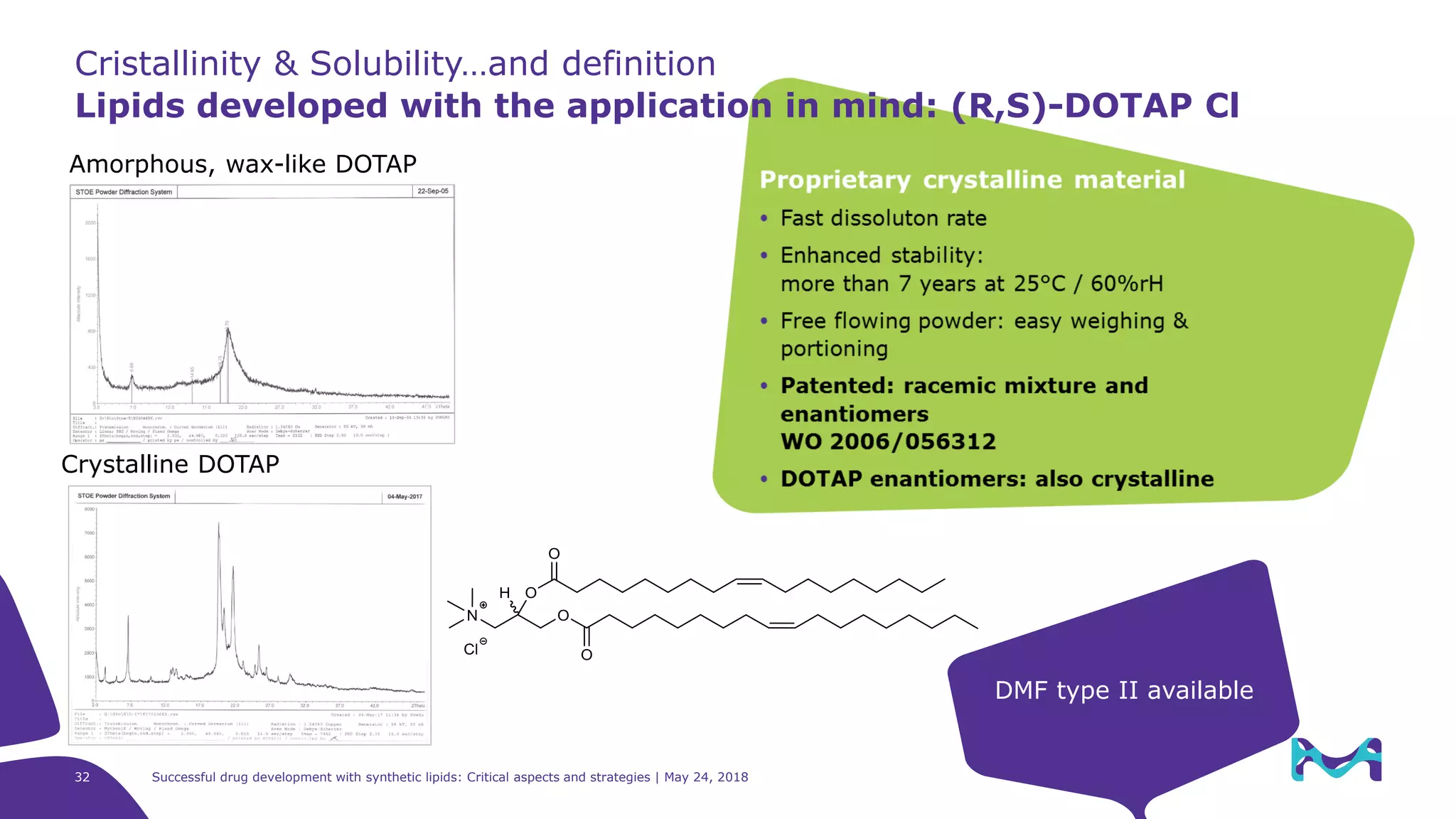
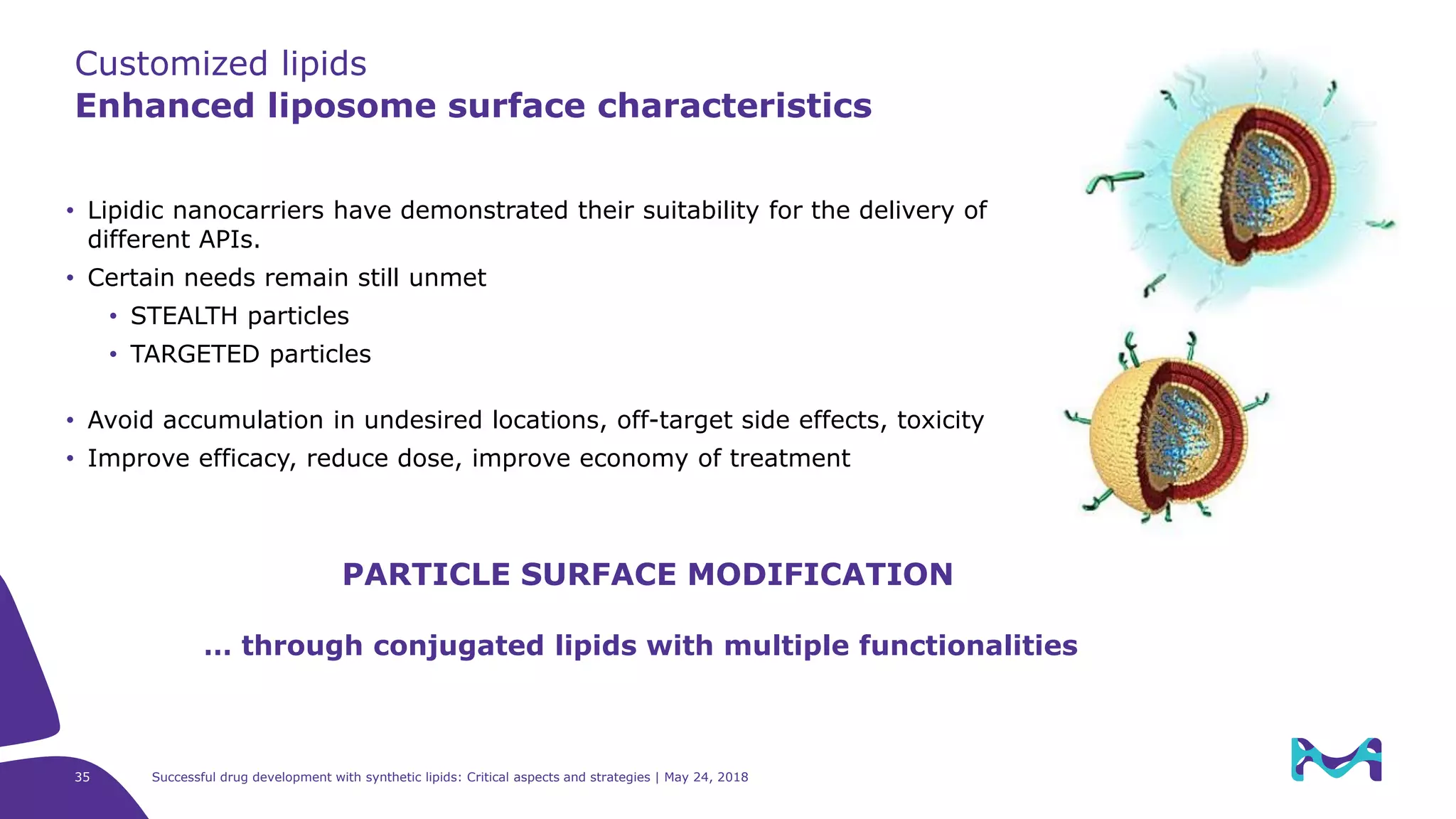
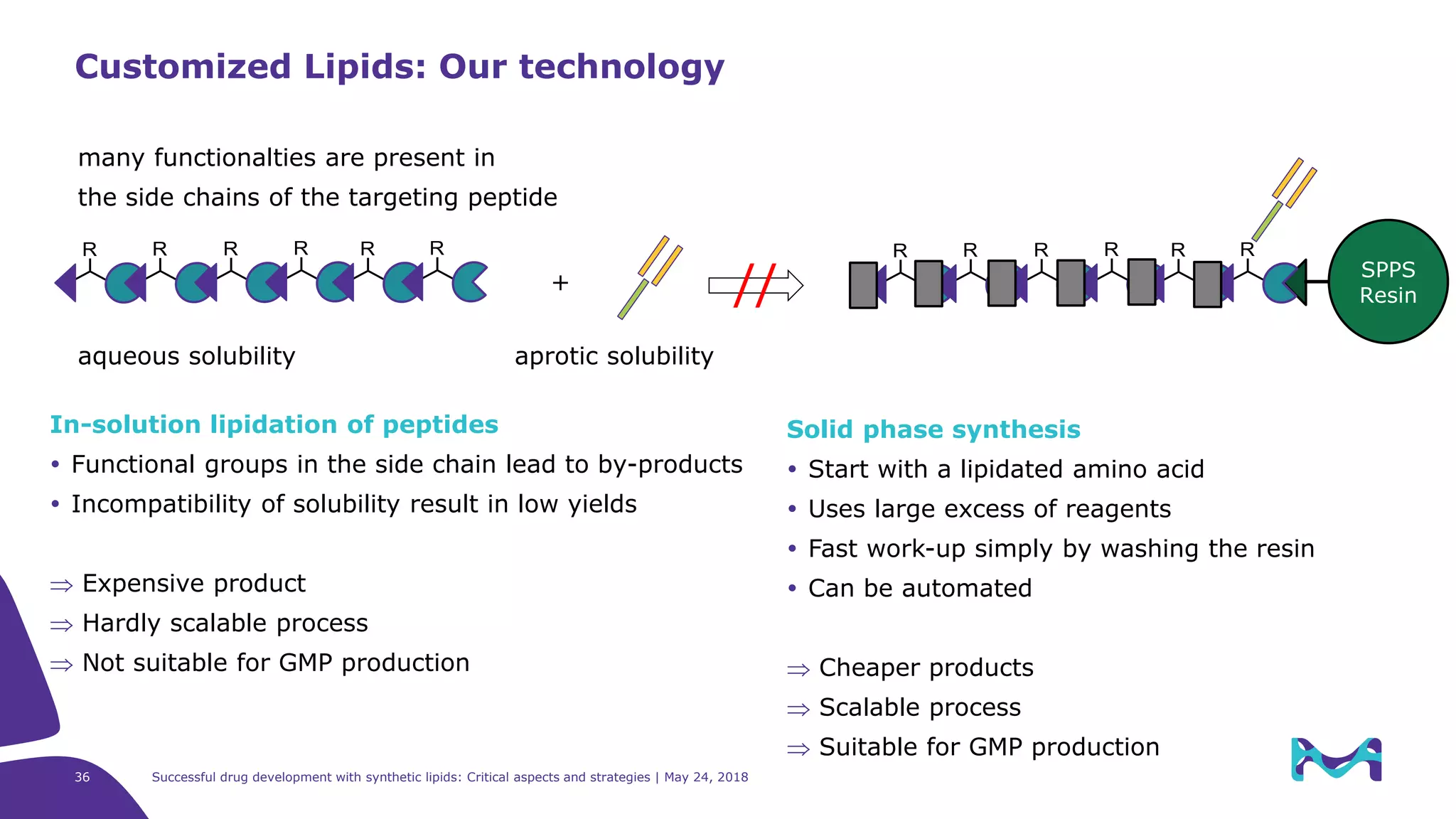
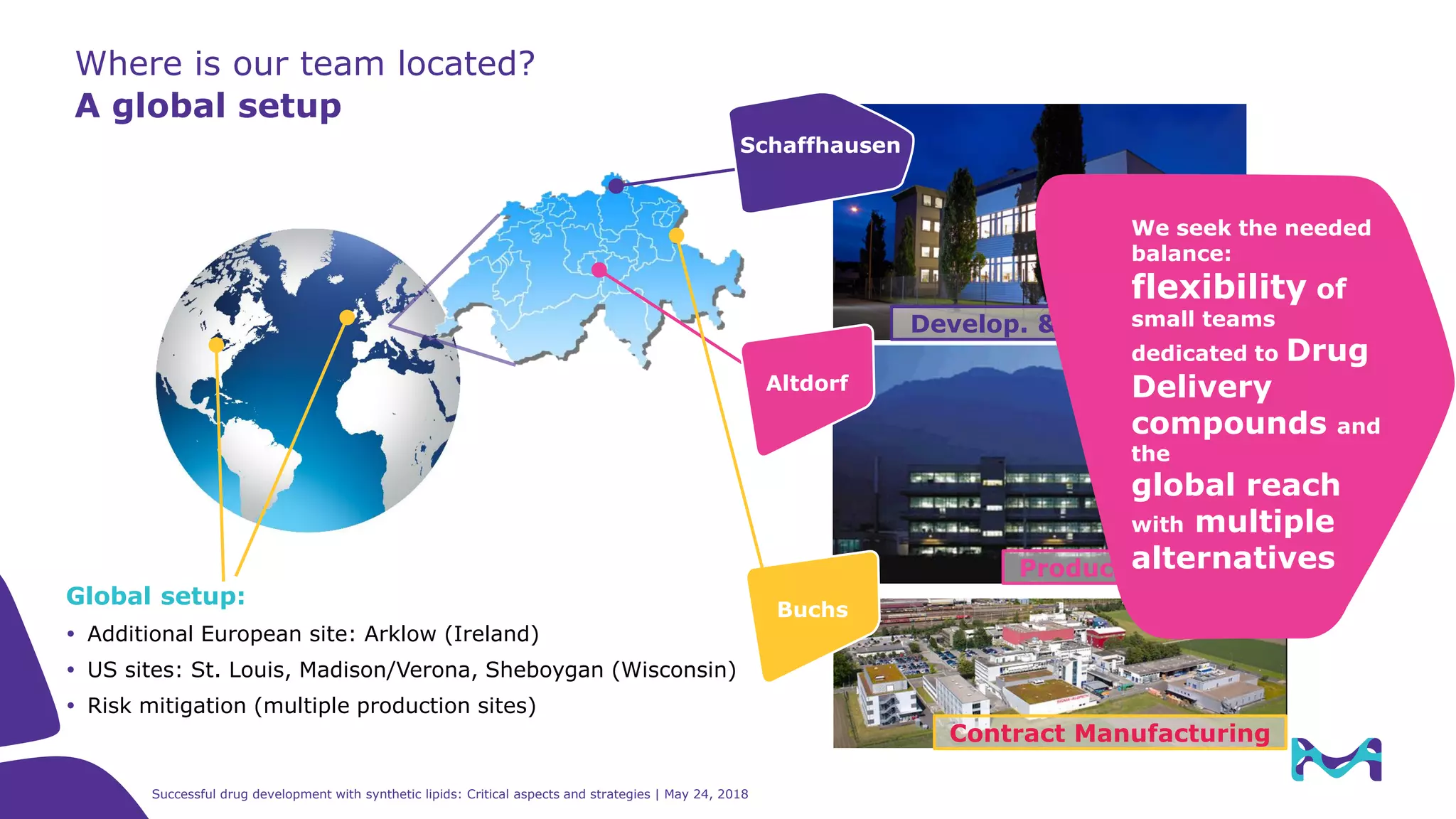
