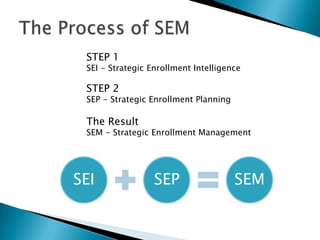
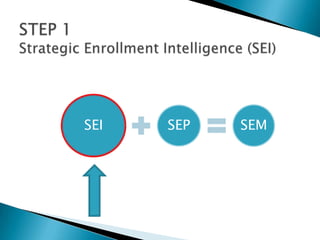
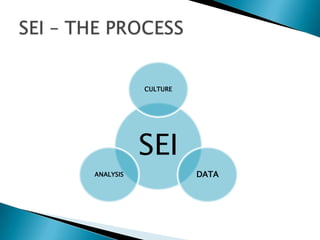
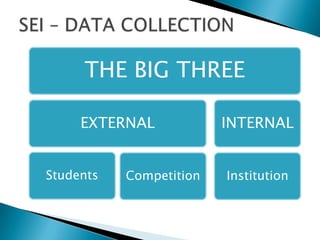
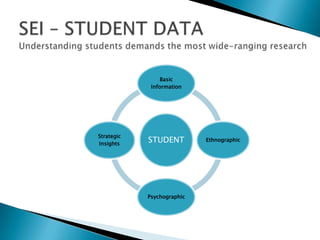
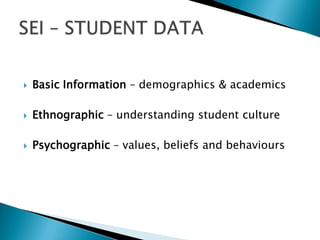
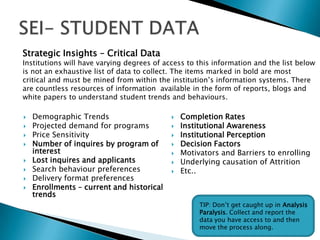
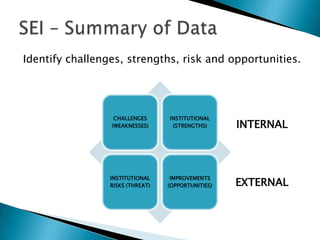
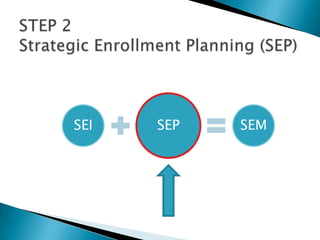
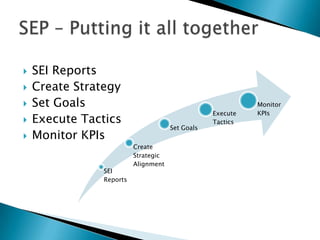
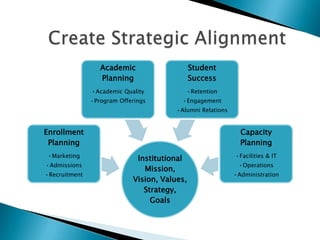
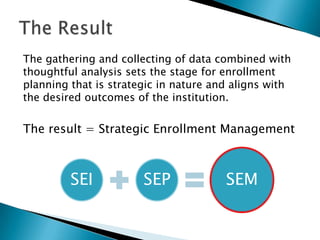
Strategic enrollment management (SEM) is a comprehensive process to help institutions achieve and maintain optimal recruitment, retention, and graduation rates. It involves three steps: strategic enrollment intelligence (SEI) which uses data analysis to understand the institution's position; strategic enrollment planning (SEP) where goals and tactics are developed; and SEM which is the ongoing process of managing enrollment outcomes through monitoring data. The document provides details on collecting and analyzing both internal and external data on students, competitors, and the institution to inform the SEM process.