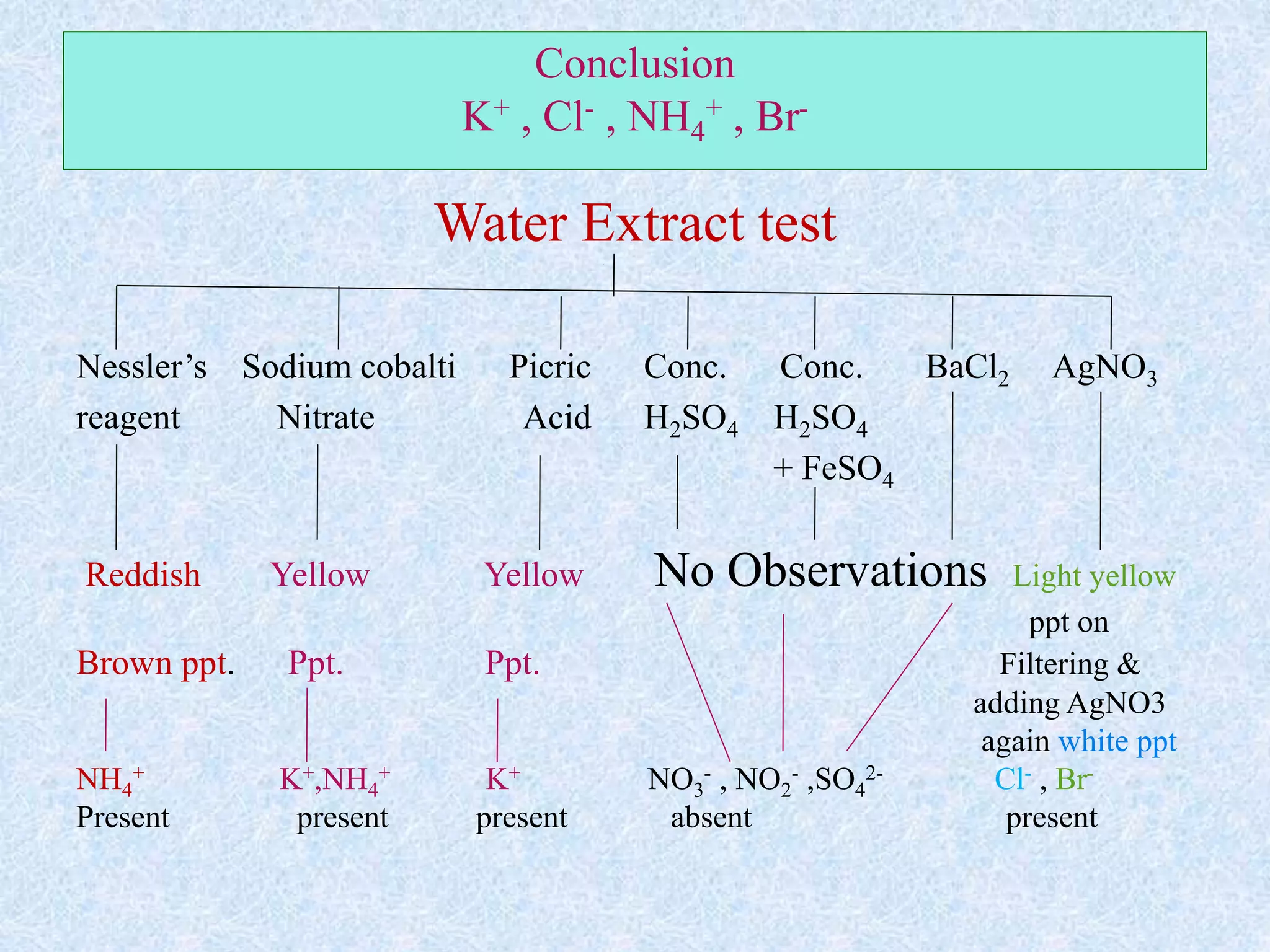
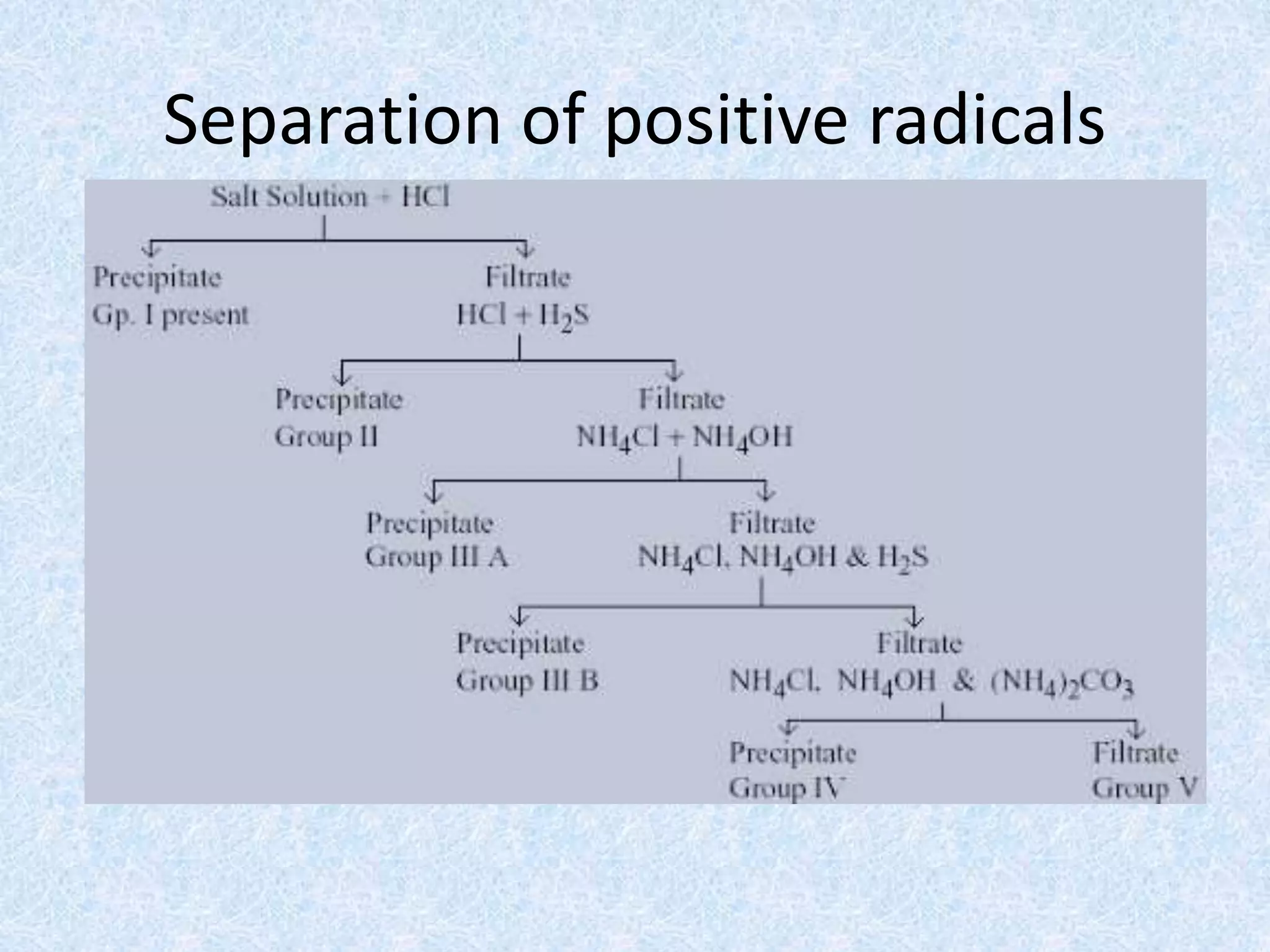
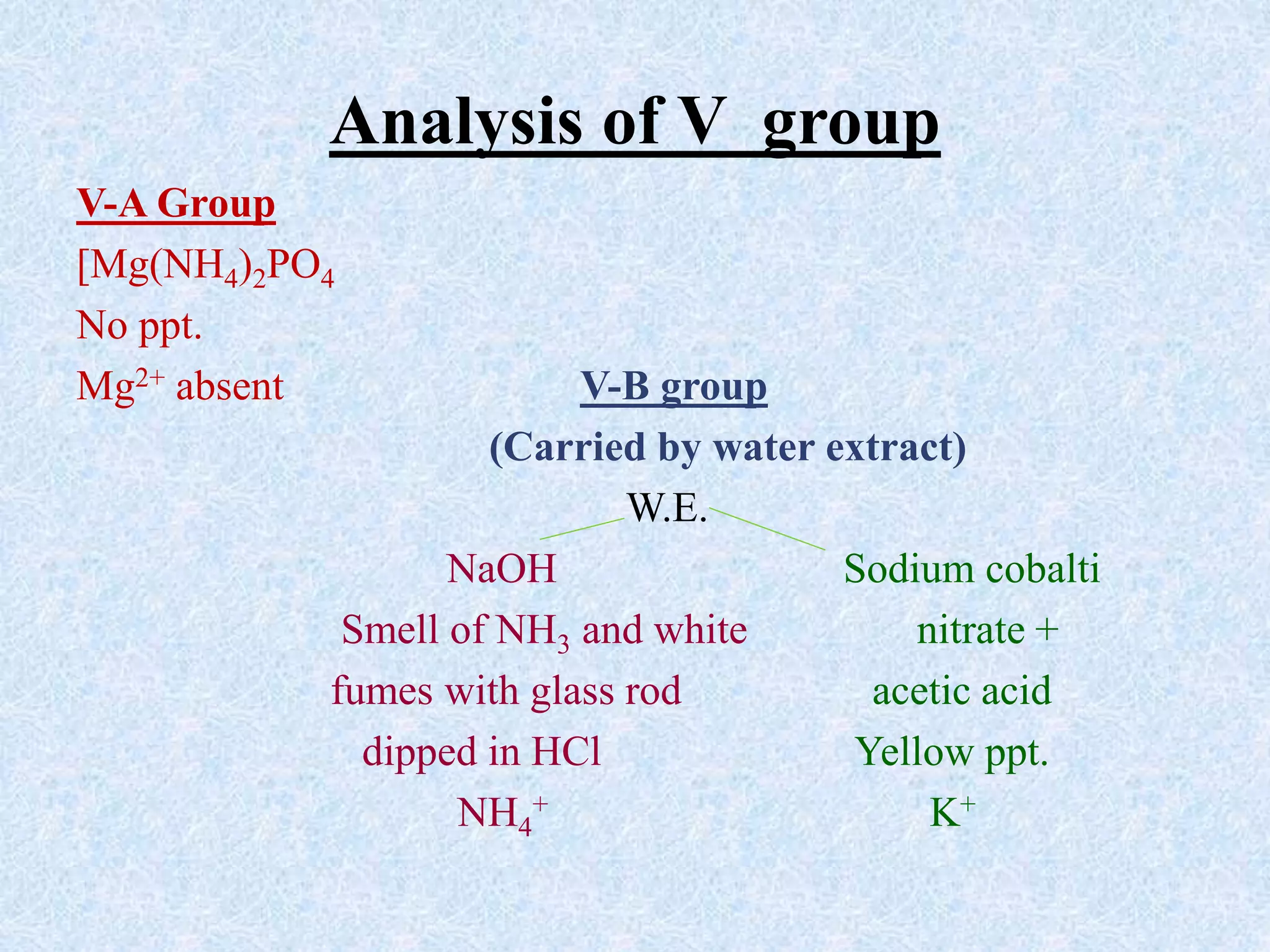
