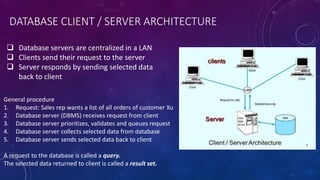
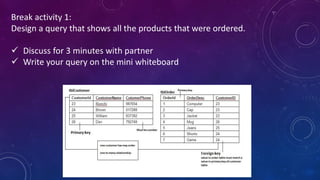
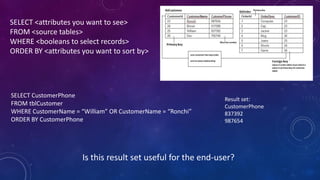
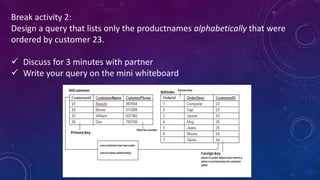
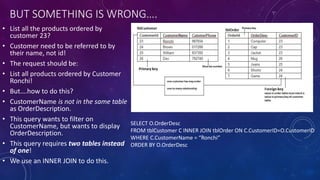
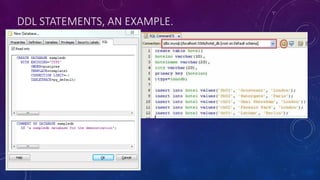
This document provides an introduction to structured query language (SQL). It discusses SQL's purpose for retrieving and manipulating data from a database. It also explains the different parts of SQL including data manipulation language (DML) for modifying data, data definition language (DDL) for designing databases and tables, and data control language (DCL) for setting user permissions. The document demonstrates writing basic SELECT queries to retrieve data from a database table and uses JOINs to retrieve data from multiple tables. It also shows DML statements for inserting, updating and deleting records in a table.