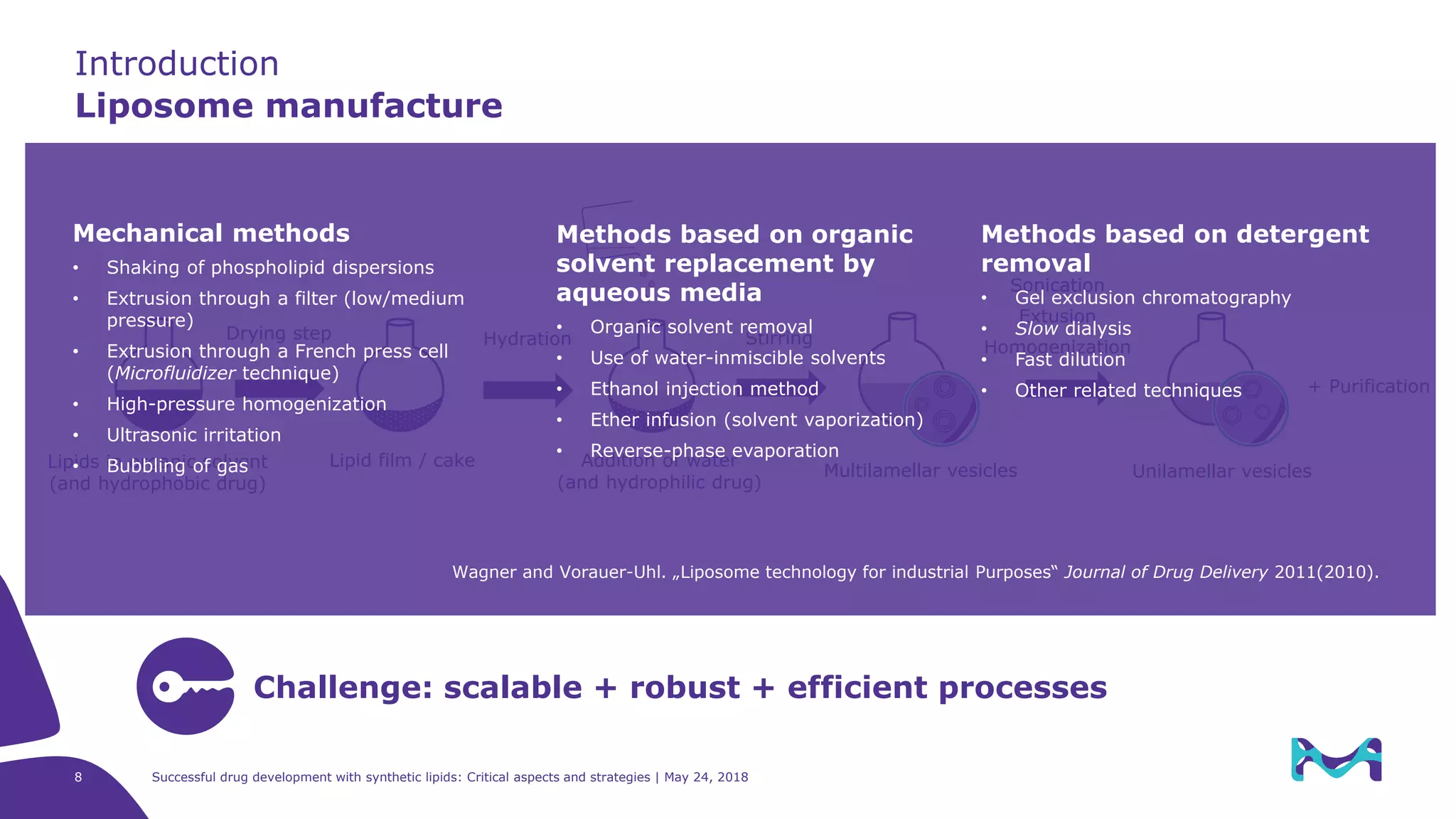
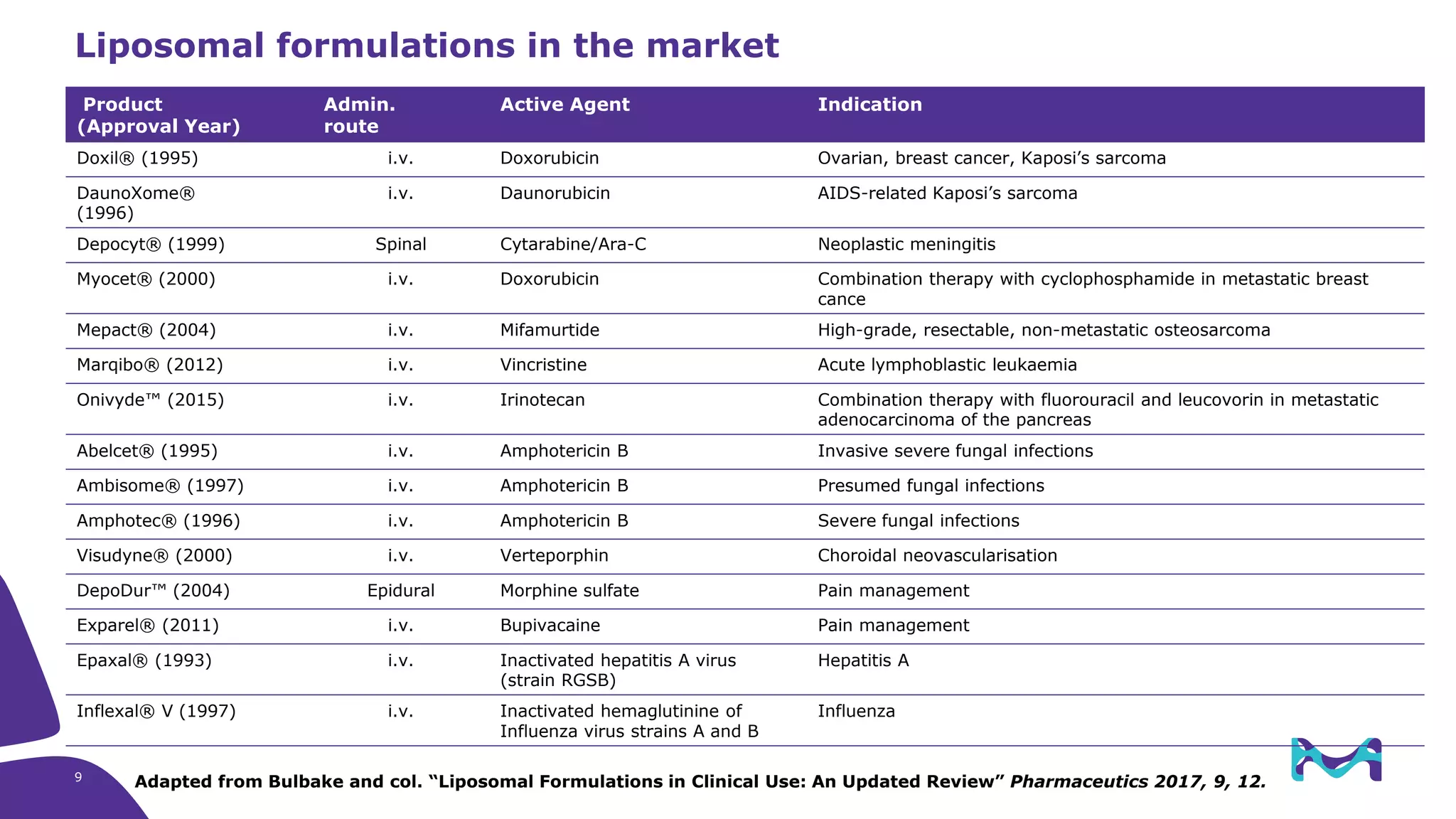
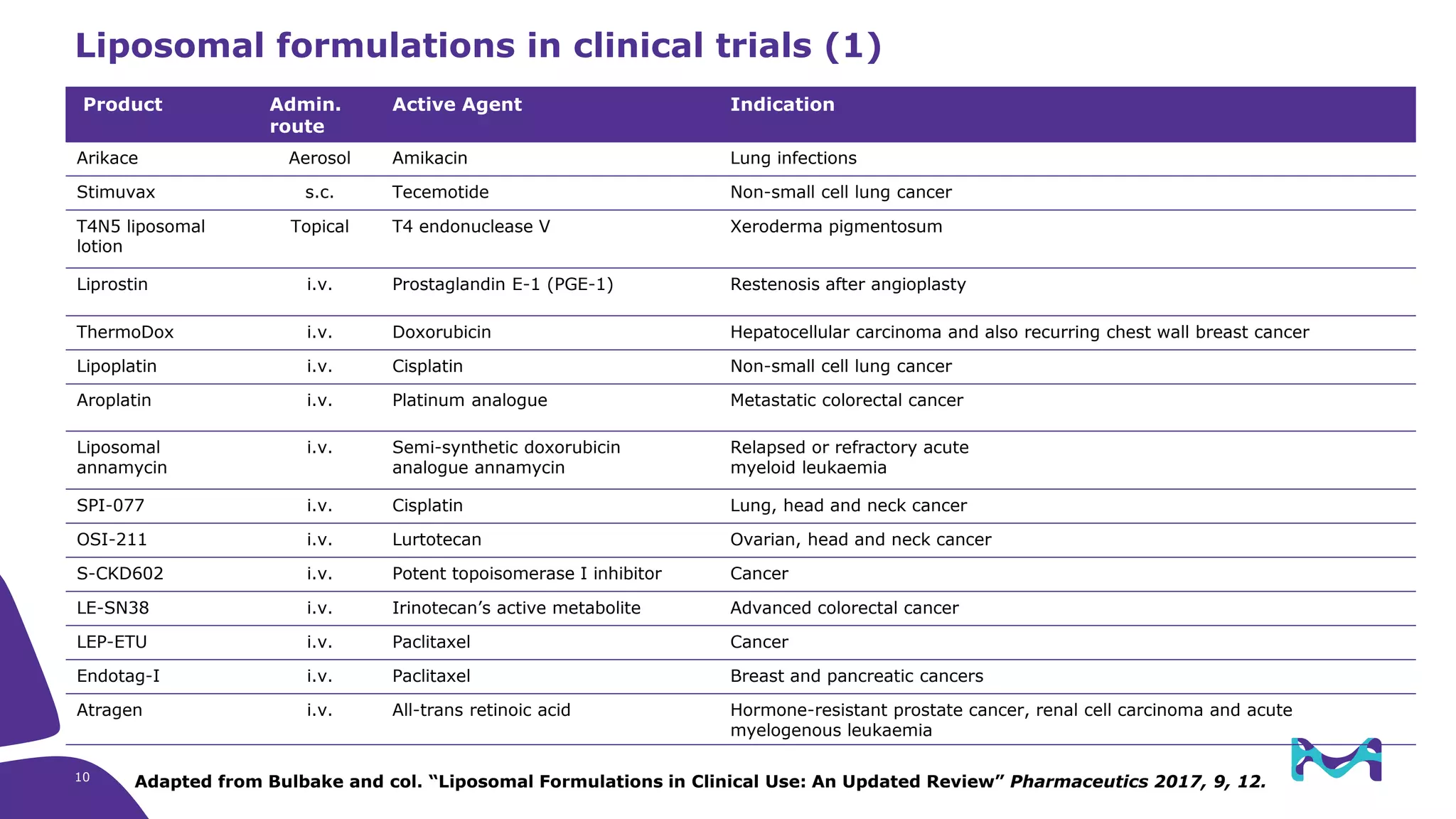
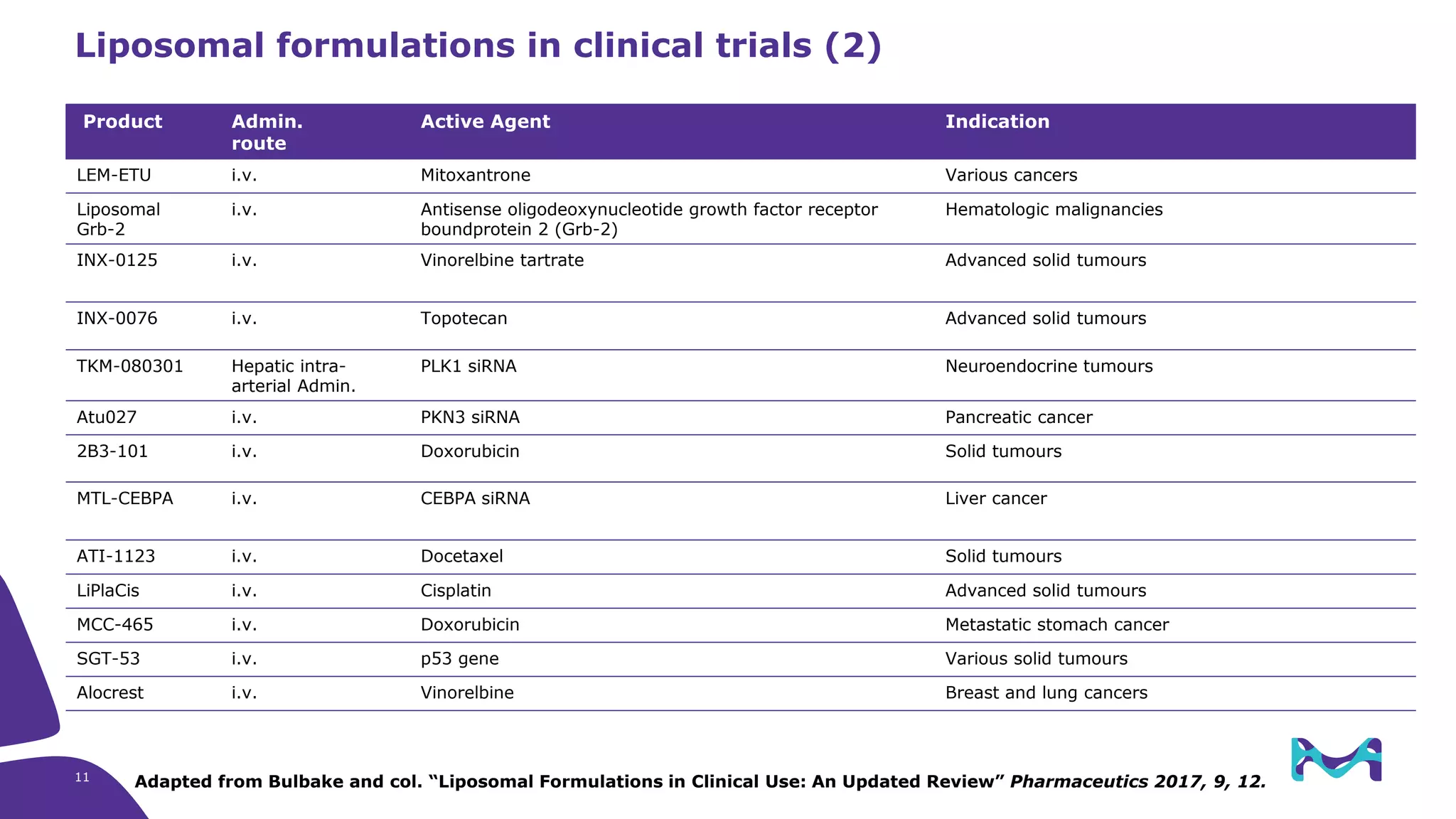
