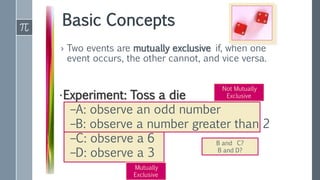
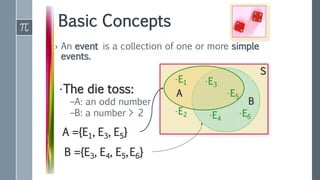
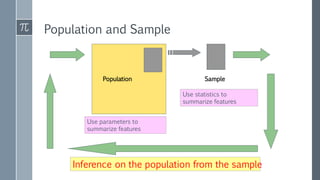
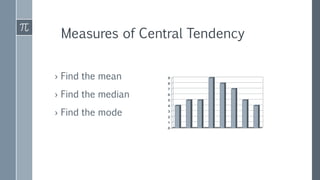
This document provides an overview of key statistical concepts for Six Sigma practitioners. It defines important terms like population, sample, parameter, and statistic. It explains the differences between descriptive and inferential statistics and discusses methods for summarizing data like measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), measures of variation (range, standard deviation), and ways to present data through graphs, charts, and distributions. Key goals of statistics in Six Sigma are to characterize processes, understand sources of variation, and determine if a process is in a state of statistical control.































































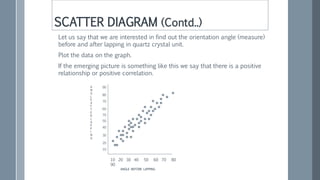

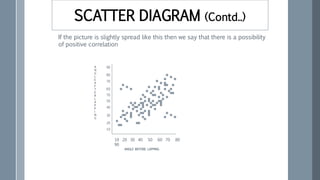

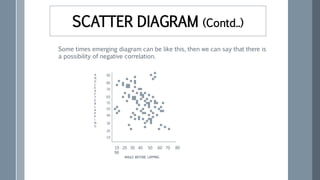
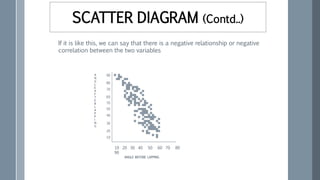
![Some examples of series of negative
correlation are:
Volume and pressure of perfect gas;
Current and resistance [keeping the
voltage constant] (R =V / I) ;
Price and demand of goods.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/statisticsfor6sigma-220914172921-3304d899/85/Statistics-for-6-Sigma-pptx-78-320.jpg)