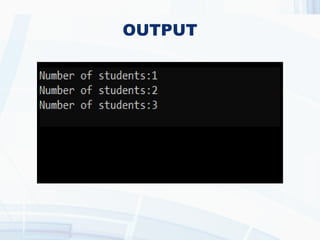
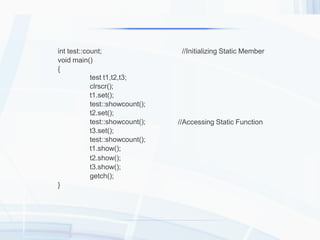
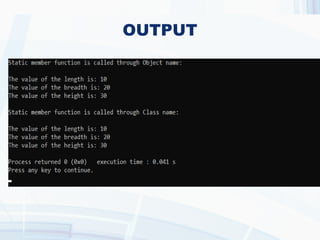
The document provides an overview of static data members and static member functions in C++. It explains their characteristics, initialization process, and provides code examples demonstrating their usage. Key points include shared access among class objects and how static functions can only access other static members.