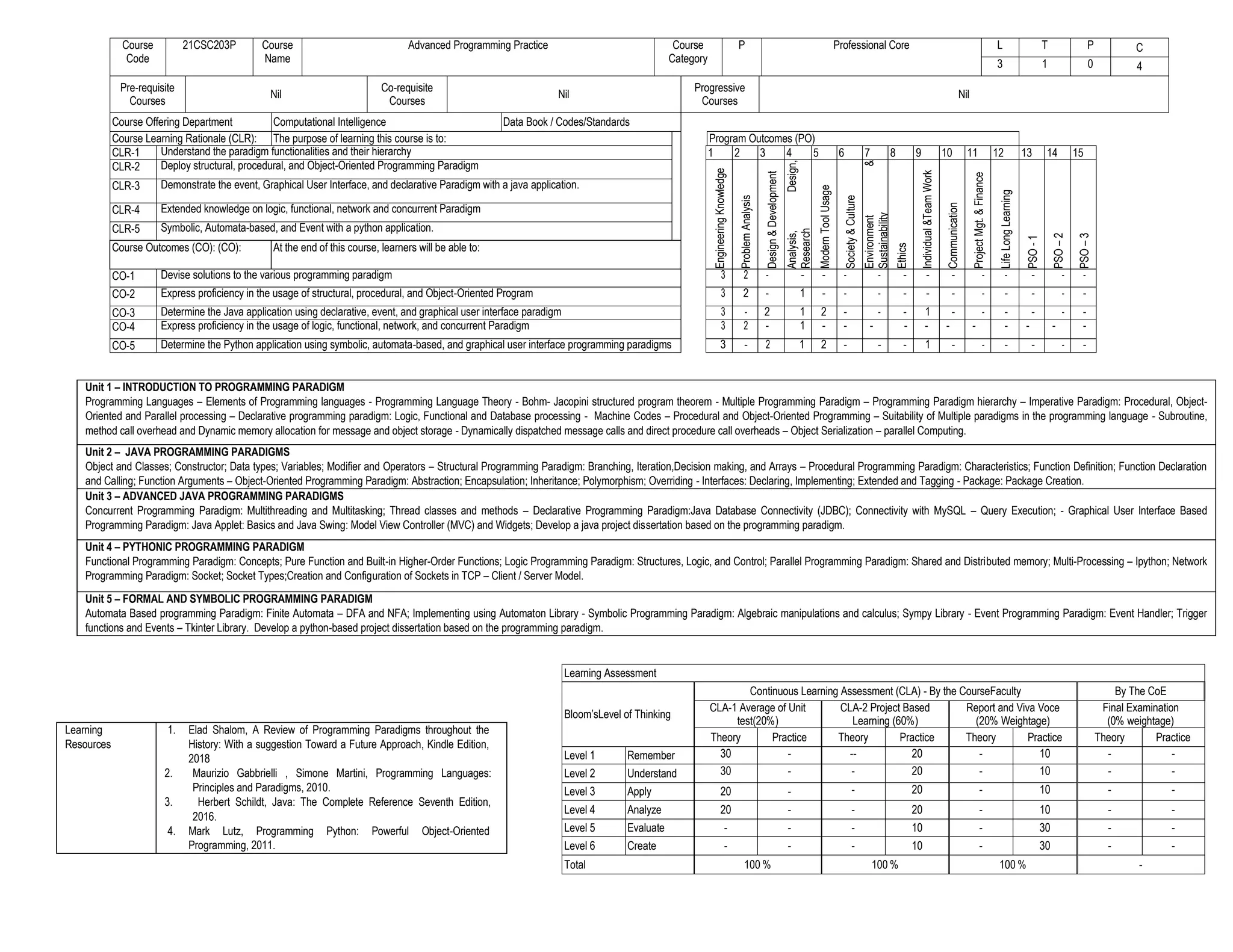
This document outlines a course on advanced programming paradigms. It covers five units: introduction to programming paradigms and languages; Java programming paradigms including object-oriented, procedural, and declarative; advanced Java including concurrent and graphical interfaces; Python paradigms including functional, logic, and parallel; and formal paradigms including automata and symbolic programming with Python. The course aims to develop understanding of paradigm functionalities and deploy various paradigms including structural, object-oriented, declarative, and graphical interfaces using Java and Python applications. Learning is assessed through unit tests, projects, reports, and final examinations.