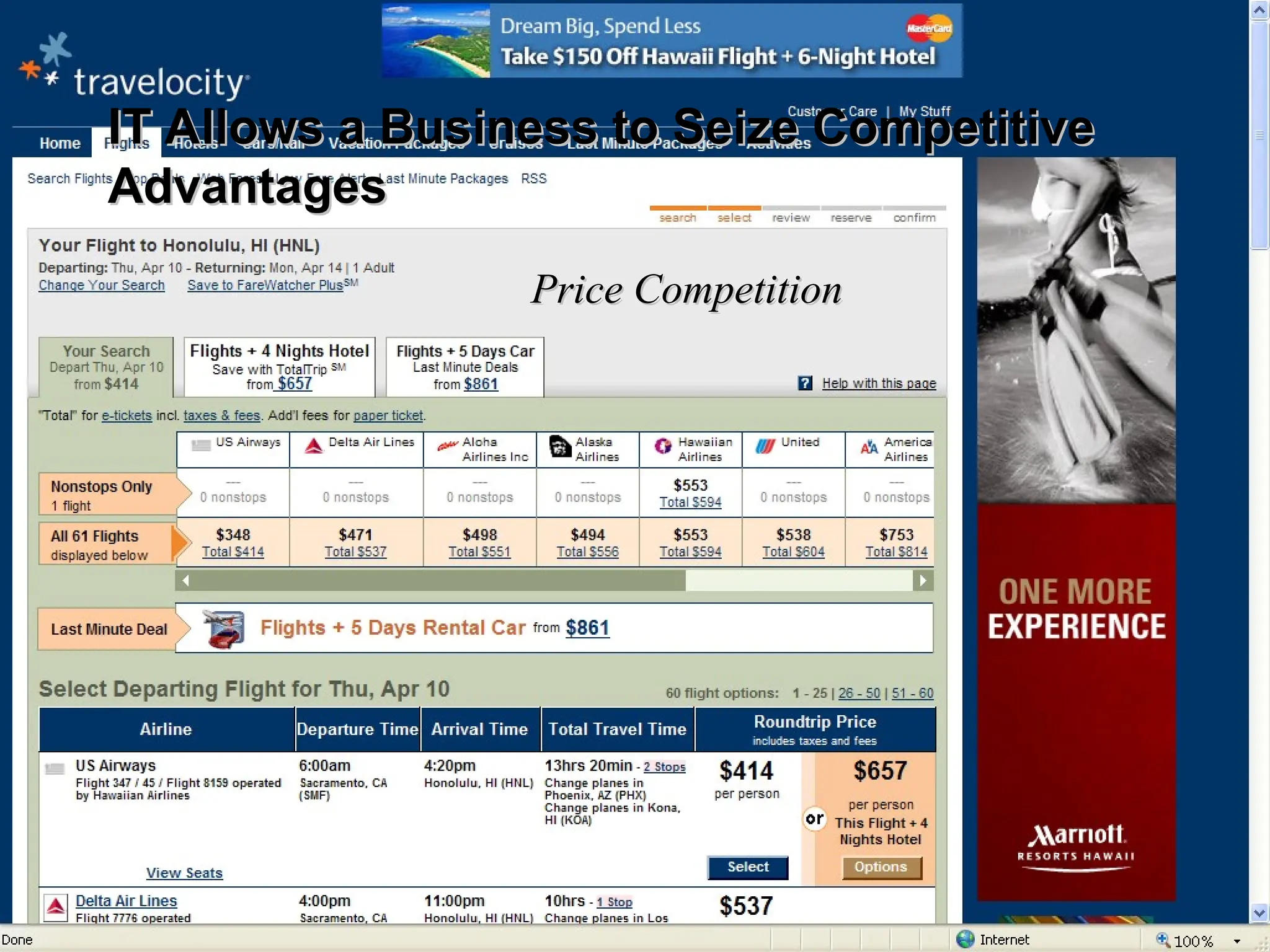
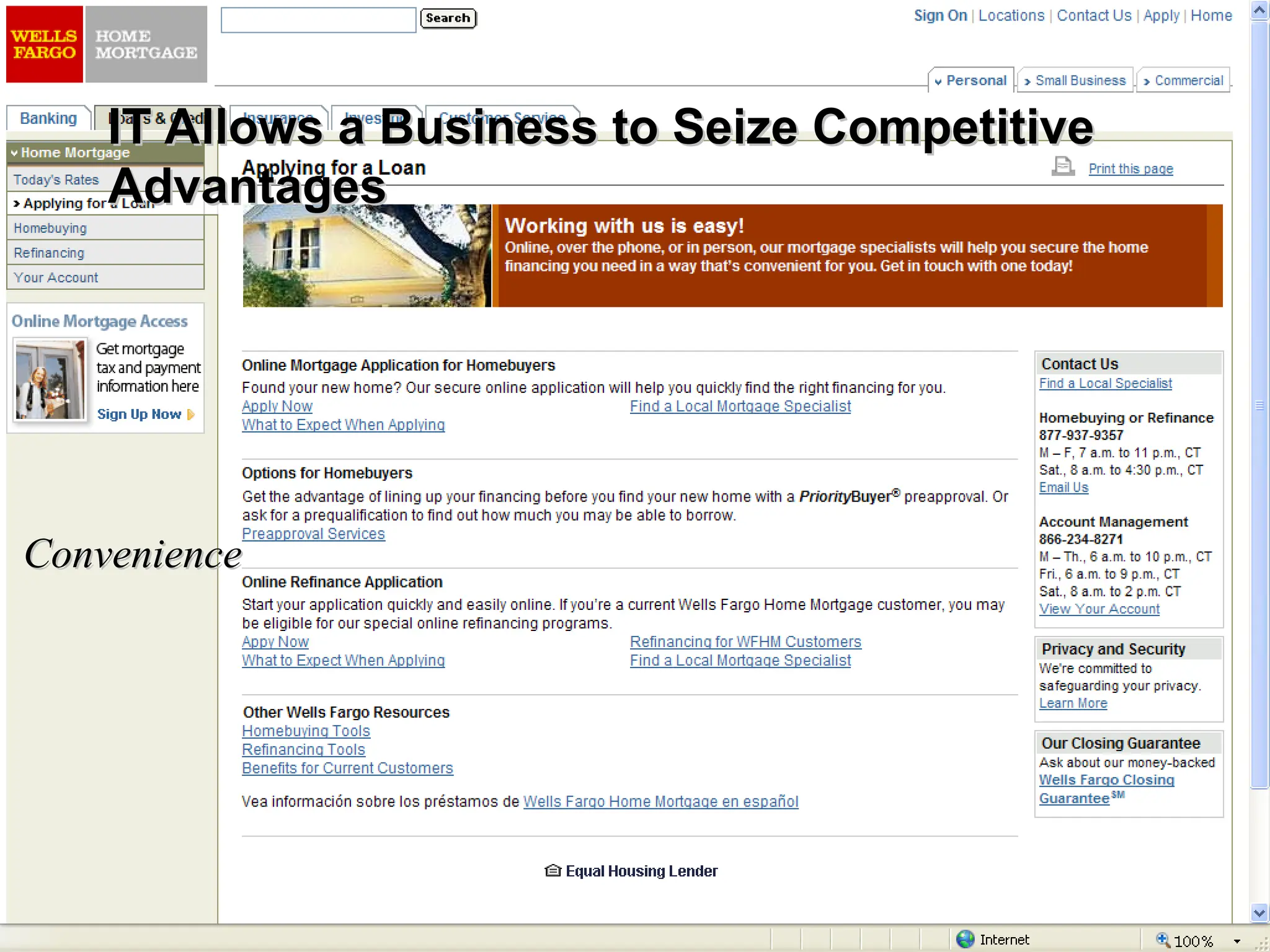
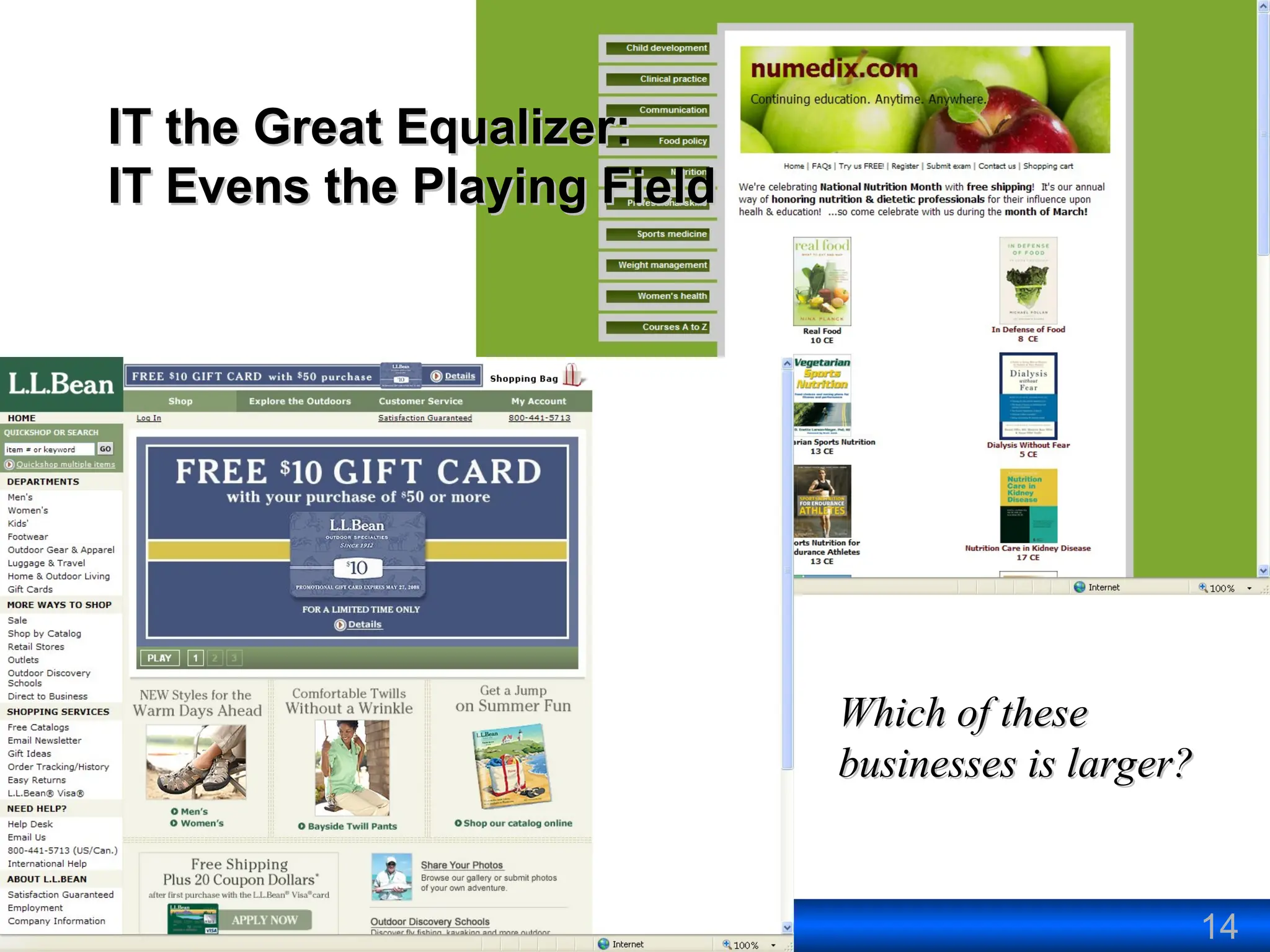
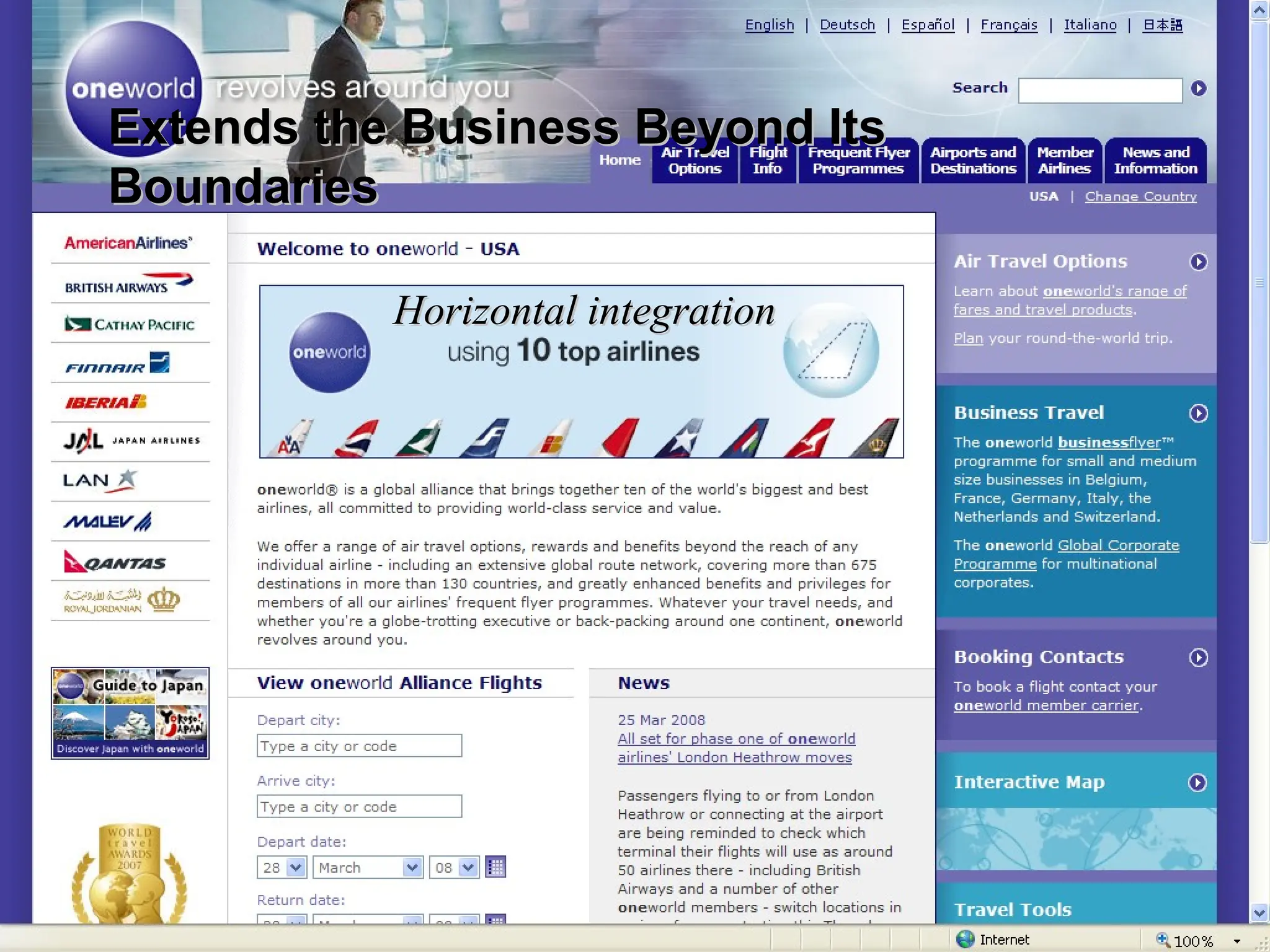
