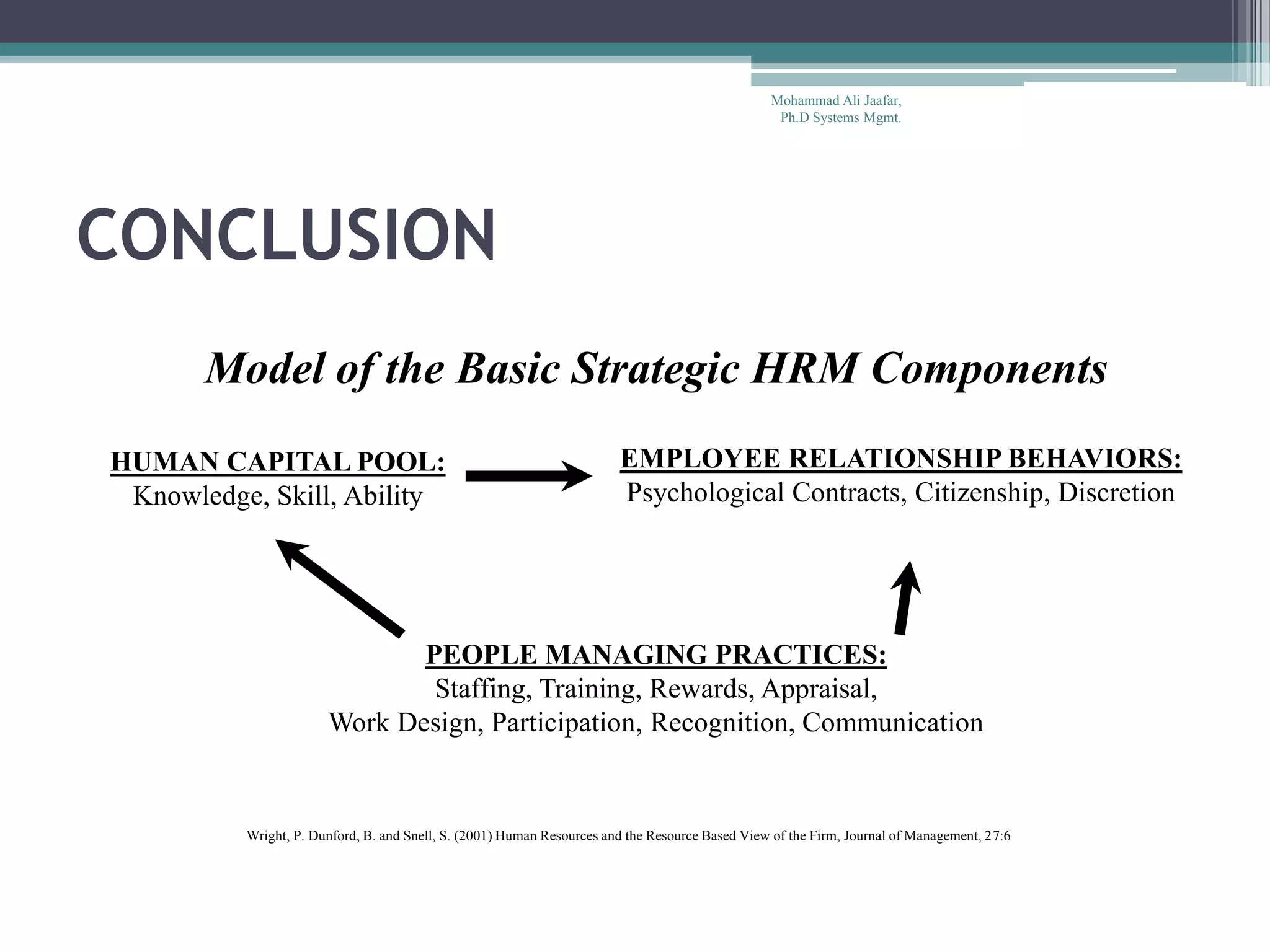
The document discusses strategic human resource management (SHRM) and its role in the employment relationship, emphasizing the integration of HR practices with organizational goals for competitive advantage. It outlines various strategies, including business and operational approaches, and highlights practices such as recruitment, training, and employee involvement that contribute to high performance. The conclusion suggests that aligning HR practices with competitive strategies can enhance organizational effectiveness, though SHRM alone may not determine a firm's success.