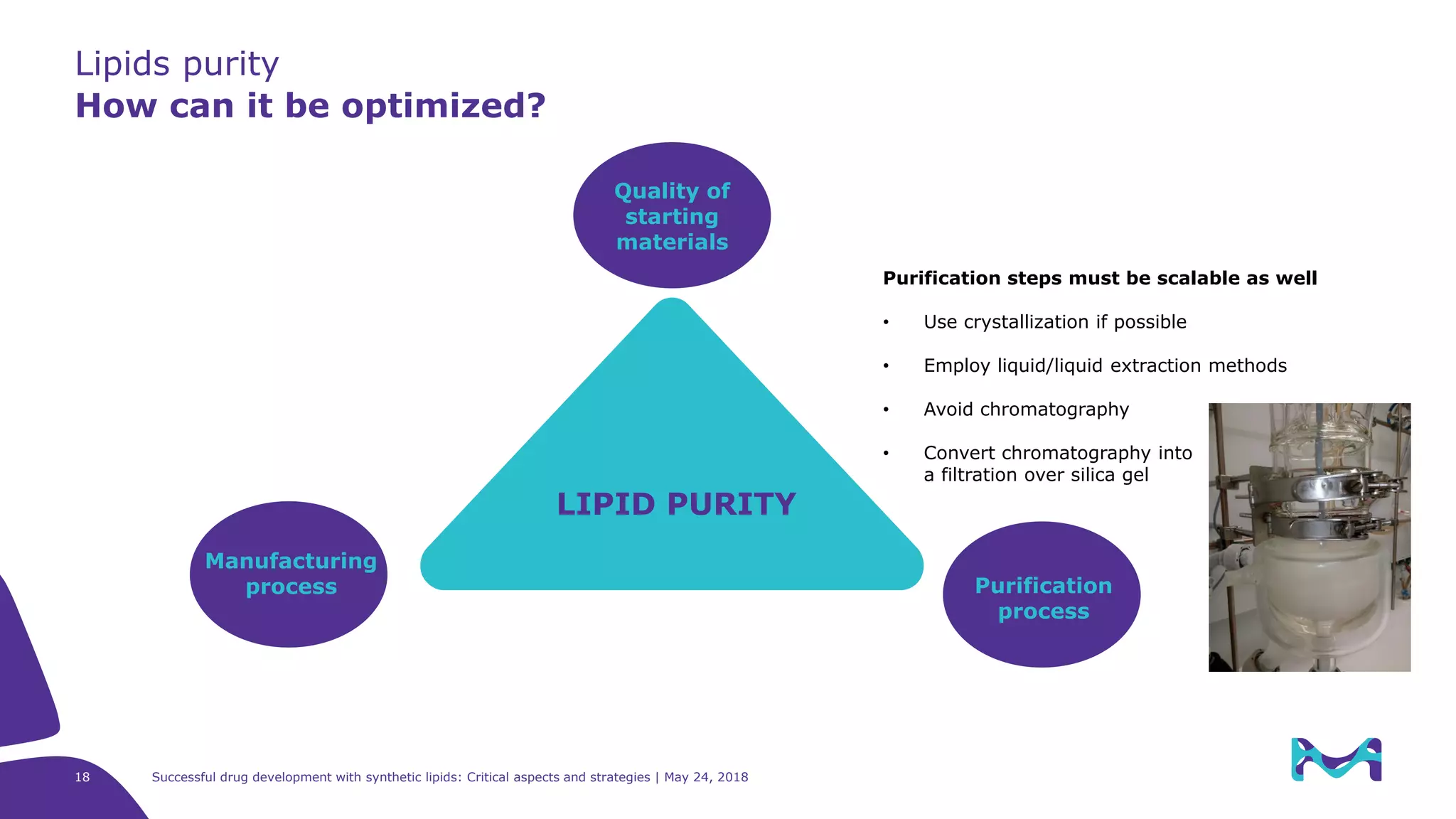
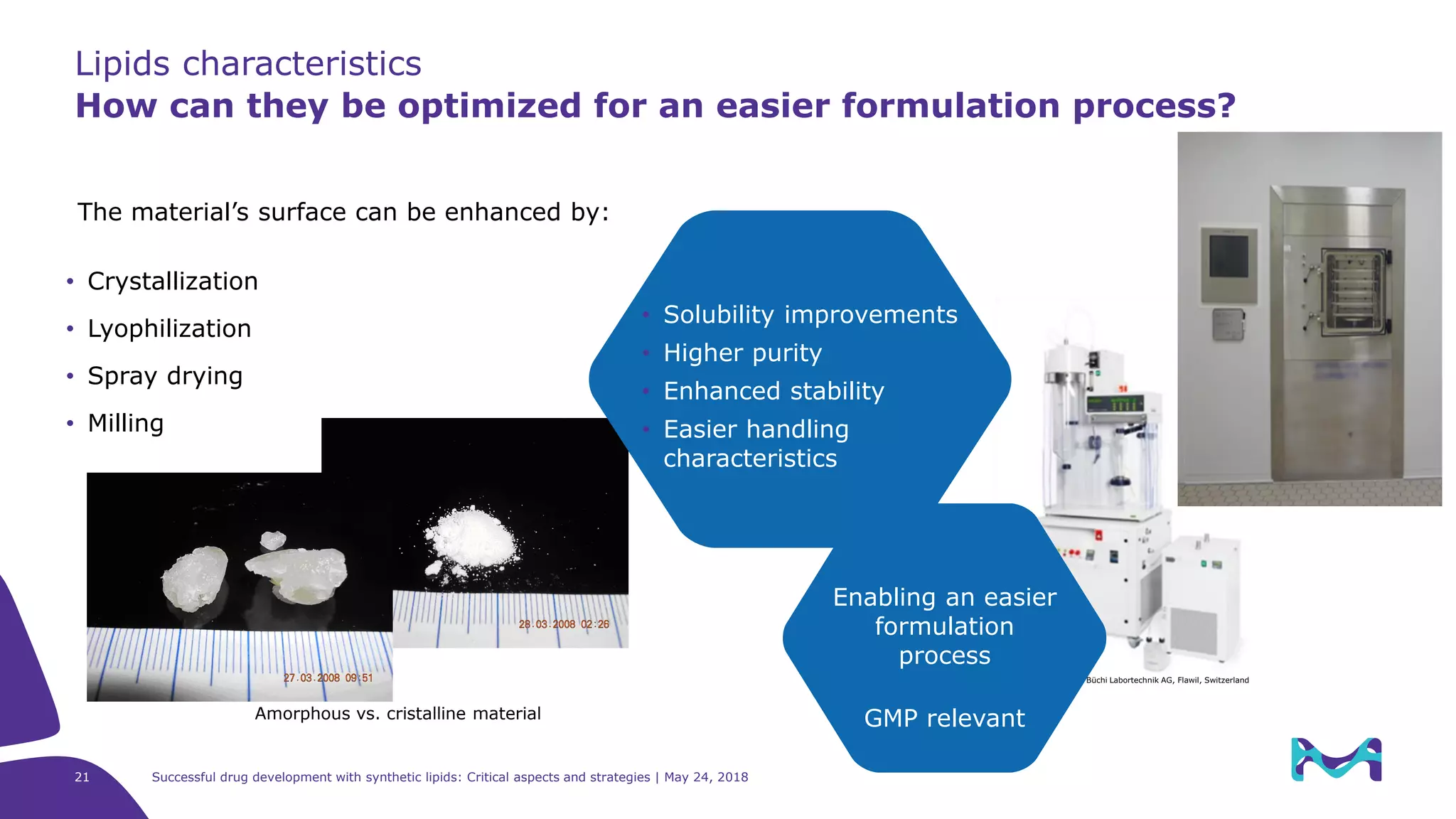
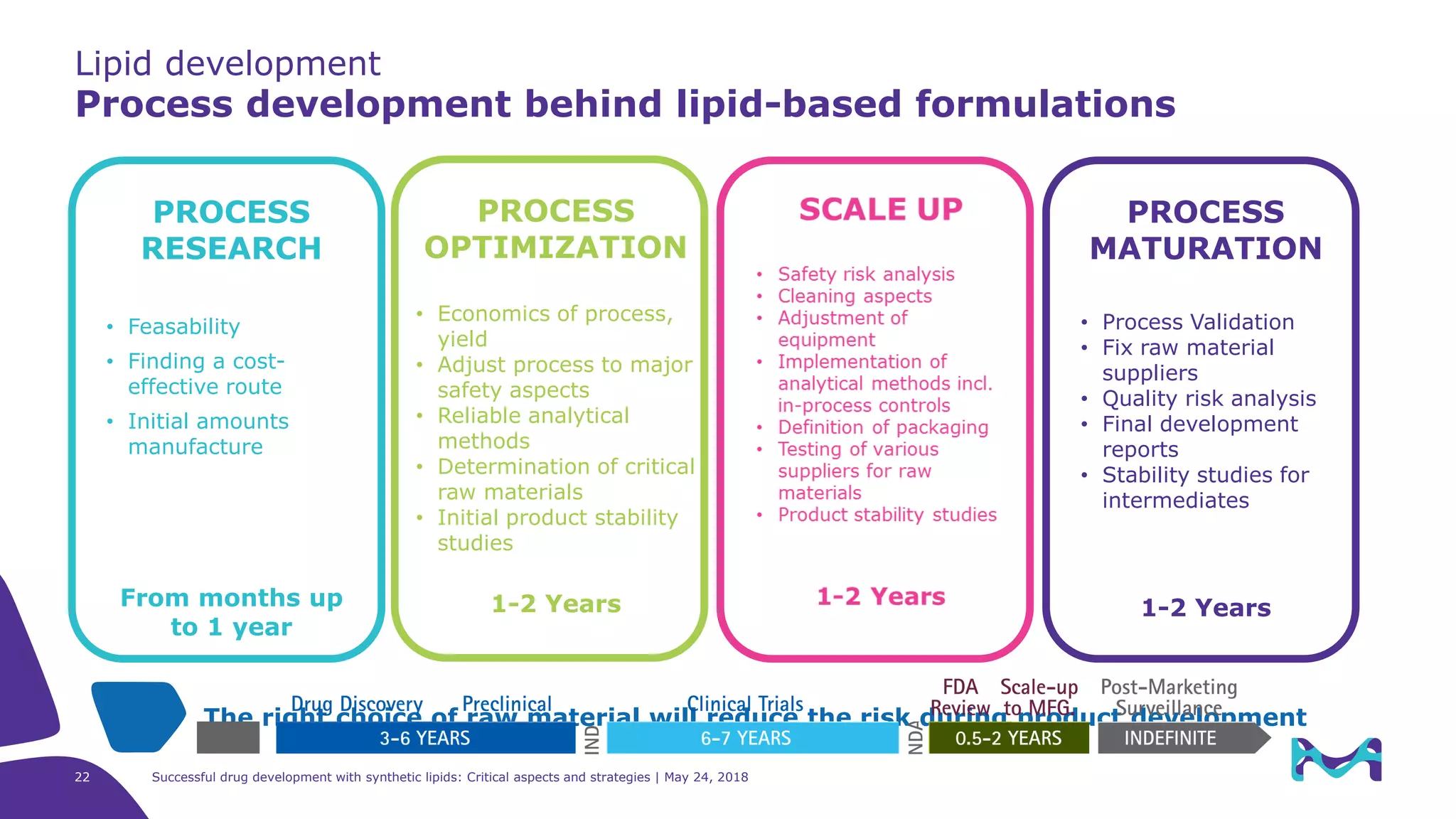
The document discusses critical aspects and strategies for successful drug development using synthetic lipids within Merck KGaA's life sciences operations. It covers the role of lipids in liposomal formulations, emphasizes the importance of lipid purity and consistent quality, and mentions regulatory considerations for developing lipid-based drug products. Additionally, it highlights challenges, process development, and enhanced surfacing techniques for improved drug delivery systems.