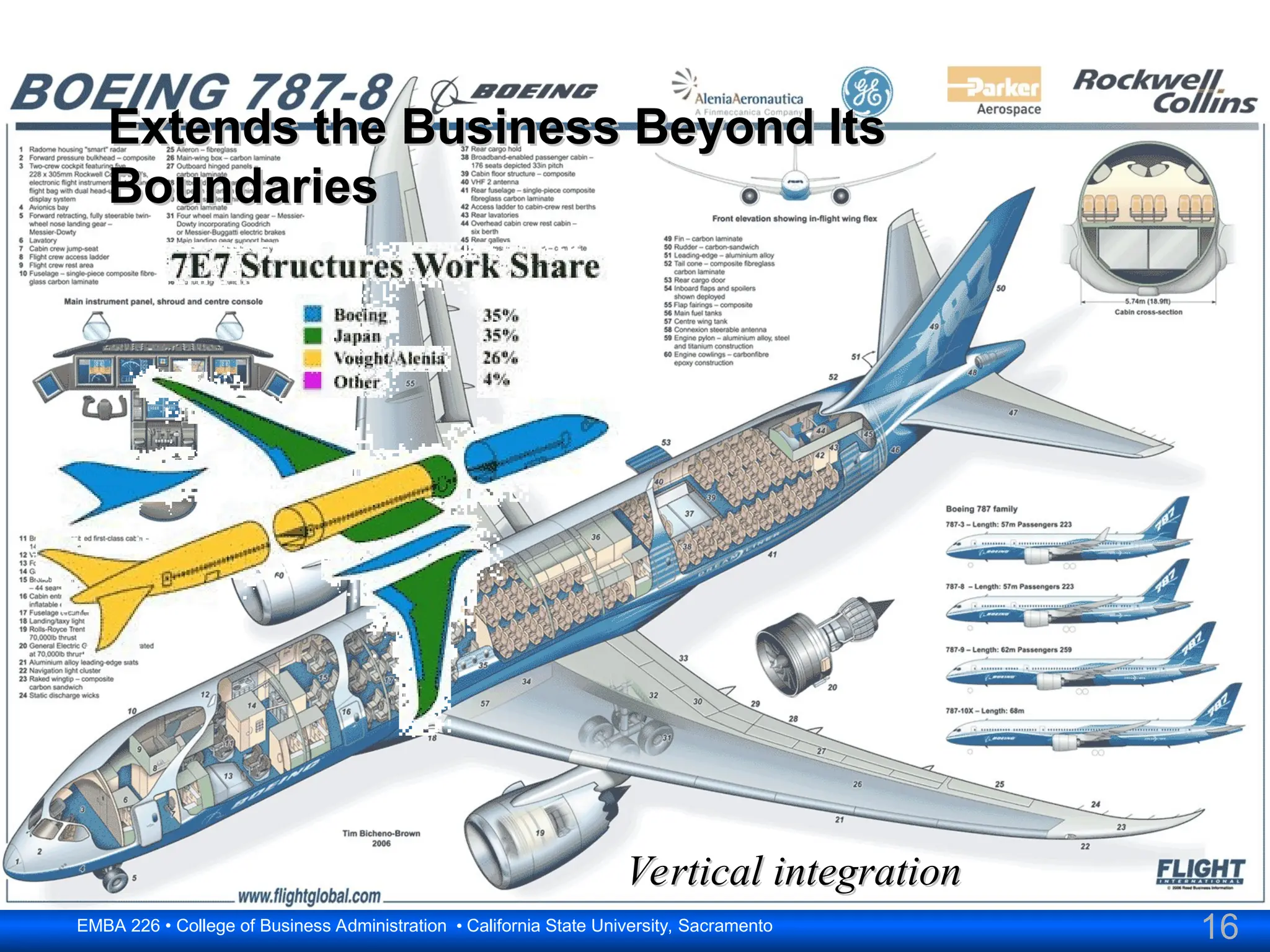
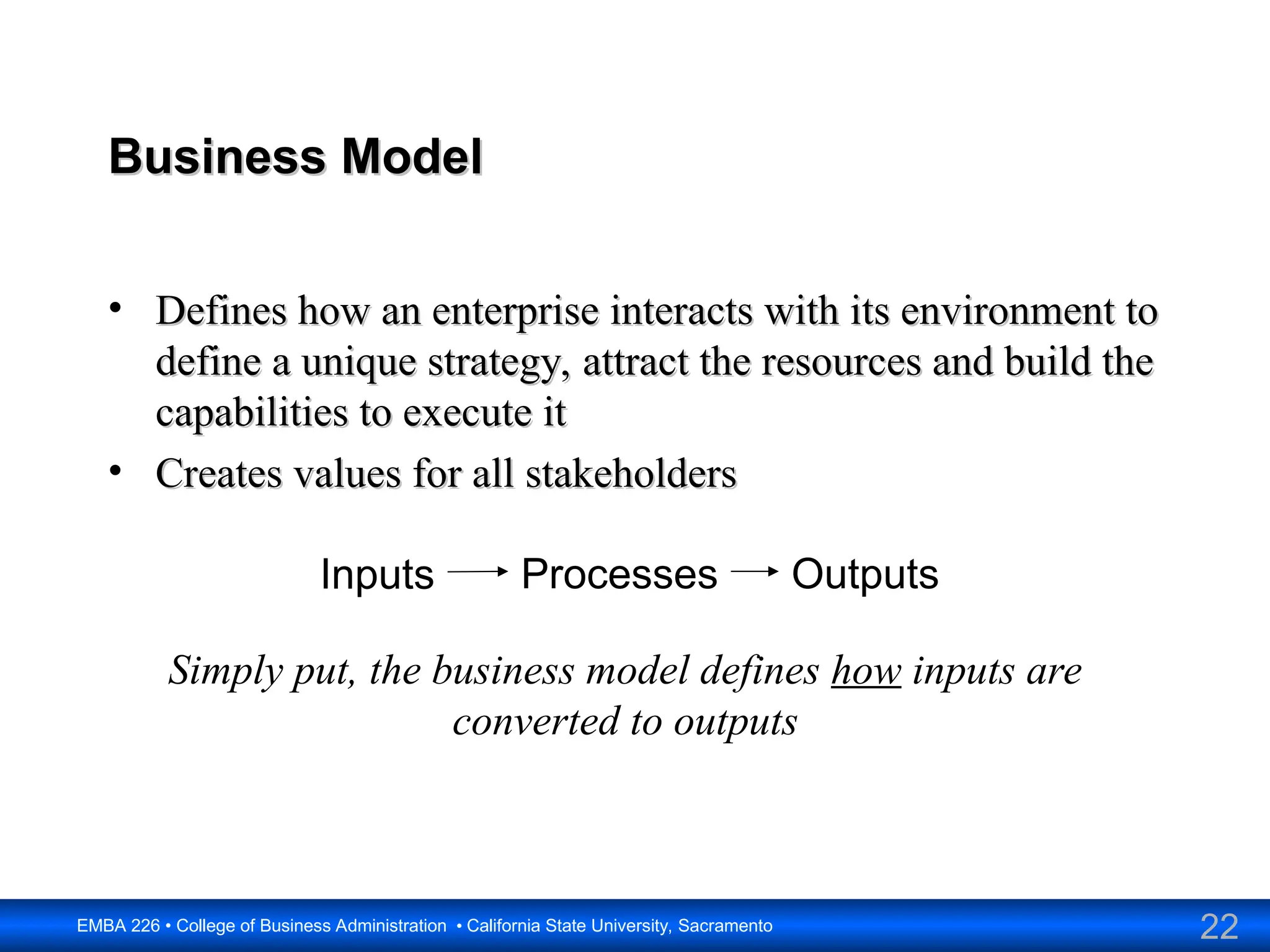
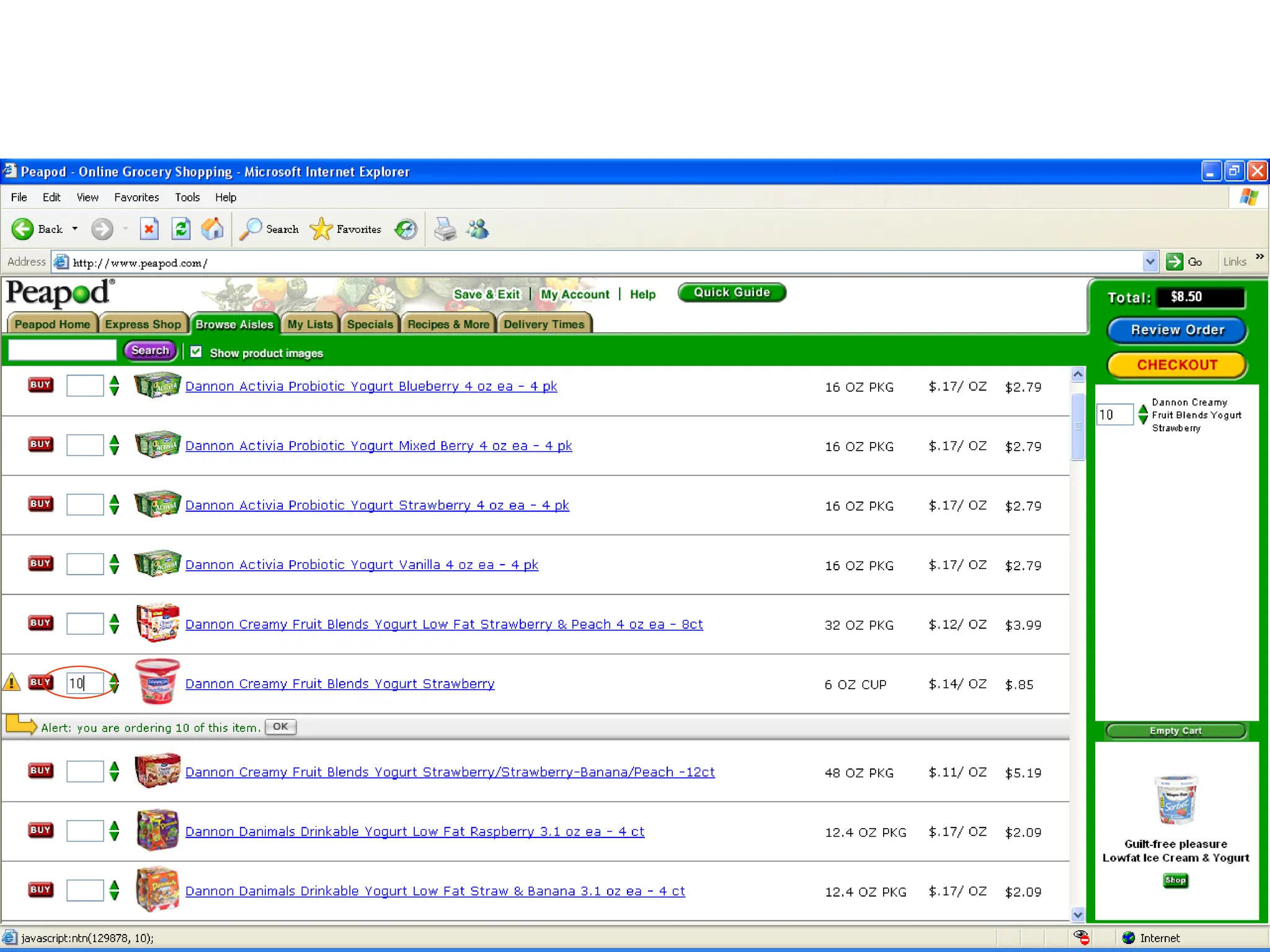
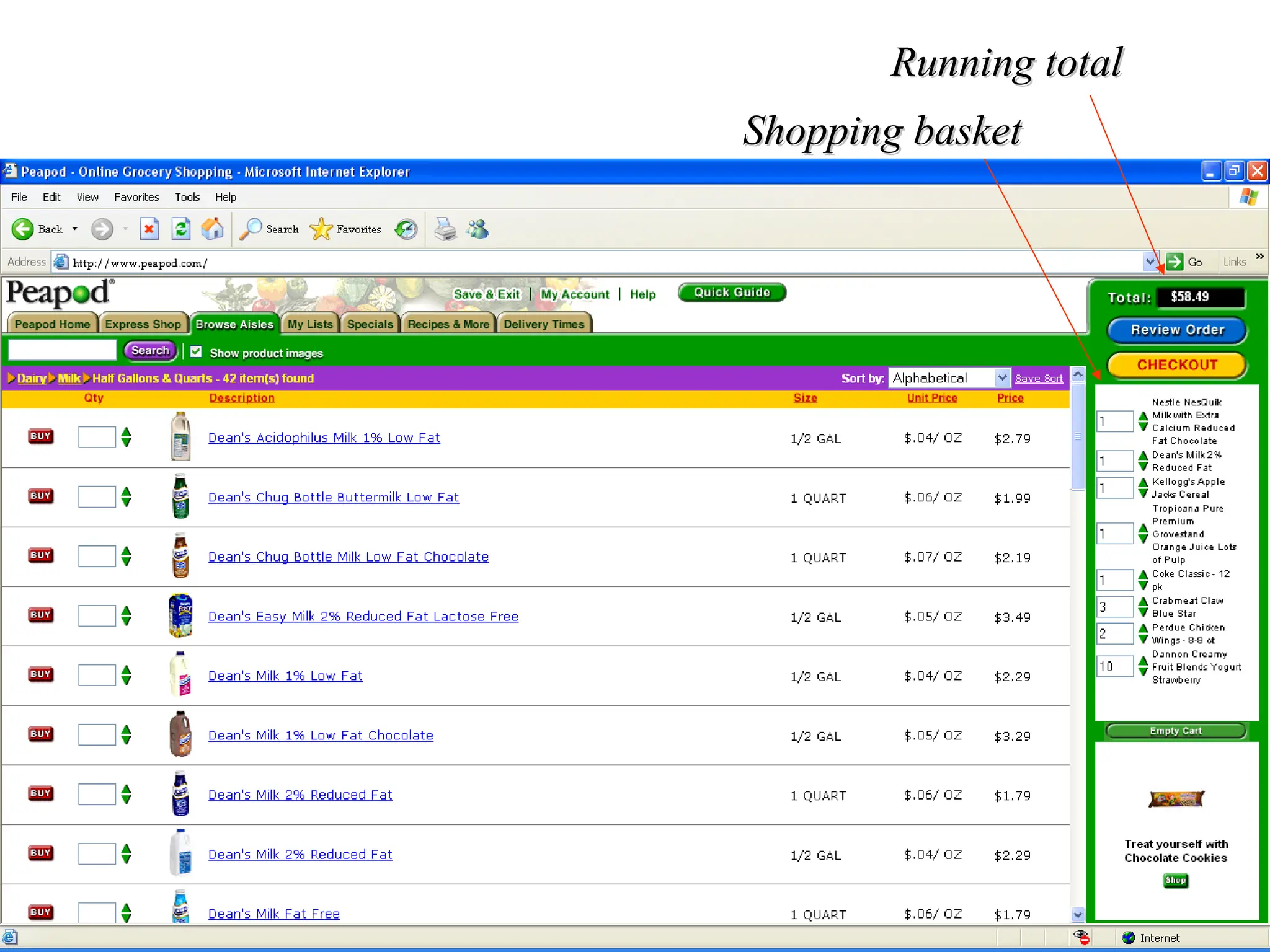
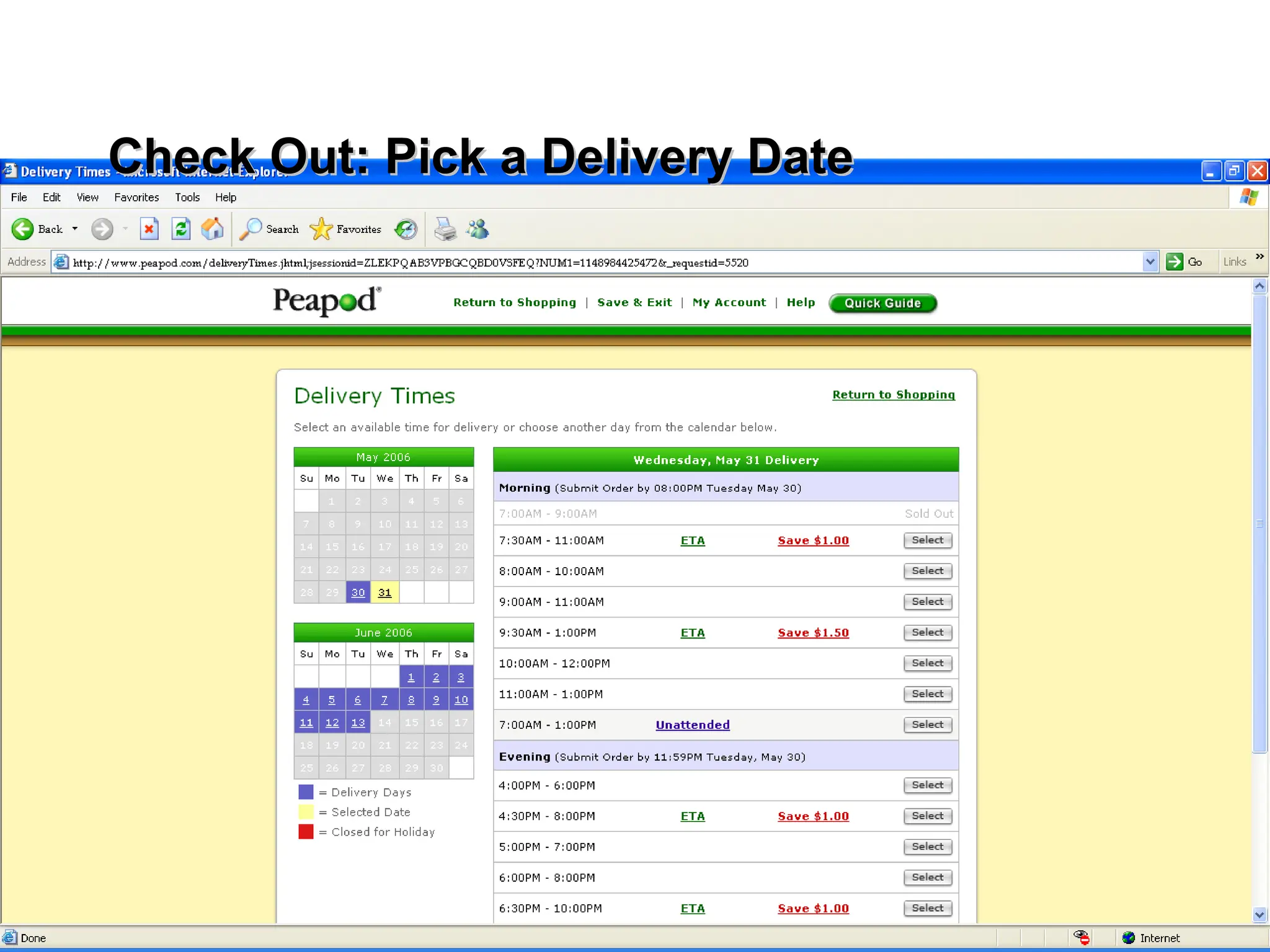
