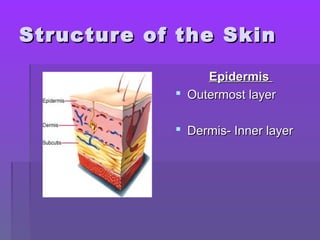
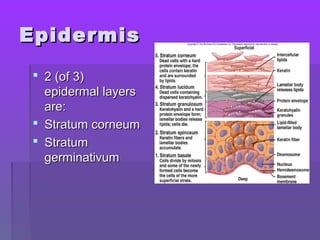
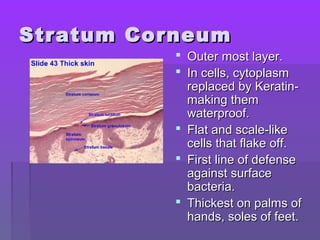
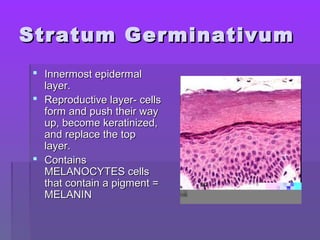
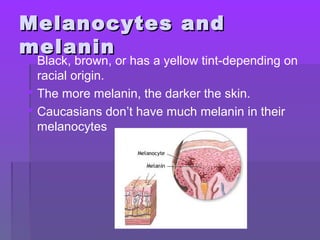
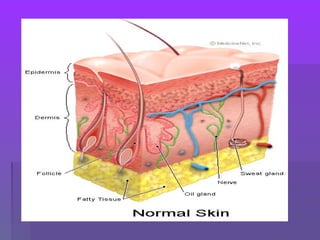
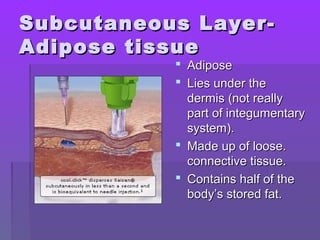
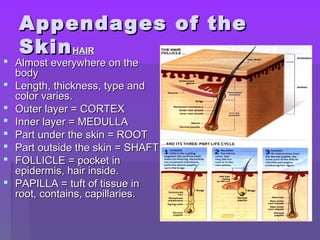
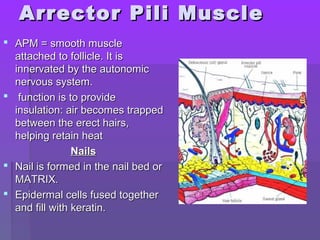
The document discusses the functions and structure of the integumentary system. The seven main functions of skin are protection, temperature regulation, vitamin D production, sensory perception, storage of substances like fat and water, excretion of fluids, and absorption of certain drugs. Structurally, skin is composed of an outer epidermis and inner dermis layer. The epidermis contains stratum corneum and stratum germinativum layers, while the dermis contains connective tissue, blood vessels, nerve endings, and appendages like hair follicles, sweat and sebaceous glands.