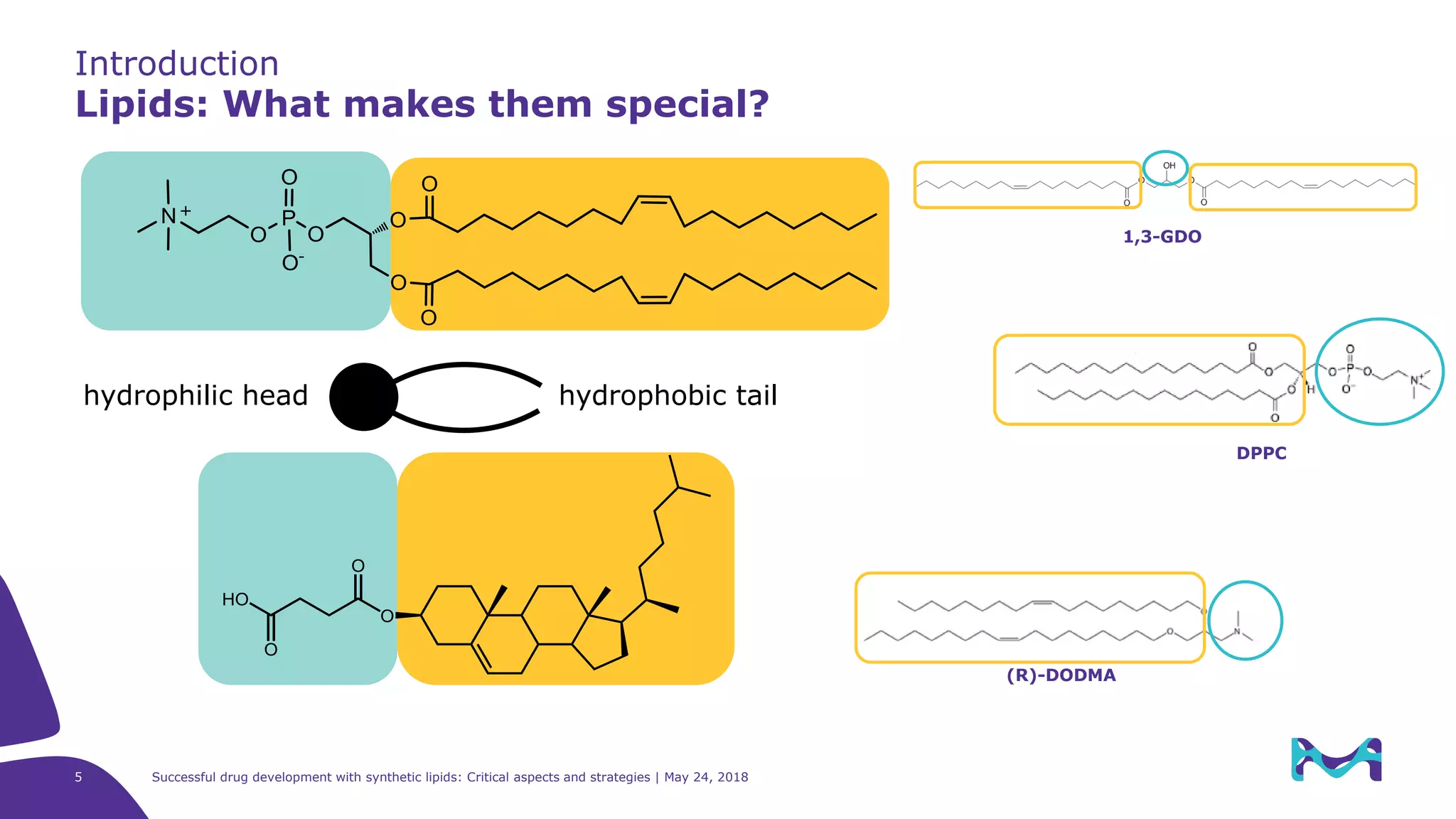
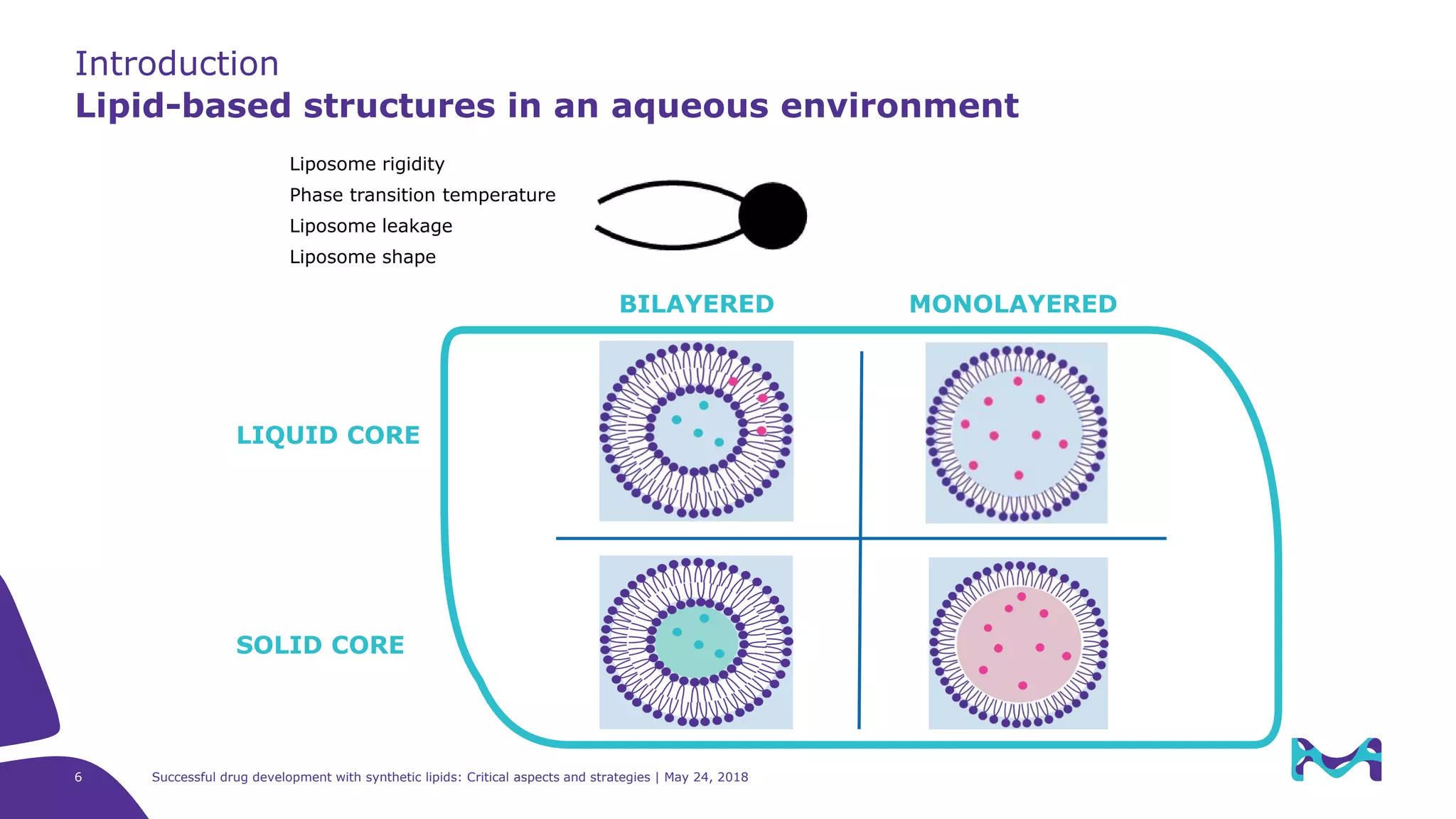
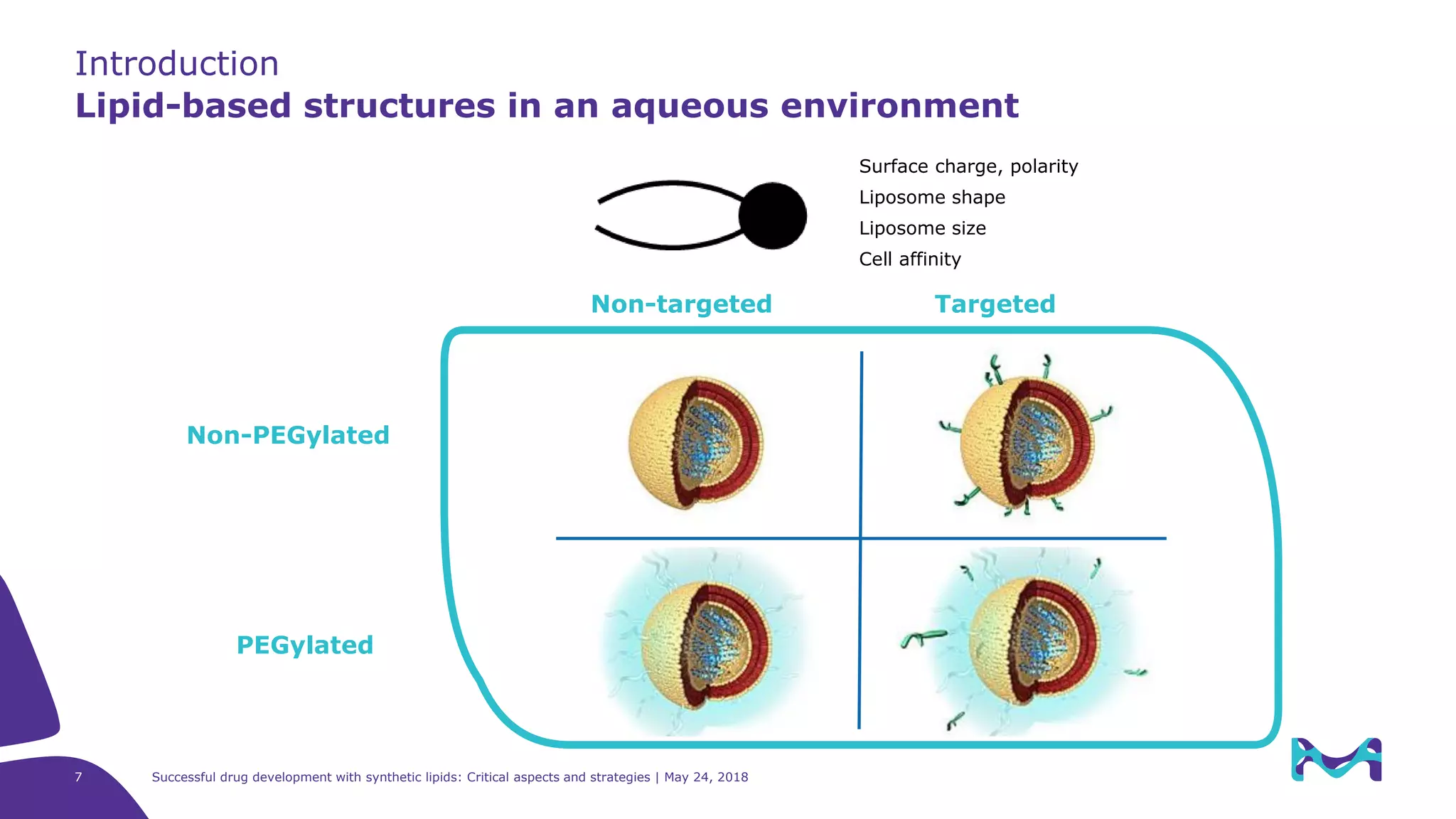





![Successful drug development with synthetic lipids: Critical aspects and strategies | May 24, 201824
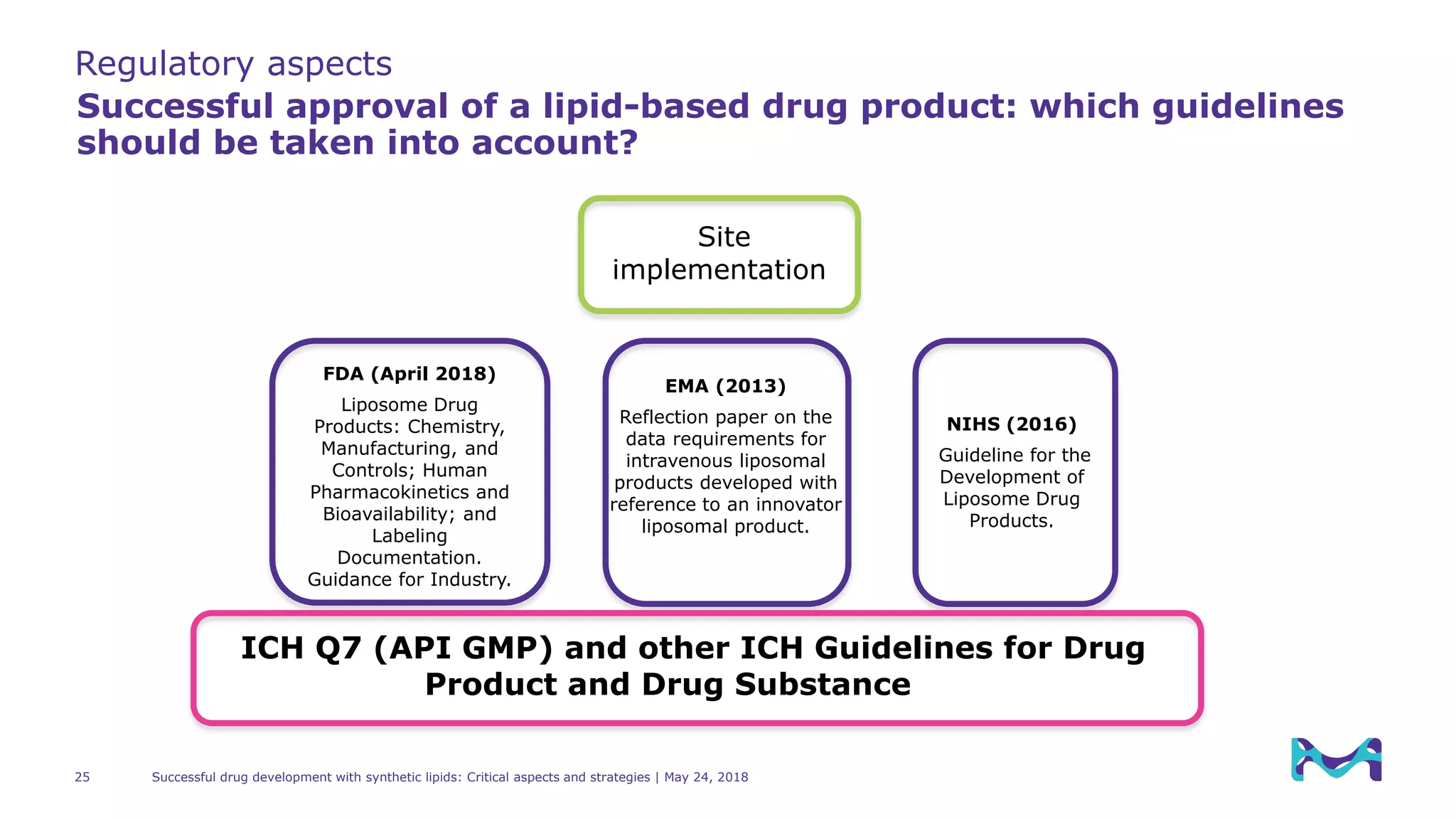
Regulatory aspects
Successful approval of a lipid-based drug product: which guidelines
should be taken into account?
“[…] The quality of lipid components, including
modified lipids (e.g., polyethylene glycol (PEG)
modified lipids), can affect the quality and
performance of the liposome drug product.
In cases of novel lipid components, the level of
detail provided in the submission should be
comparable to that for a drug substance.[…] see
ICH Q11 Development and Manufacture of Drug
Substances […]”
“[…] The quality and purity of the lipid
starting materials is essential for the later
quality of the drug product, therefore the
appropriate characterization and specification
of the lipid starting material is considered as
vital. […]
The level of information to be provided
with the relevant submission depends on
complexity of the excipients. […]”
“[…] Because the quality of liposome components
such as lipids can affect the quality of whole
liposome drug products, the quality of liposome
components should be appropriately controlled […]
In liposome drug products, lipid components […] and
molecules for liposome modification […] contribute to
an improvement in the in vivo stability,
pharmacokinetics, and intracellular behavior of the
active substance. Therefore, liposome components,
especially ligands (targeting moiety) and antibodies
that have a significant impact on the function of
the drug product, should be evaluated and
controlled to a greater extent than general
excipients to ensure their intended
properties.[…]”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/successfuldrugdevelopmentwithsyntheticlipids-criticalaspectsandstrategies-180524160105/75/Successful-Drug-Development-with-Synthetic-Lipids-Critical-Aspects-and-Strategies-24-2048.jpg)