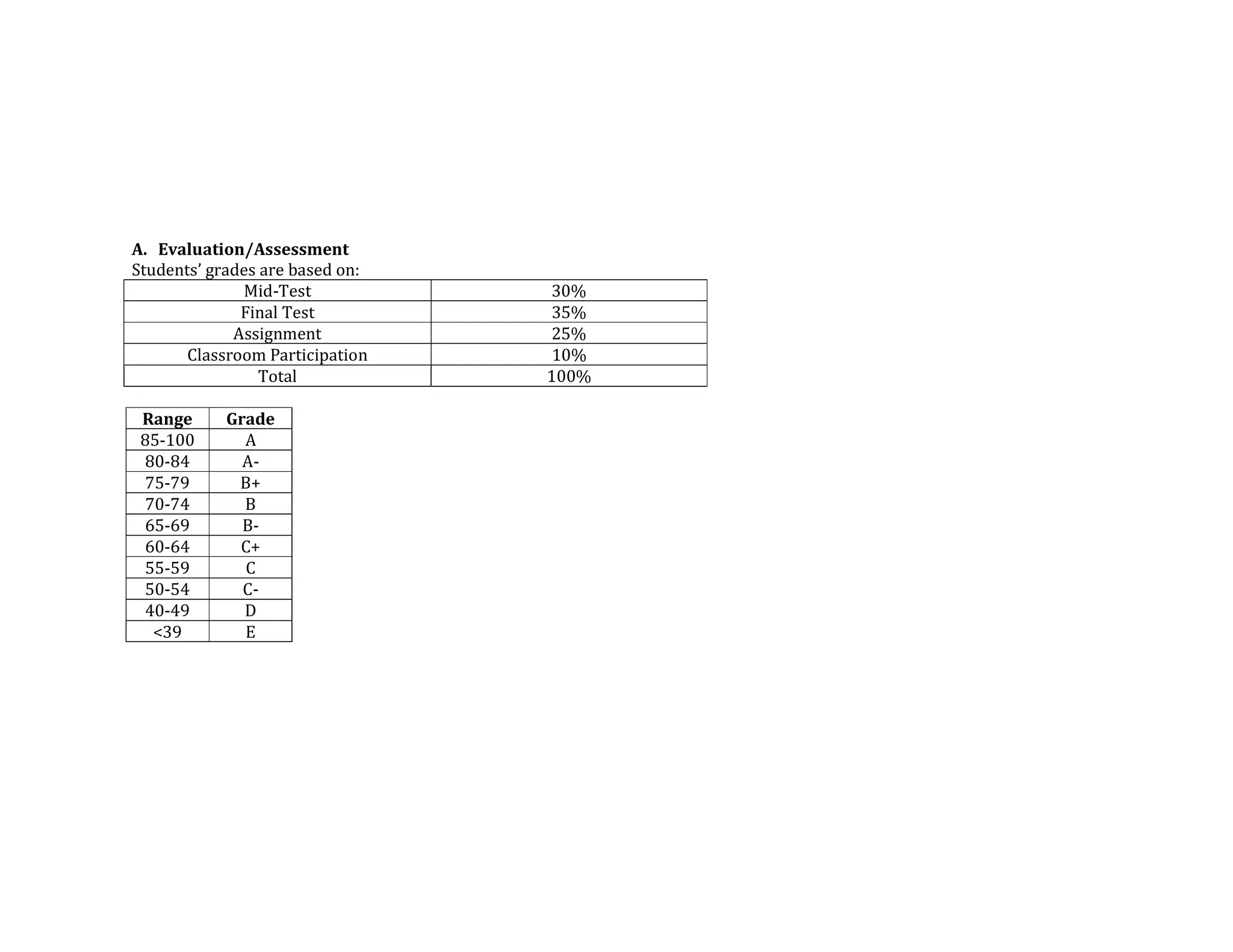
The document outlines the syllabus for a course in English Syntax at Universitas Negeri Padang, detailing its learning outcomes, course structure, topics, and assessment criteria. Students will explore syntactical concepts through lectures, discussions, and various assessments, focusing on analyzing phrases, clauses, and sentences. The syllabus also includes a week-by-week breakdown of lessons, materials, and evaluation methods.