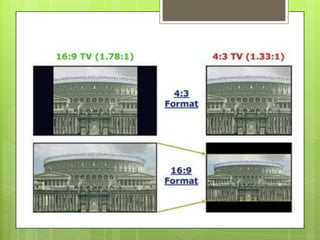
This document discusses subtitles, including the different types (real-time, offline, soft, built-in, hard), file formats, and the technical aspects of video processing like frame rate, aspect ratio, resolution, and compression. It also covers software and hardware requirements for encoding subtitles, how to configure subtitles, and examples of using subtitles.