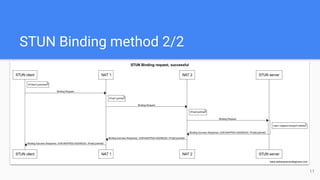
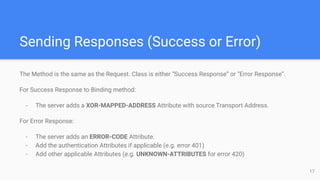
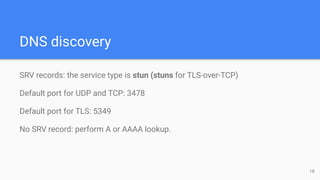
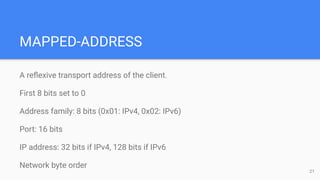
The STUN protocol allows clients to discover their public IP address and port when they are behind a NAT. It works by having a client send a request to a STUN server, which responds with the client's reflexive transport address as seen by the server. STUN can also be used to check connectivity and maintain NAT bindings over time. It defines a packet format with a header and attributes, as well as request/response and indication transactions. Common usages of STUN include ICE for NAT traversal and SIP outbound for VoIP calls. The document discusses STUN operations, messages, attributes and security considerations.

![STUN: Session Traversal Utilities for NAT
RFC 5389 (8489)
"[STUN] can be used by an endpoint to determine the IP address and port allocated
to it by a NAT. It can also be used to check connectivity between two endpoints, and
as a keep-alive protocol to maintain NAT bindings."
Combination with other protocols:
- Connectivity checks: ICE (RFC 8845)
- Relay: TURN (RFC 5766, 8656) 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stunprotocol-210309132927/85/STUN-protocol-2-320.jpg)