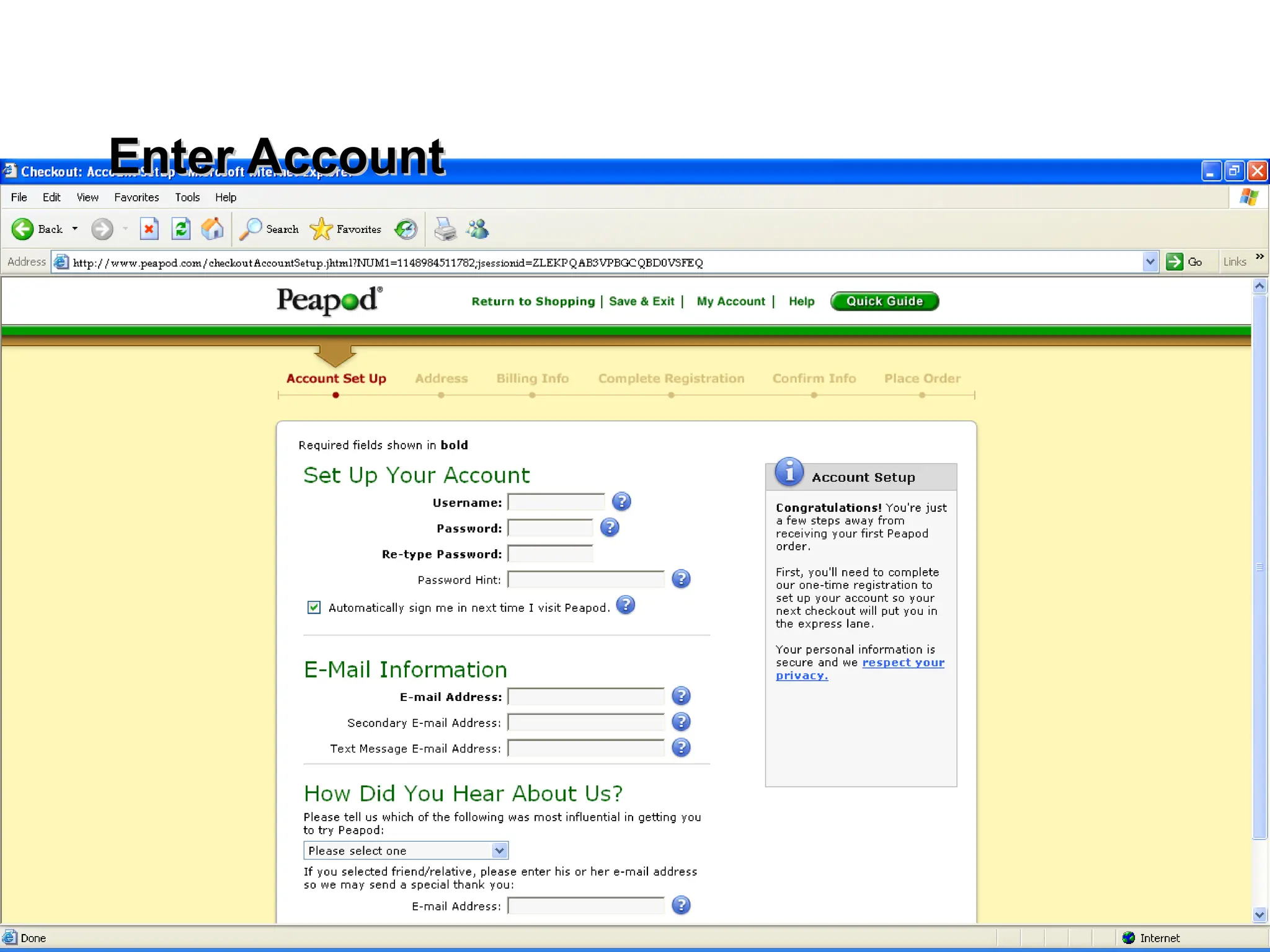
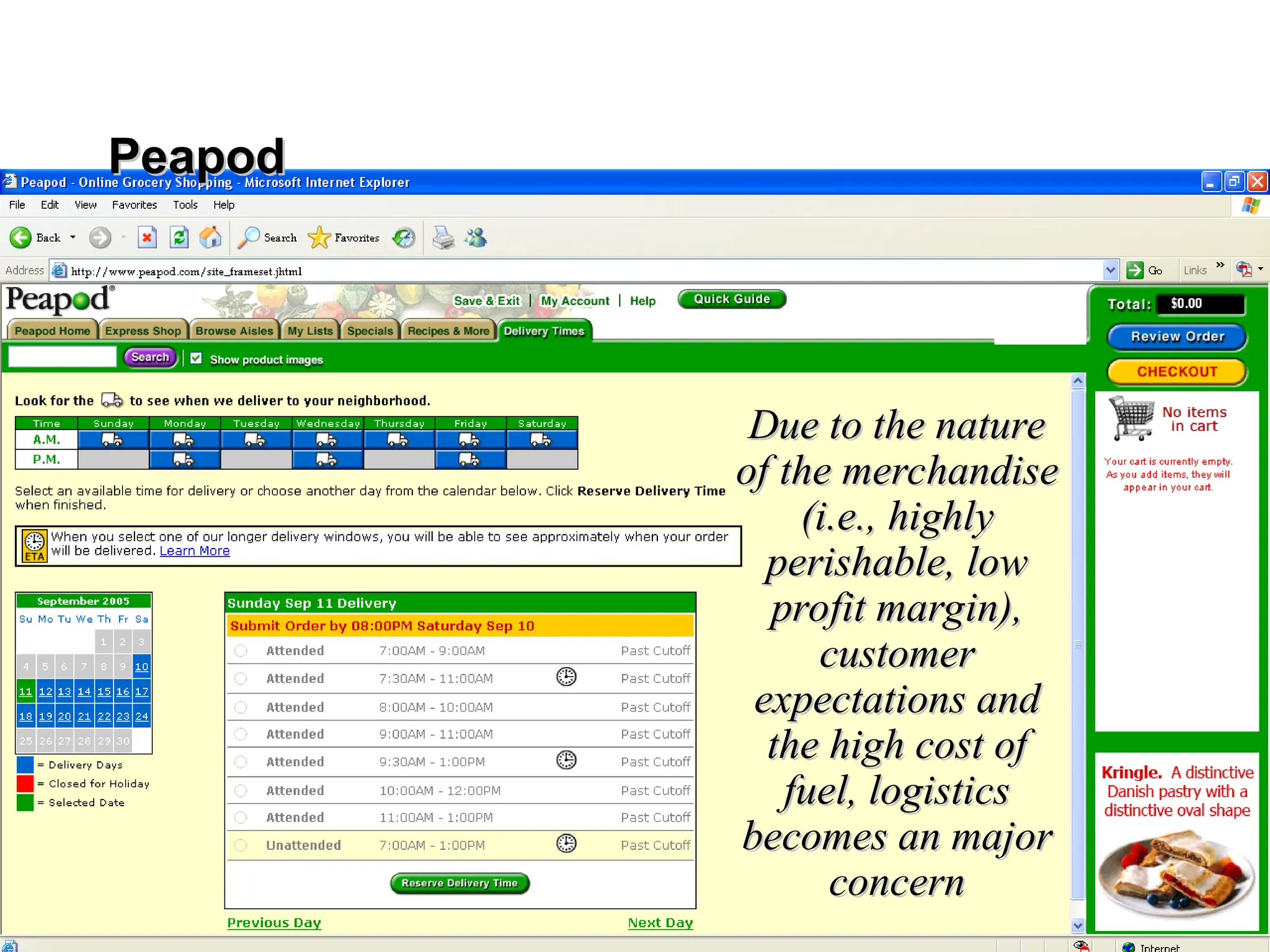
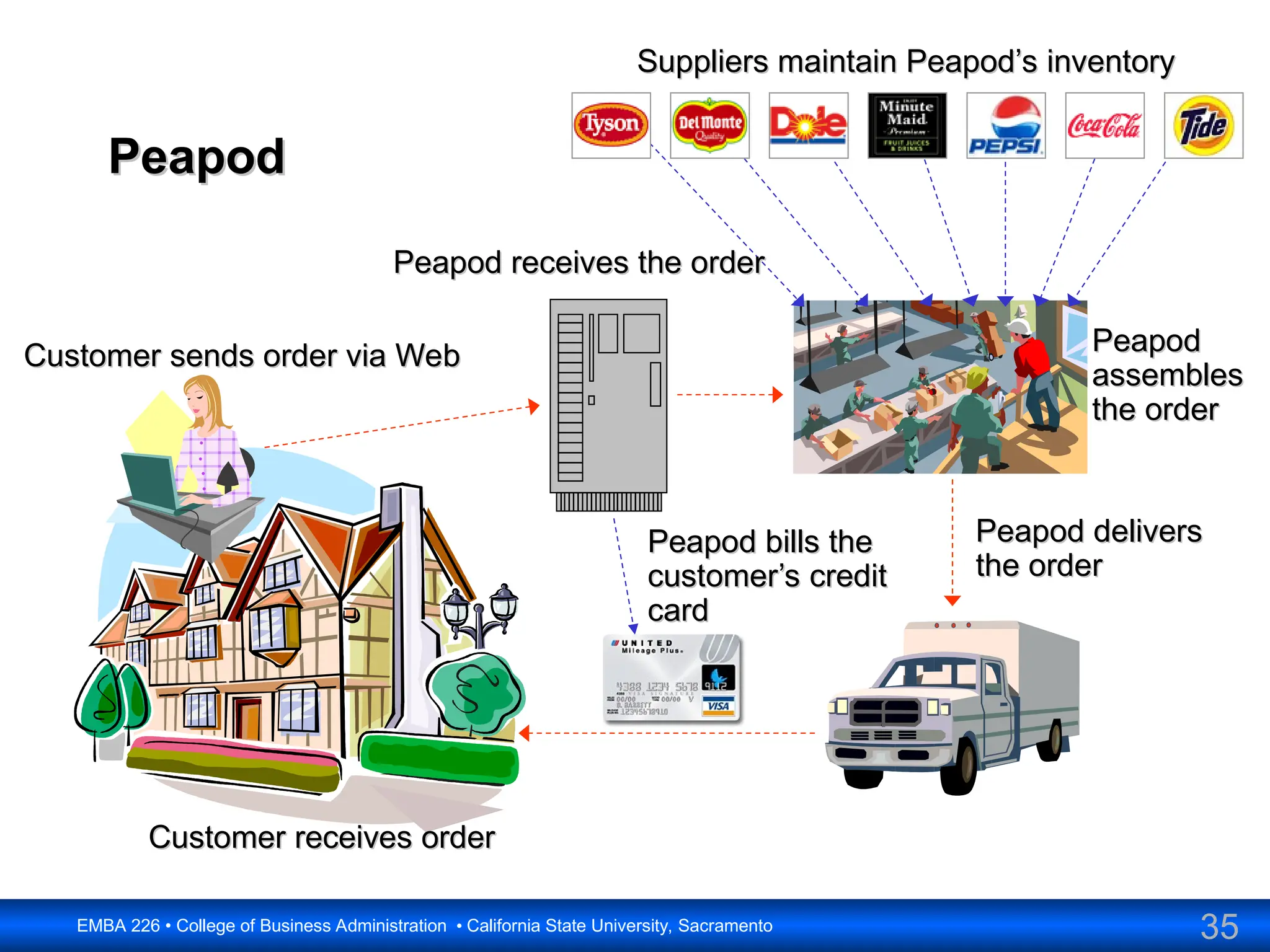
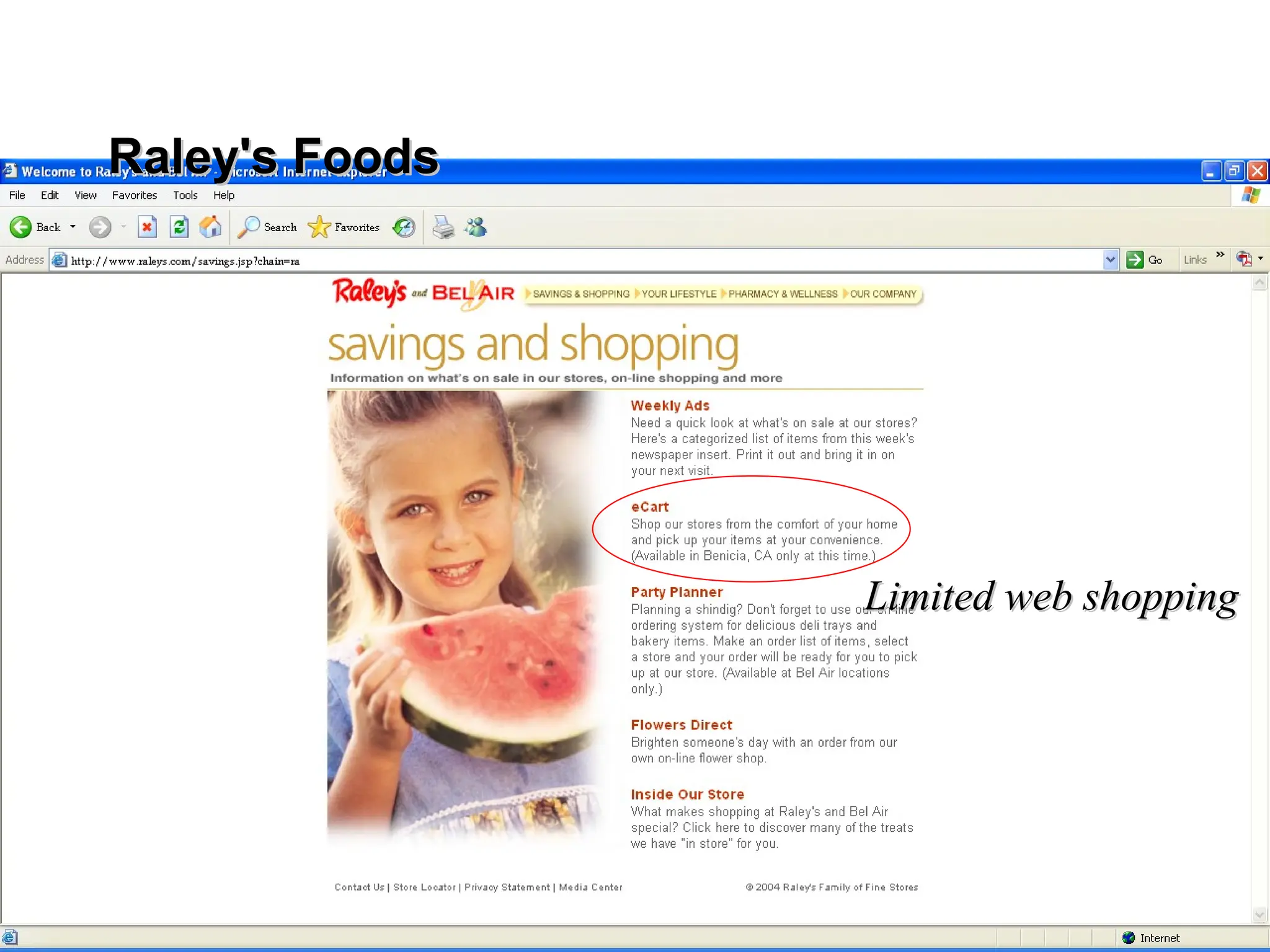
