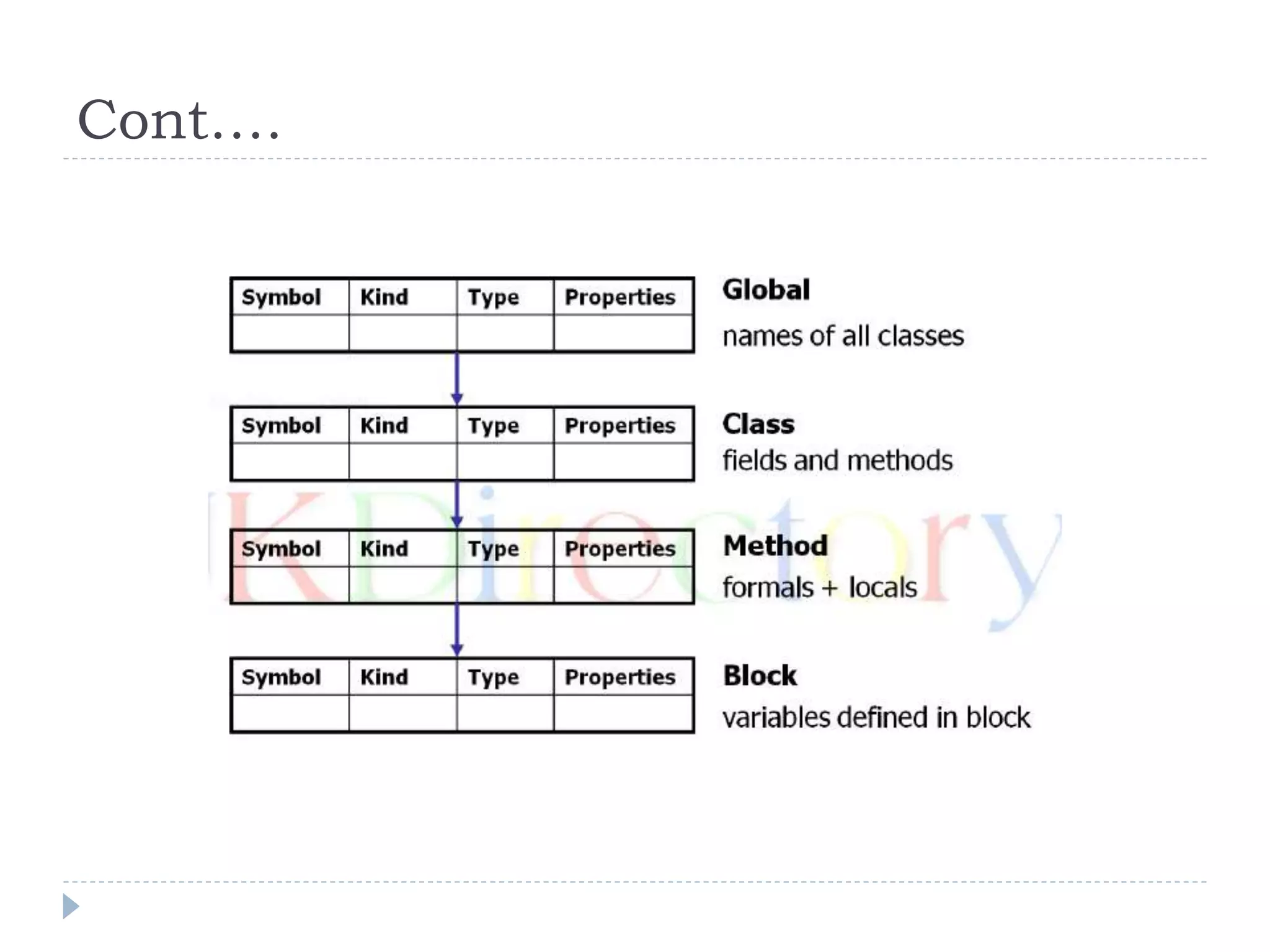
A symbol table is a data structure used by compilers and interpreters to associate identifiers in a program's source code with information like their type and scope. It stores identifiers and attributes in a structured format. Symbol tables are used for name resolution, type checking, and generating intermediate or target code. They support basic operations like insertion, lookup, and updating attributes. Common implementations include ordered lists, binary search trees, and hash tables.