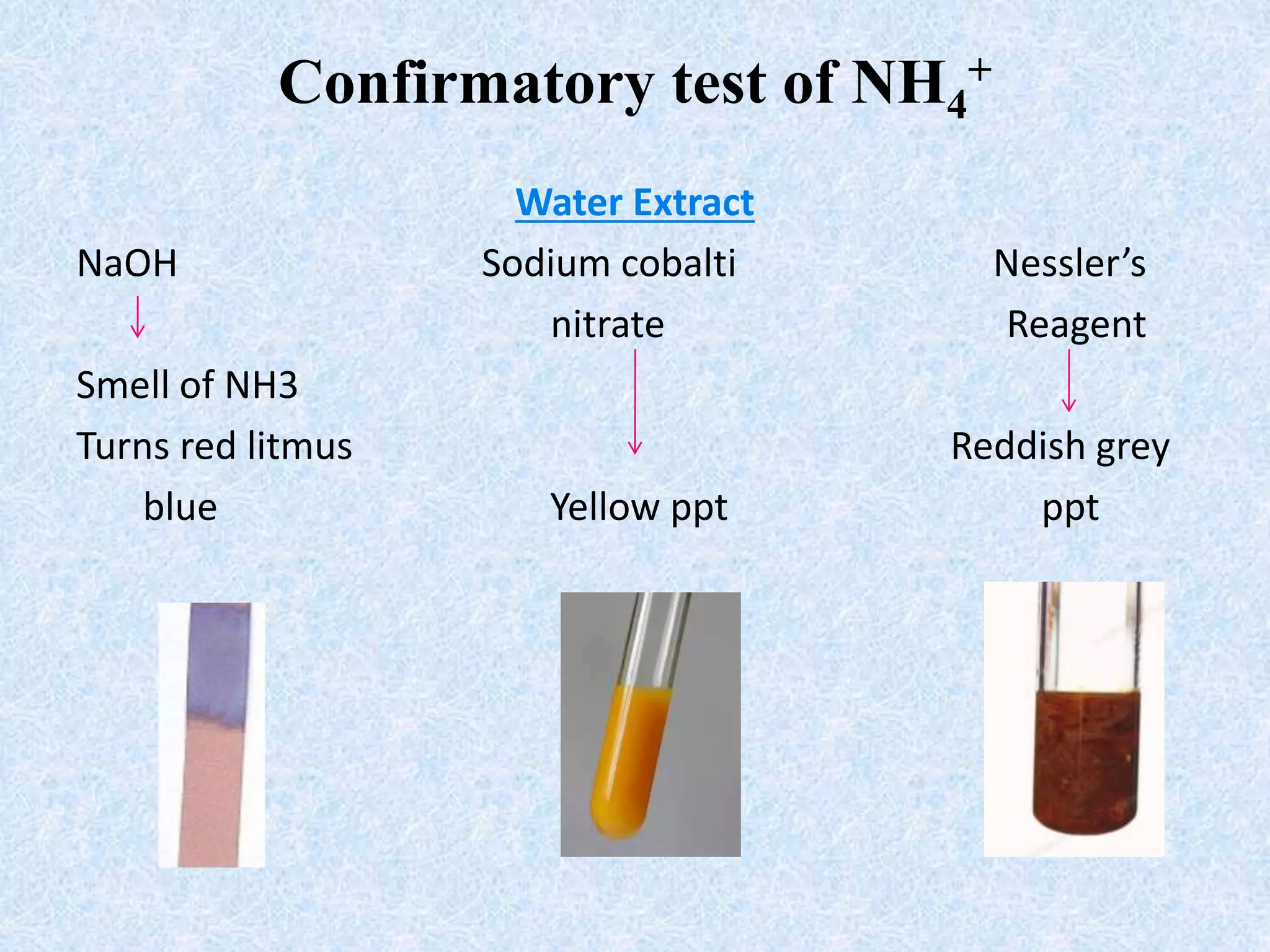
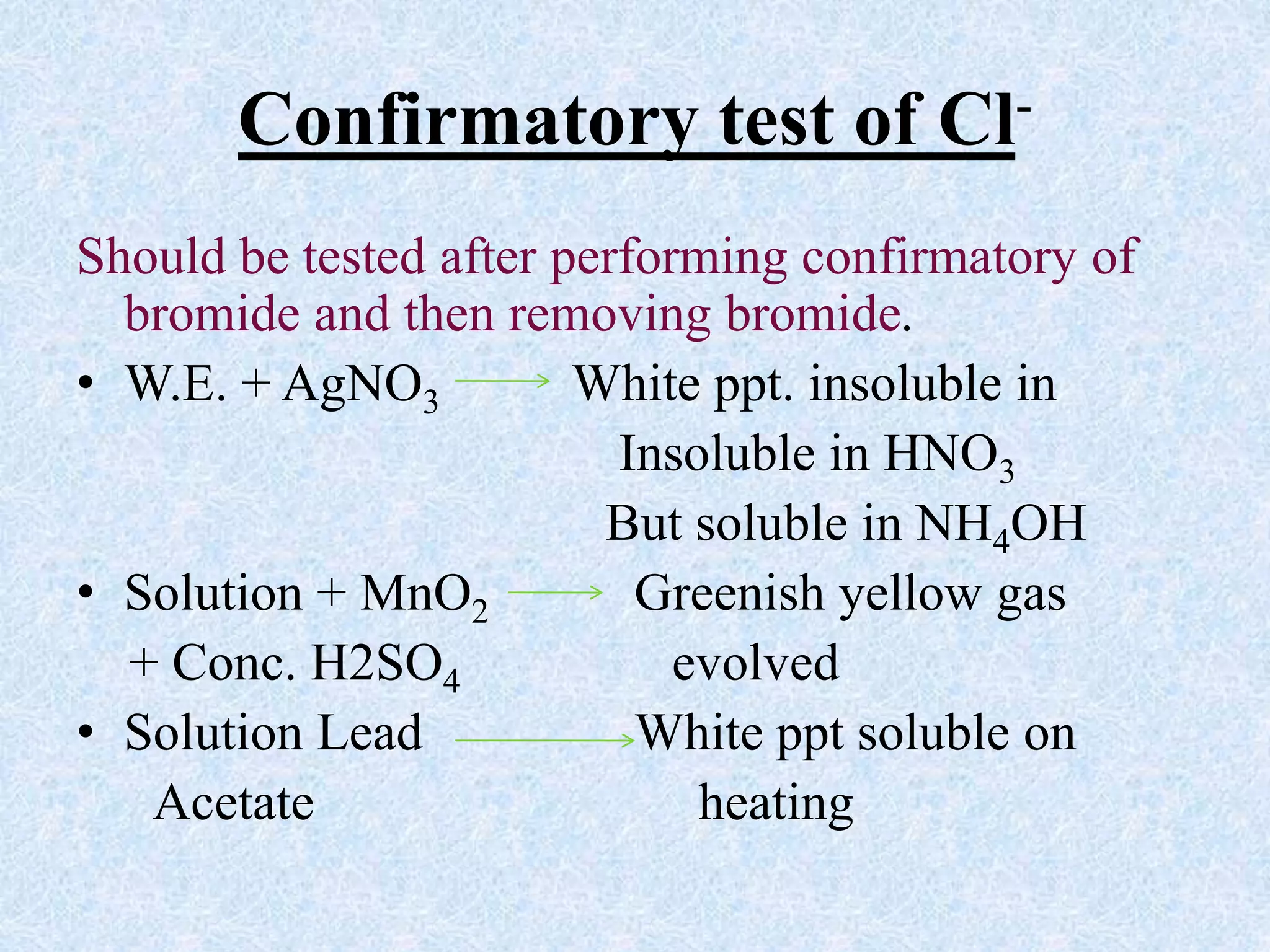
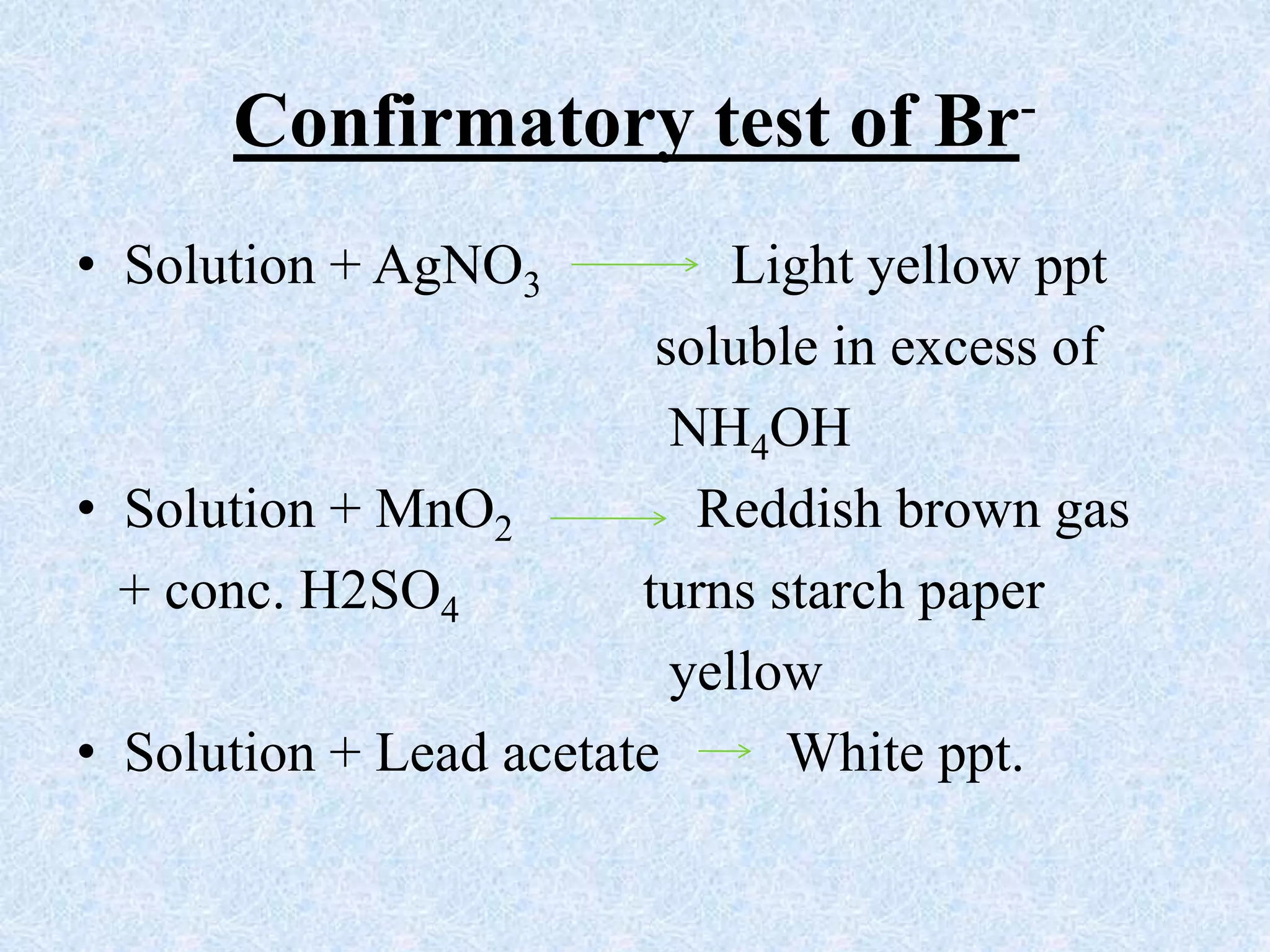
The document describes qualitative analysis of inorganic salts containing K+, NH4+, Cl-, and Br-. Preliminary tests identified the substance as a white crystalline solid soluble in water, with an ammonia smell. Dry tests included heating, which caused melting, and a violet flame test result. Wet tests identified the positive ions as K+ and NH4+ and the negative ions as Cl- and Br- through reactions with specific reagents and gas tests. The conclusion is that the inorganic salt contains K+, NH4+, Cl- and Br-.