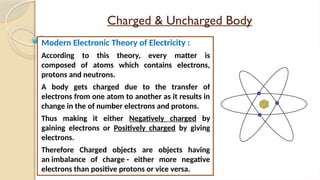
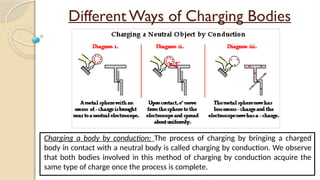
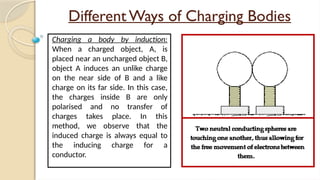
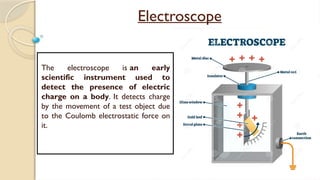
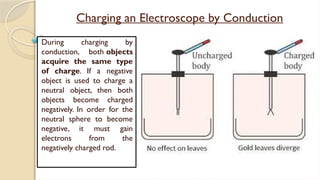
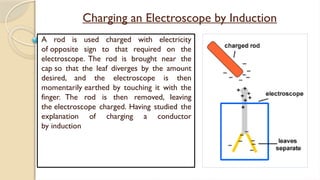
Static electricity is the imbalance of electric charges on a material, contrasting with current electricity where charges flow. Bodies can be charged through friction, conduction, or induction, affecting their charge and behavior. The electroscope is an instrument to detect electric charge, which can be charged by both conduction and induction methods.