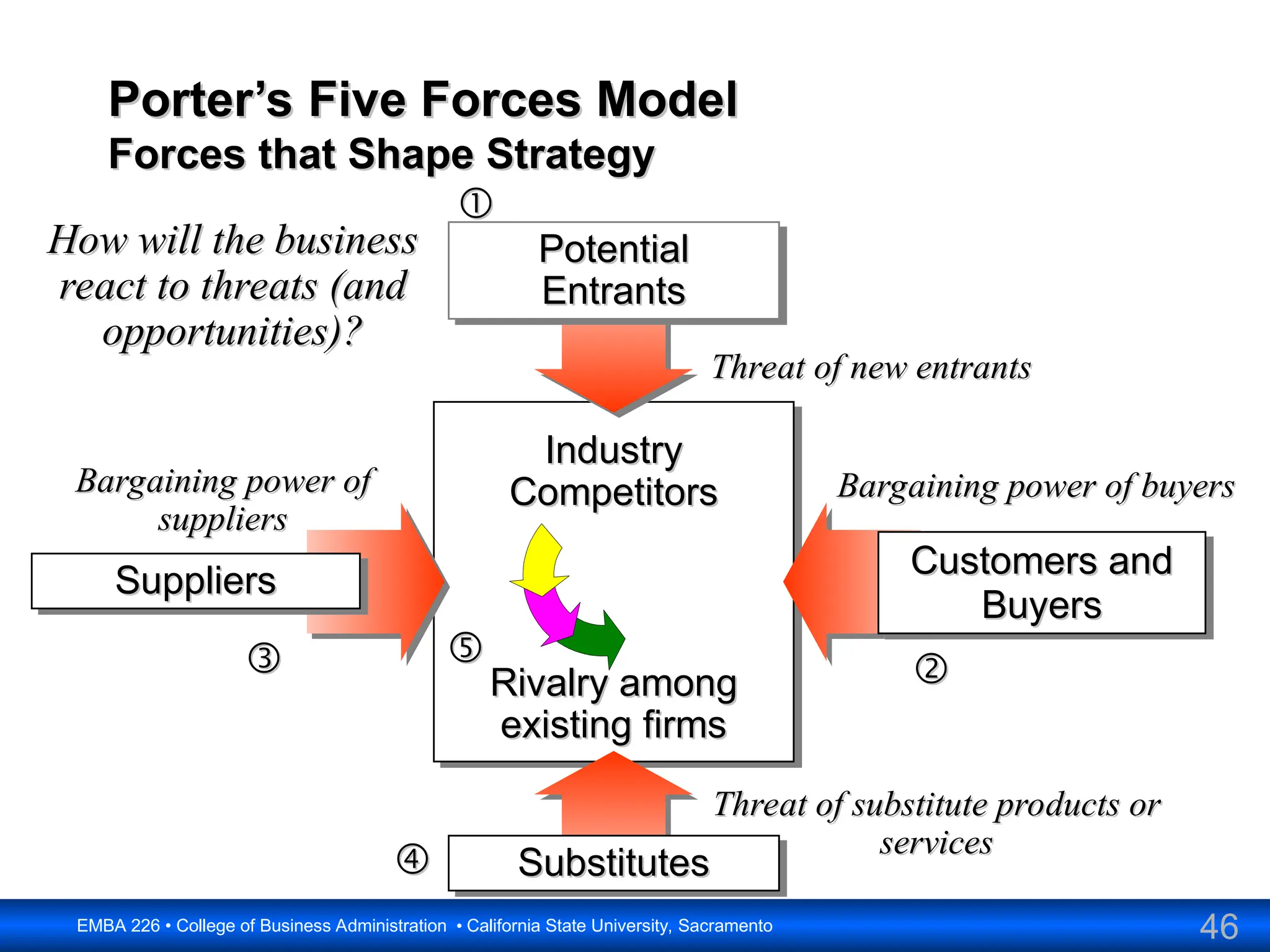
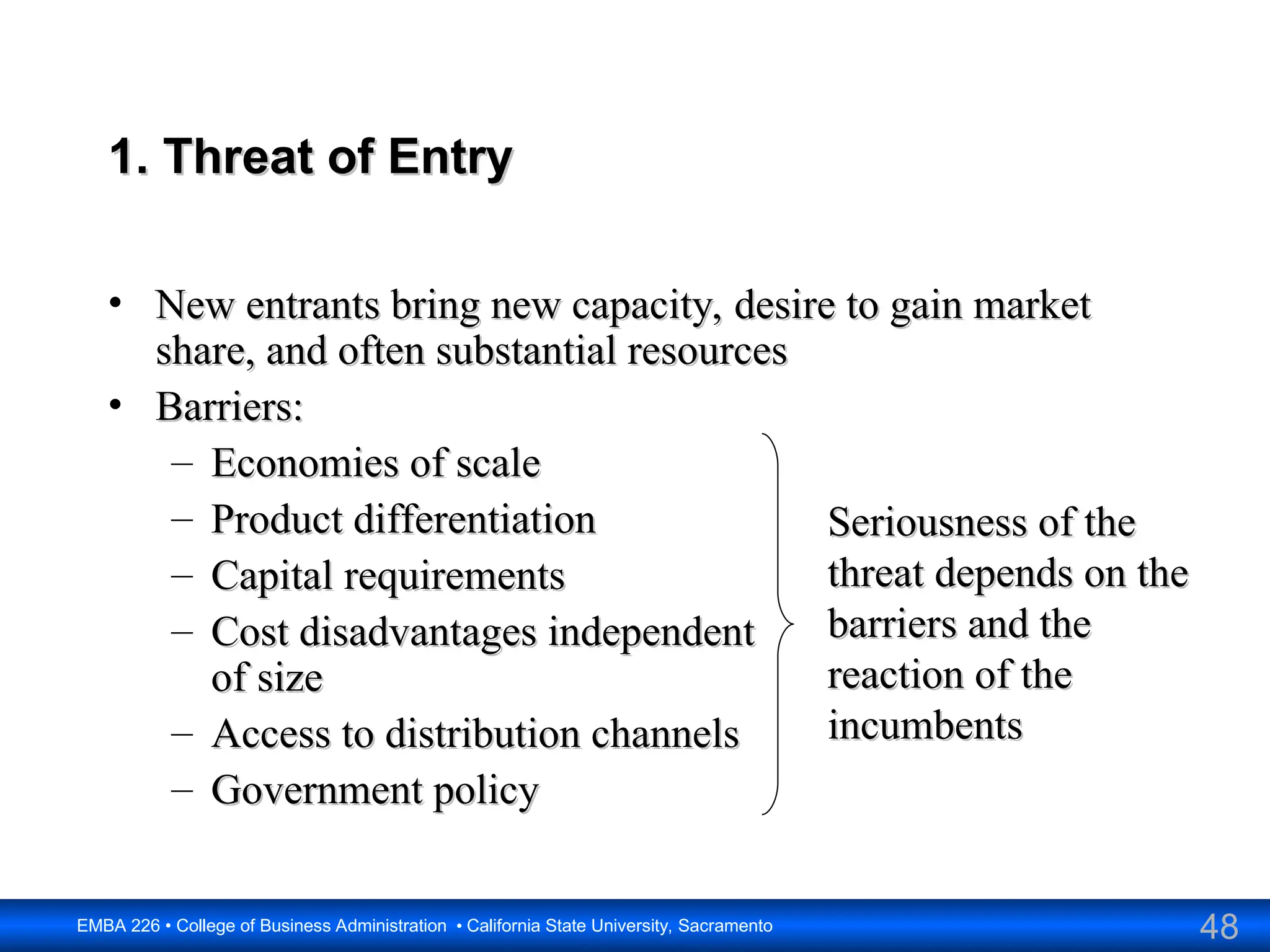
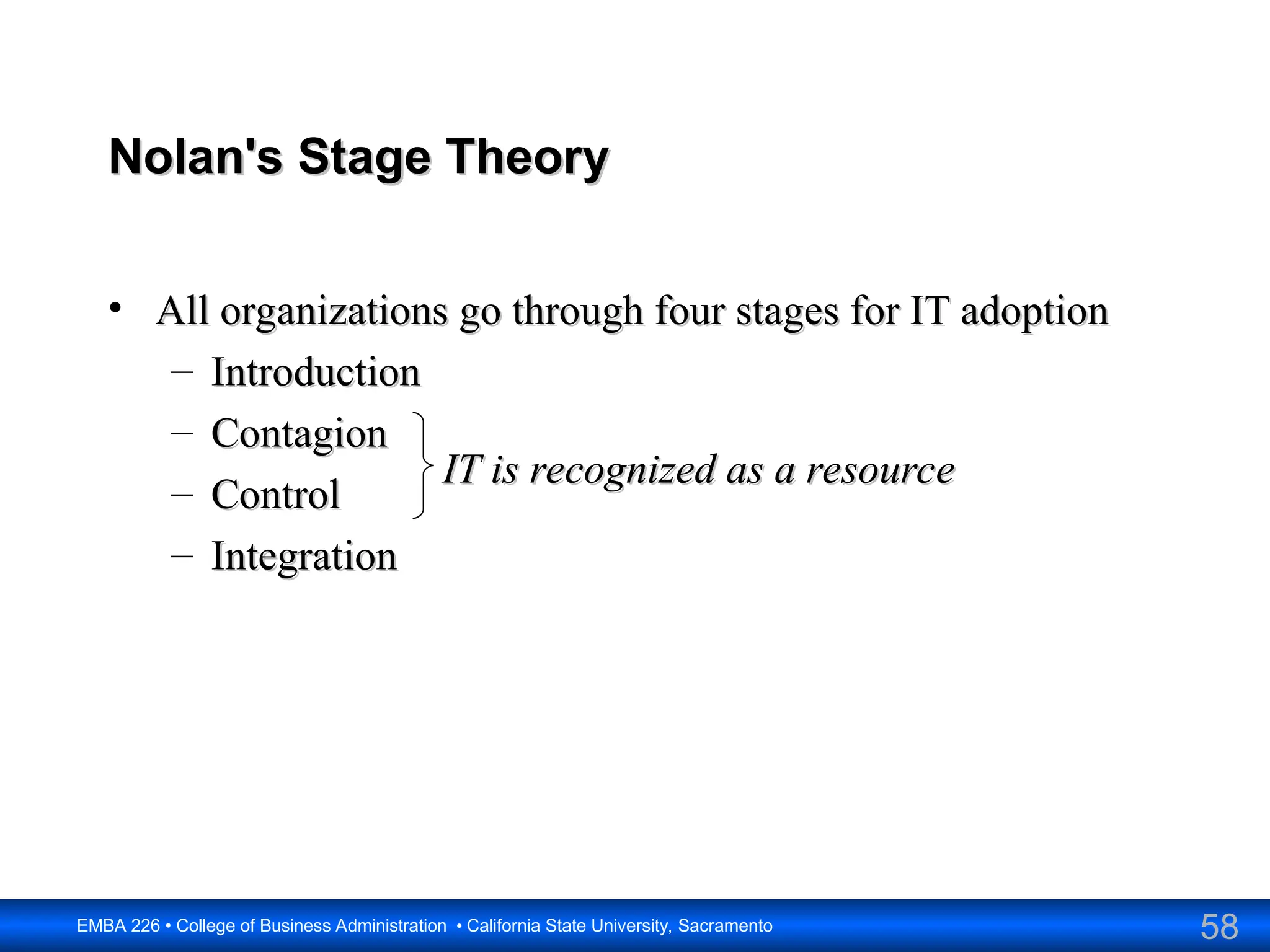
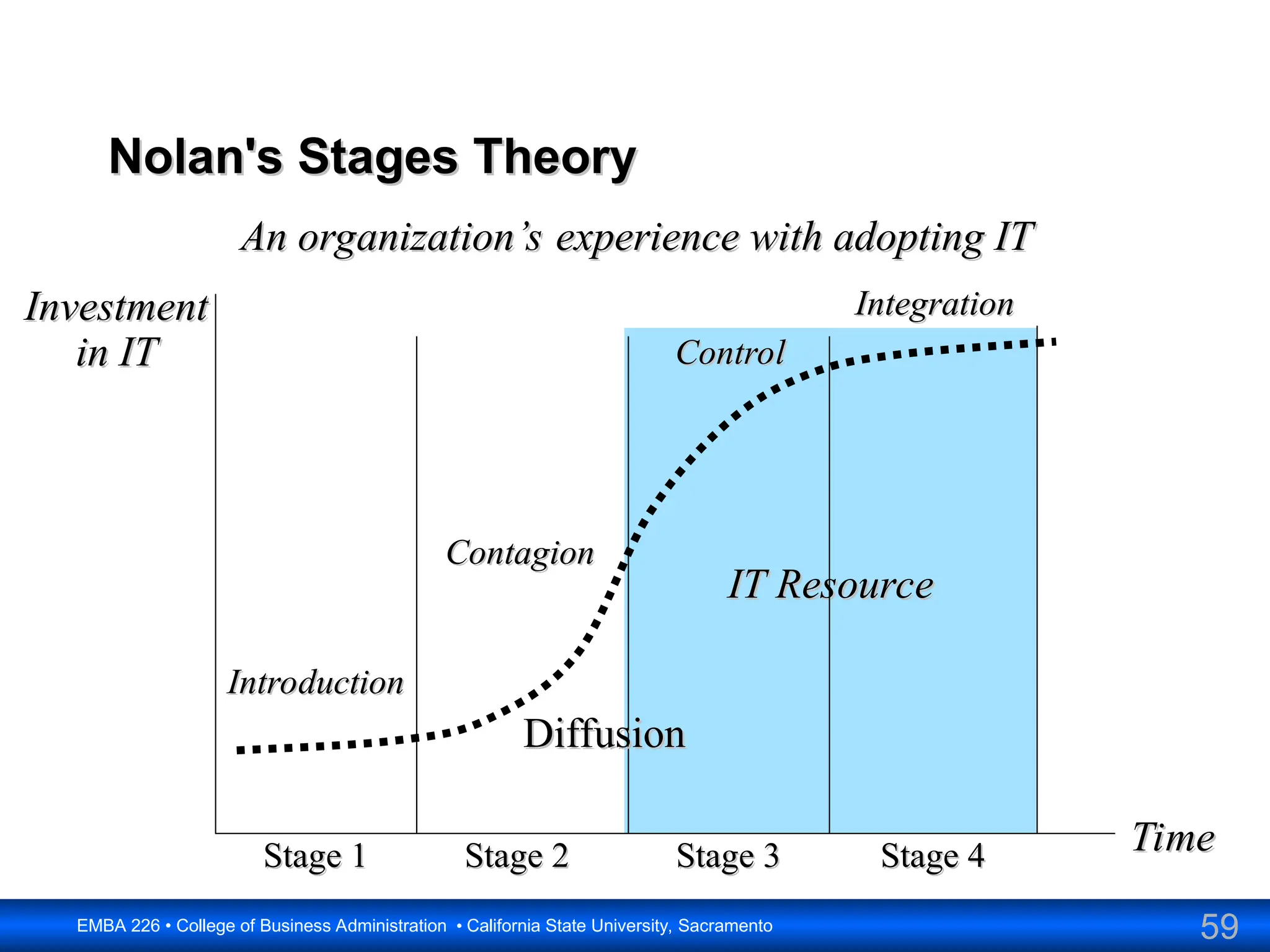
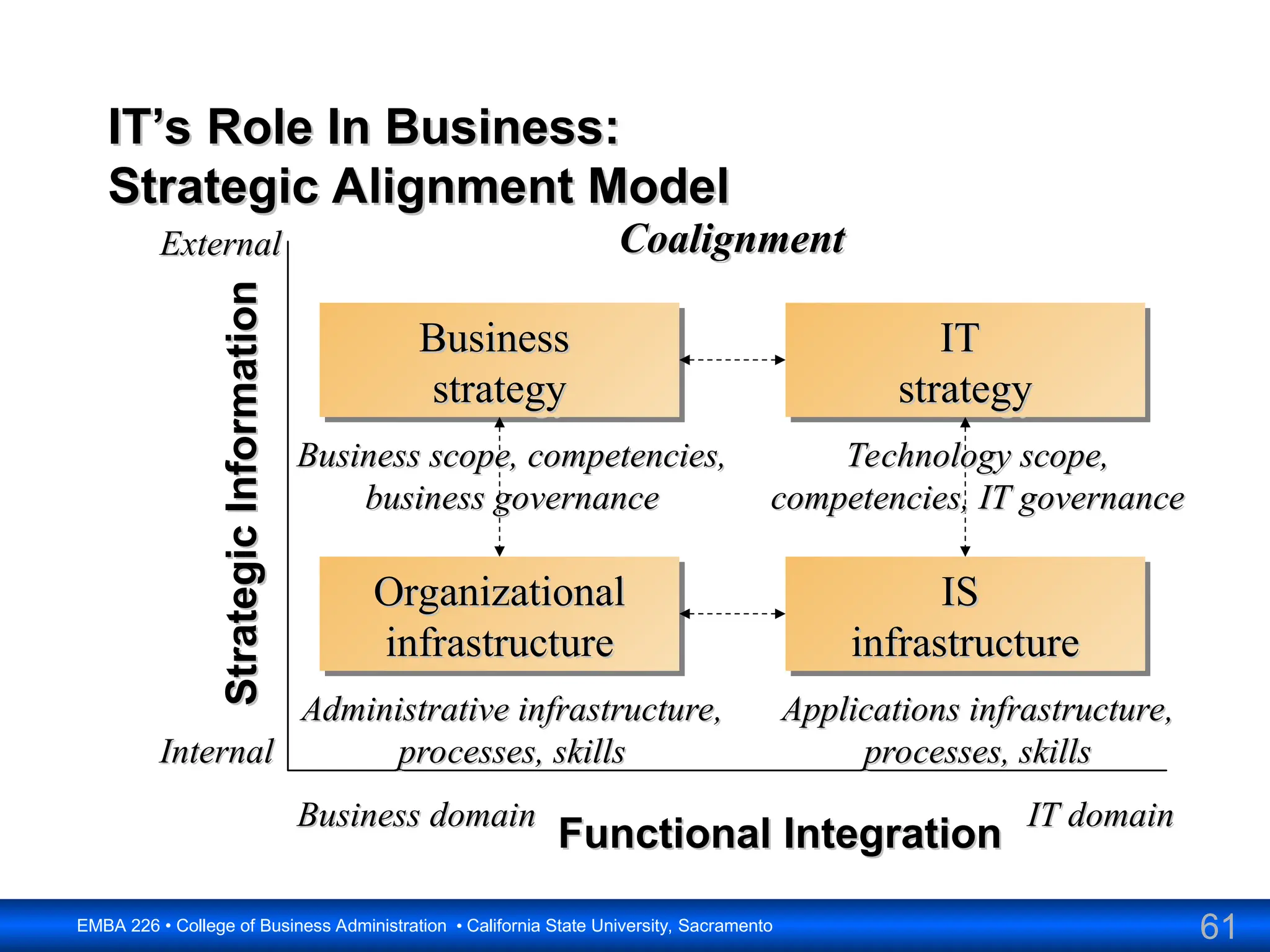
