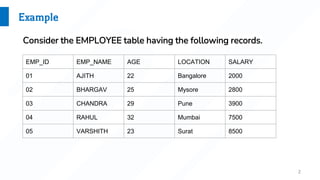
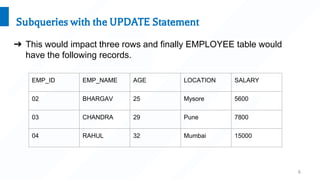
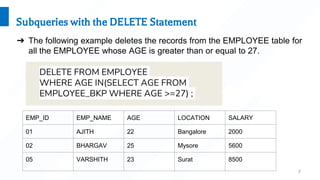
A subquery is a query nested inside another SQL query. Subqueries can be used with SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements and operators like =, <, >, etc. Examples show subqueries used to select records from a table where a field value matches one returned from a nested select, to insert all records from one table to another using a subquery, and to update or delete records in a table where a field value meets conditions in a subquery.