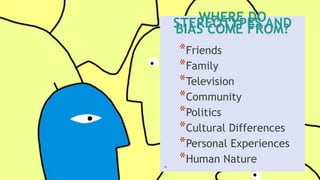
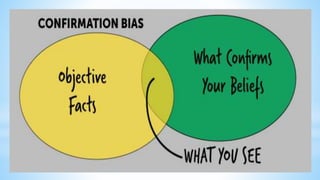
This document discusses stereotypes, bias, and how they can affect people and organizations. It defines stereotypes as preconceived ideas that attribute characteristics to an entire group. Bias is a tendency towards a certain perspective that can prevent impartiality. Stereotypes and bias can come from various social influences and experiences. They can negatively impact perceptions, attitudes, behaviors, and interactions in educational settings by lowering achievement, disproportionate discipline, and widening achievement gaps. The document examines common stereotypes around gender, age, socioeconomic status, and race. It also explores unconscious biases that live in the brain and can influence decisions and judgments.