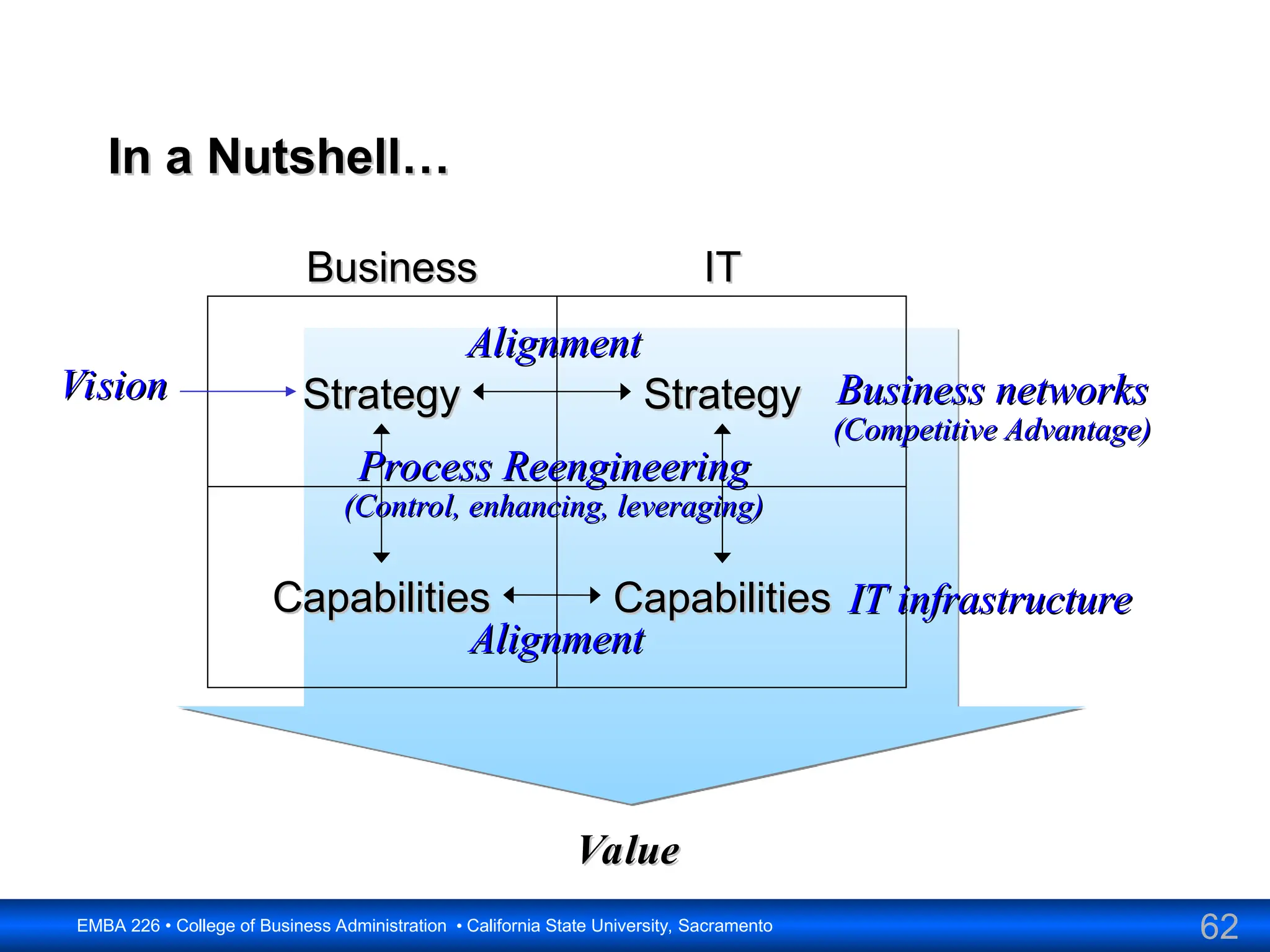
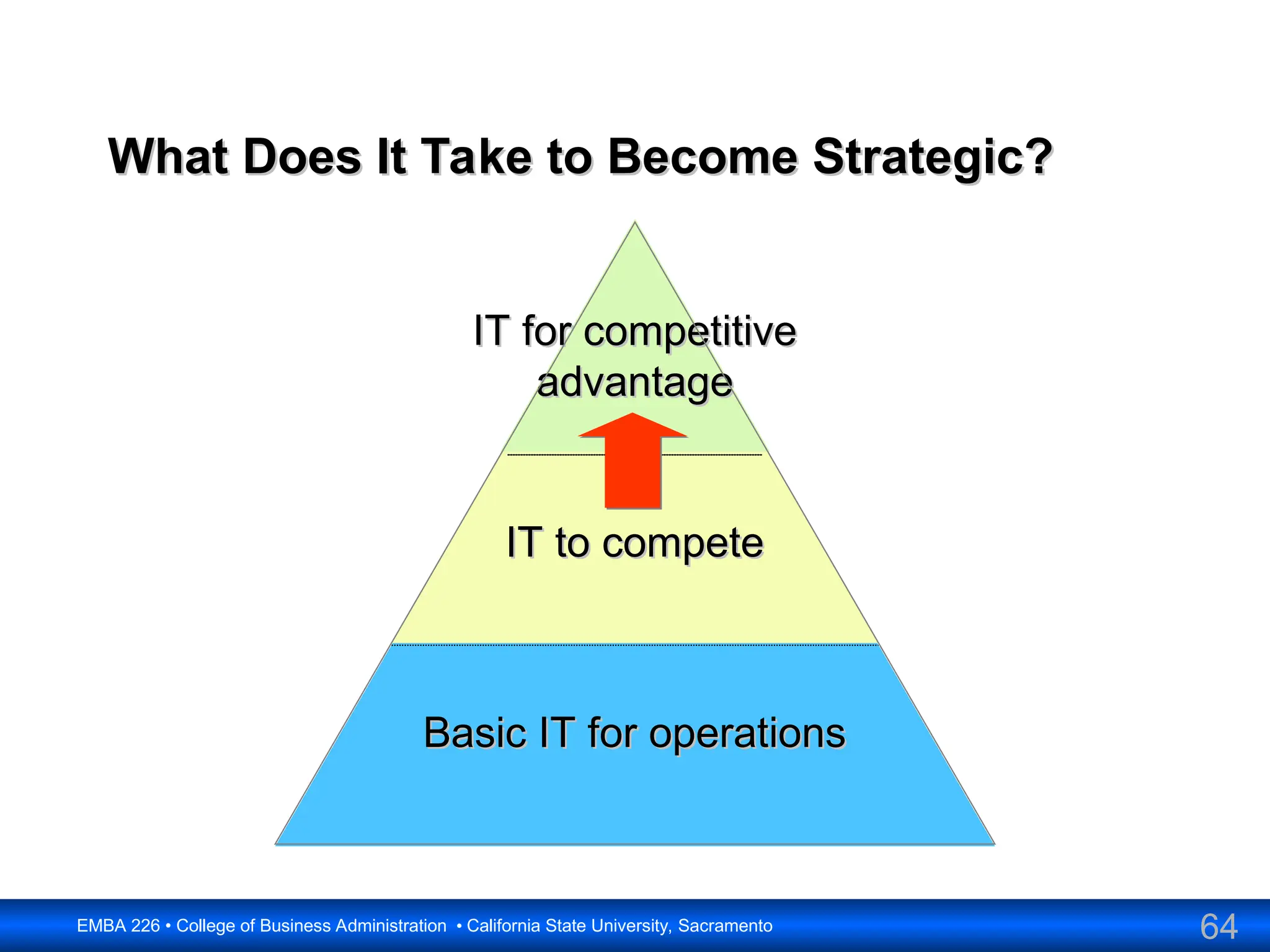
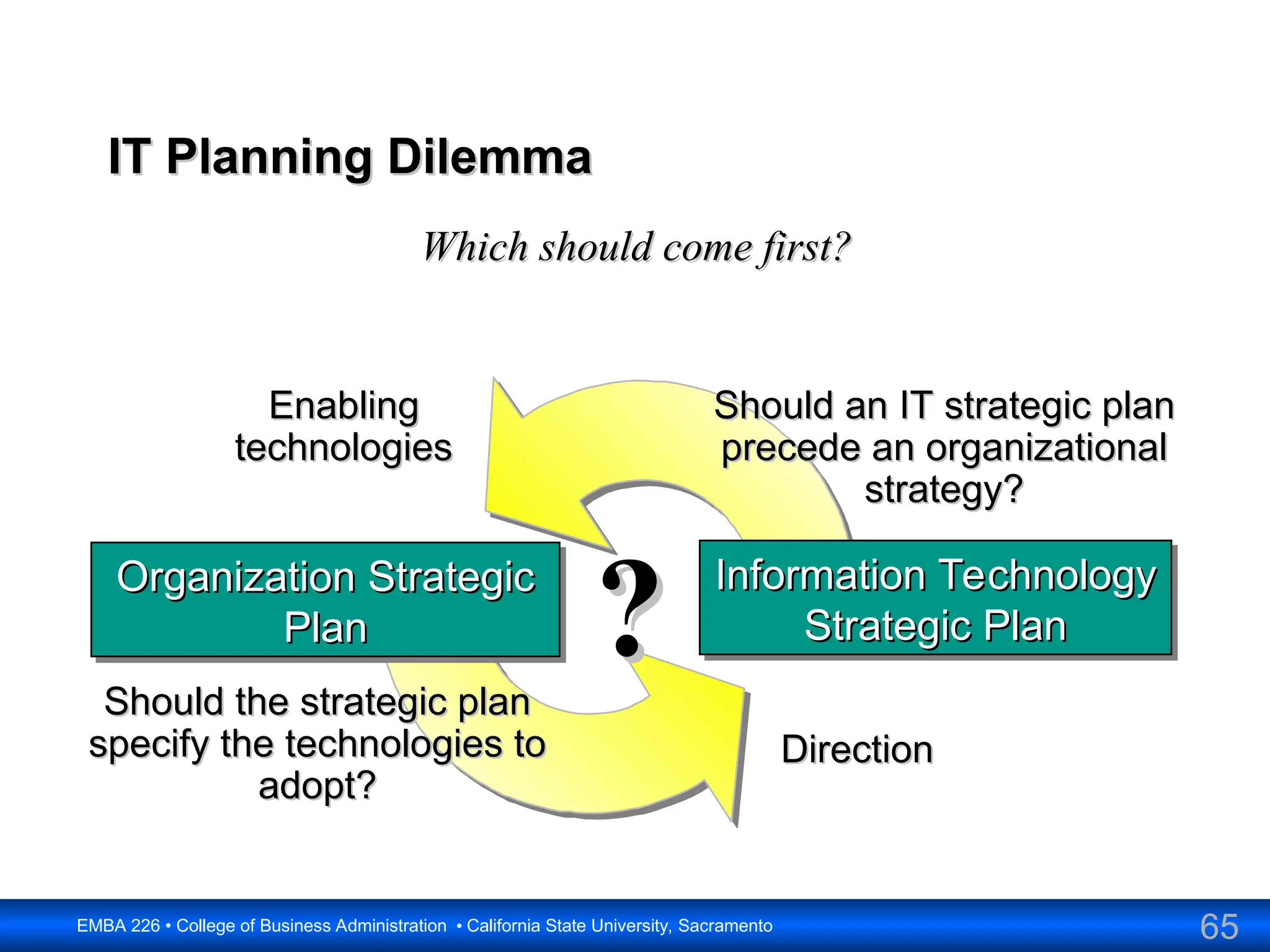
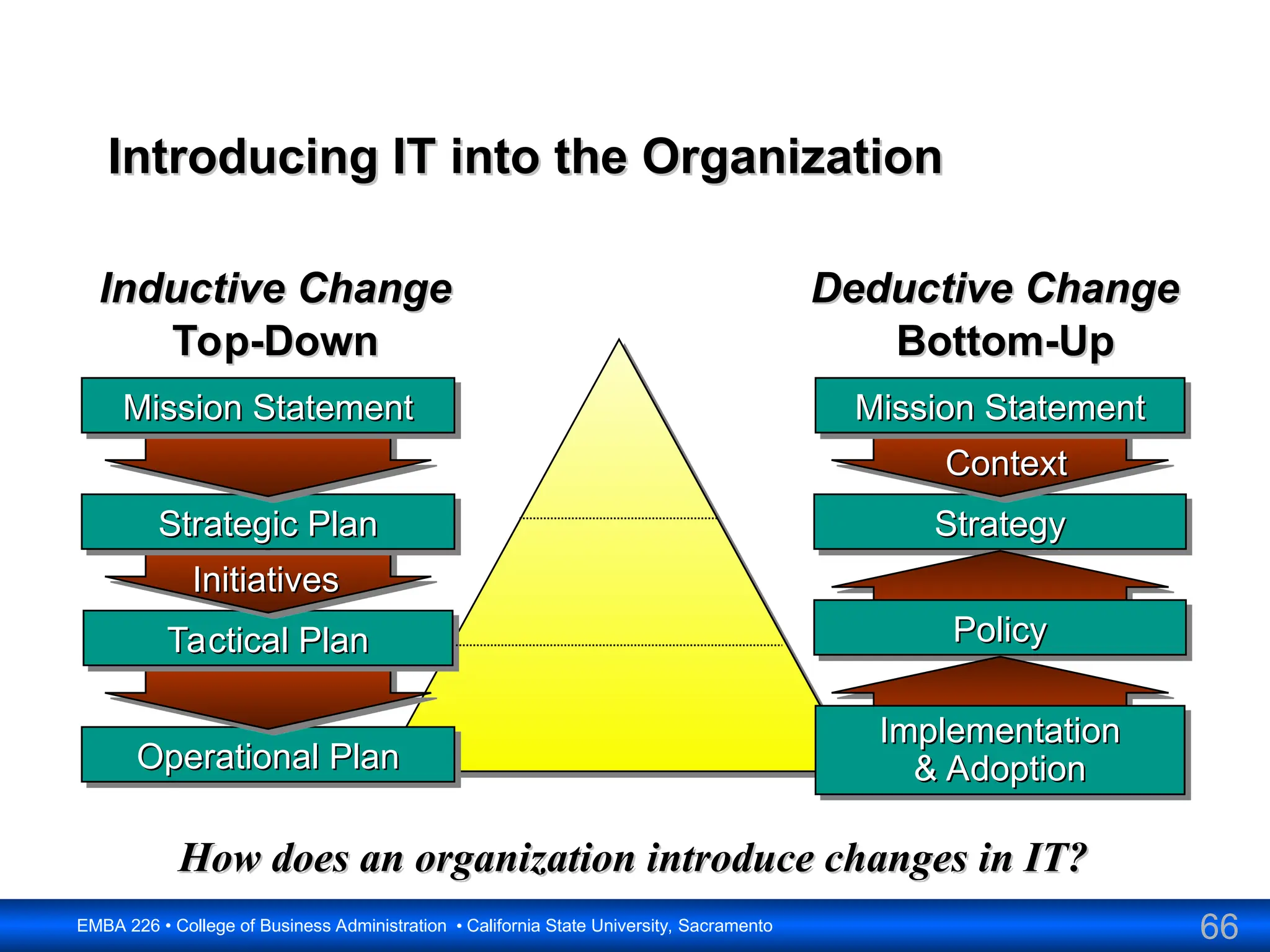
