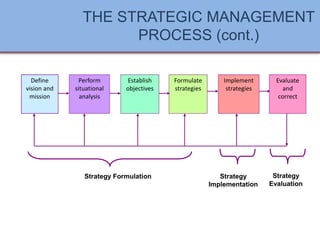
Strategic management is defined as the art and science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating cross-functional decisions to help an organization achieve its objectives. The strategic management process consists of three main stages: strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation, focusing on setting missions, analyzing situations, and adjusting strategies as needed. Effective strategic management leads to improved performance and communication within enterprises, while avoiding common pitfalls such as inadequate involvement from key personnel and hasty decisions.