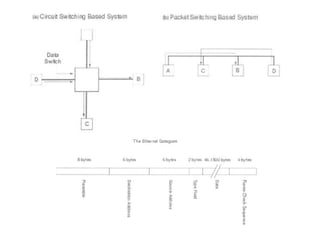
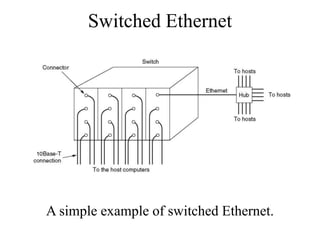
Switching allows communication between nodes in a network by transferring input sample points to the correct output ports at the correct time. There are different types of switching including digital switching where sample point amplitudes are 0s and 1s, circuit switching which establishes a dedicated physical path, and packet switching which breaks messages into packets that are transmitted asynchronously. Switching techniques include crossbar switching, bus and cable switches, token passing, and Ethernet approaches using cables, rings, or star networks with hubs or switches.