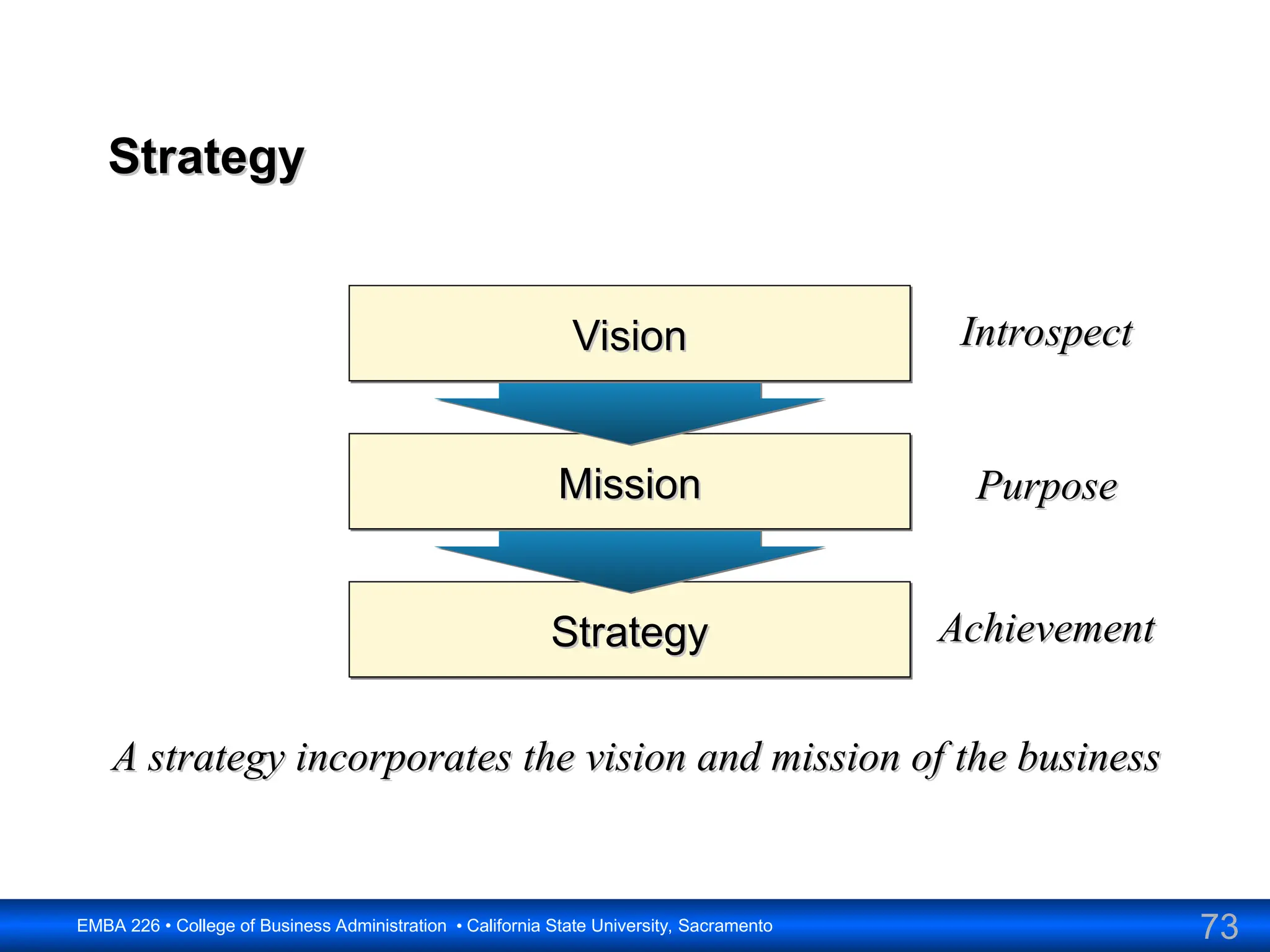
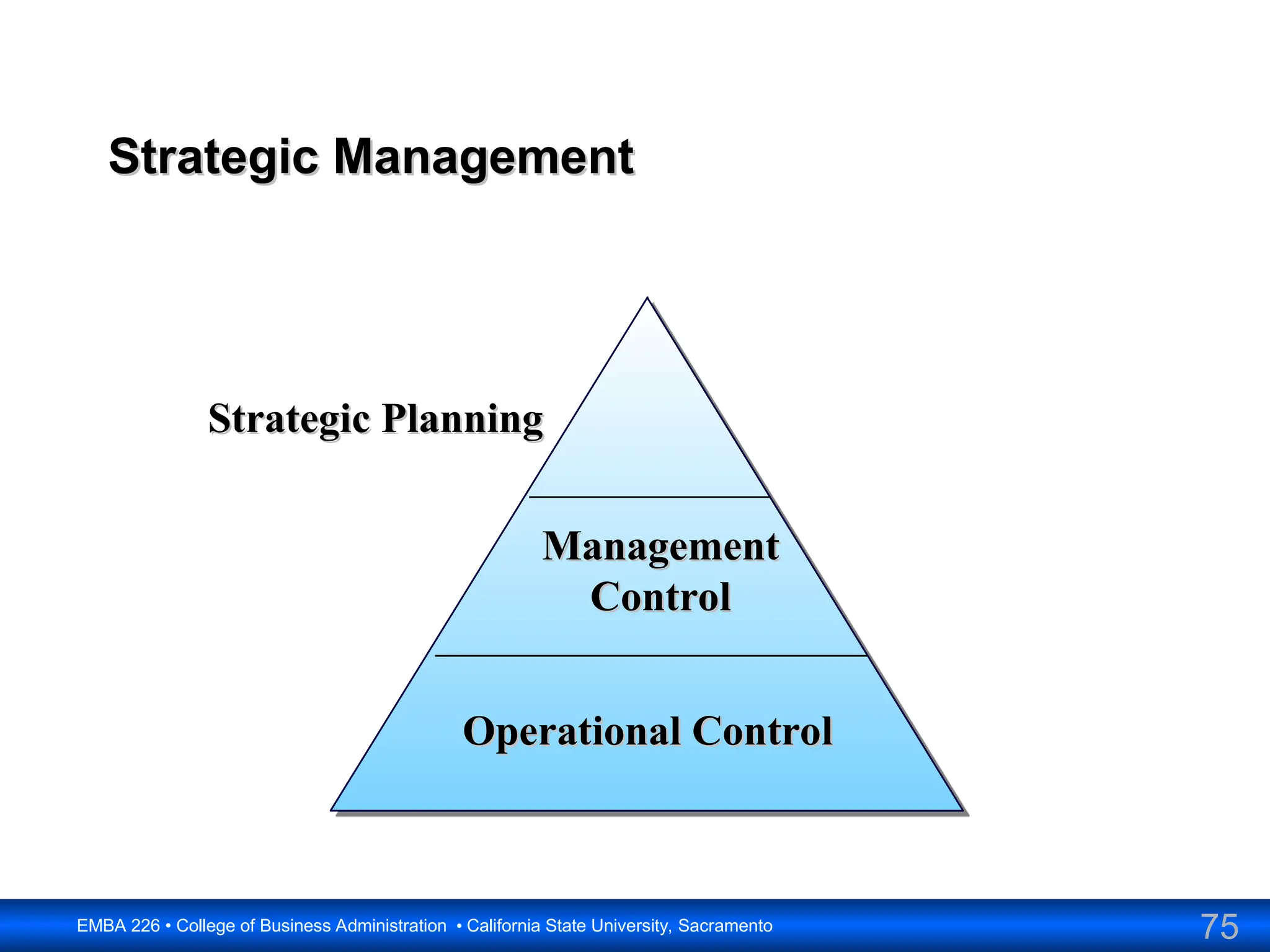
The document outlines the objectives and frameworks of an EMBA course related to the strategic role of information technology in business. Key concepts include Porter’s Five Forces model, the strategic grid for technology solutions, and the importance of aligning IT with business strategy to seize competitive advantages. The course emphasizes the transformative impact of IT on business processes, organizational structure, and competitive positioning.