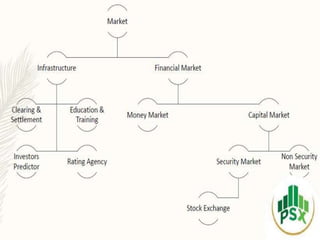
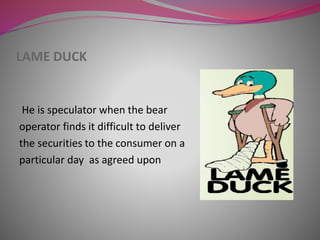
The document discusses stock exchanges in Pakistan. It defines a stock exchange as an organized market where securities like shares and stocks are bought and sold. It then describes key features of stock exchanges such as their role in capital formation and price stabilization. It provides details on the three main stock exchanges in Pakistan - the Karachi Stock Exchange, Lahore Stock Exchange, and Islamabad Stock Exchange. It also defines important terms used in stock exchanges like brokers, jobbers, speculation, and different types of speculators.