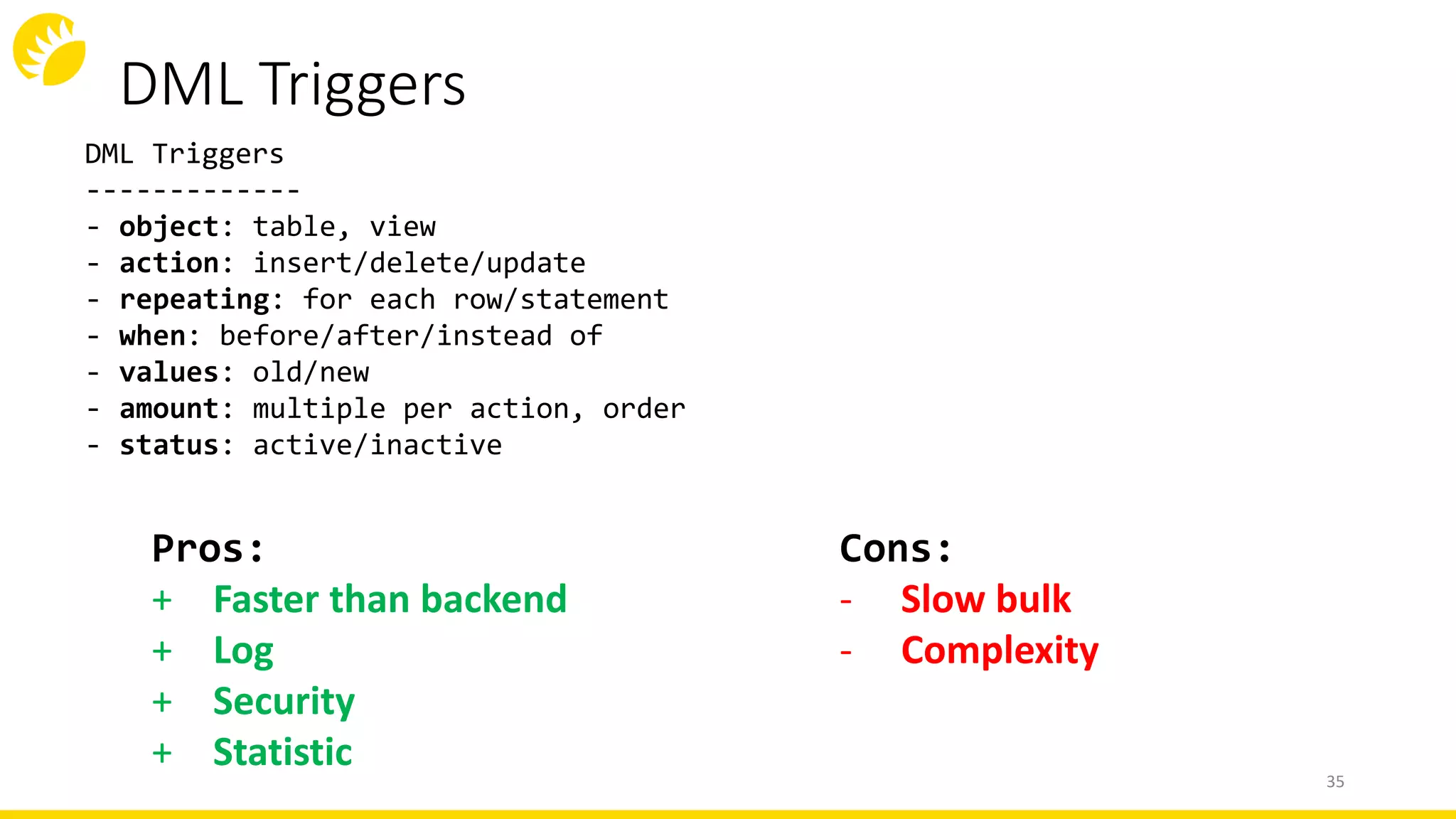
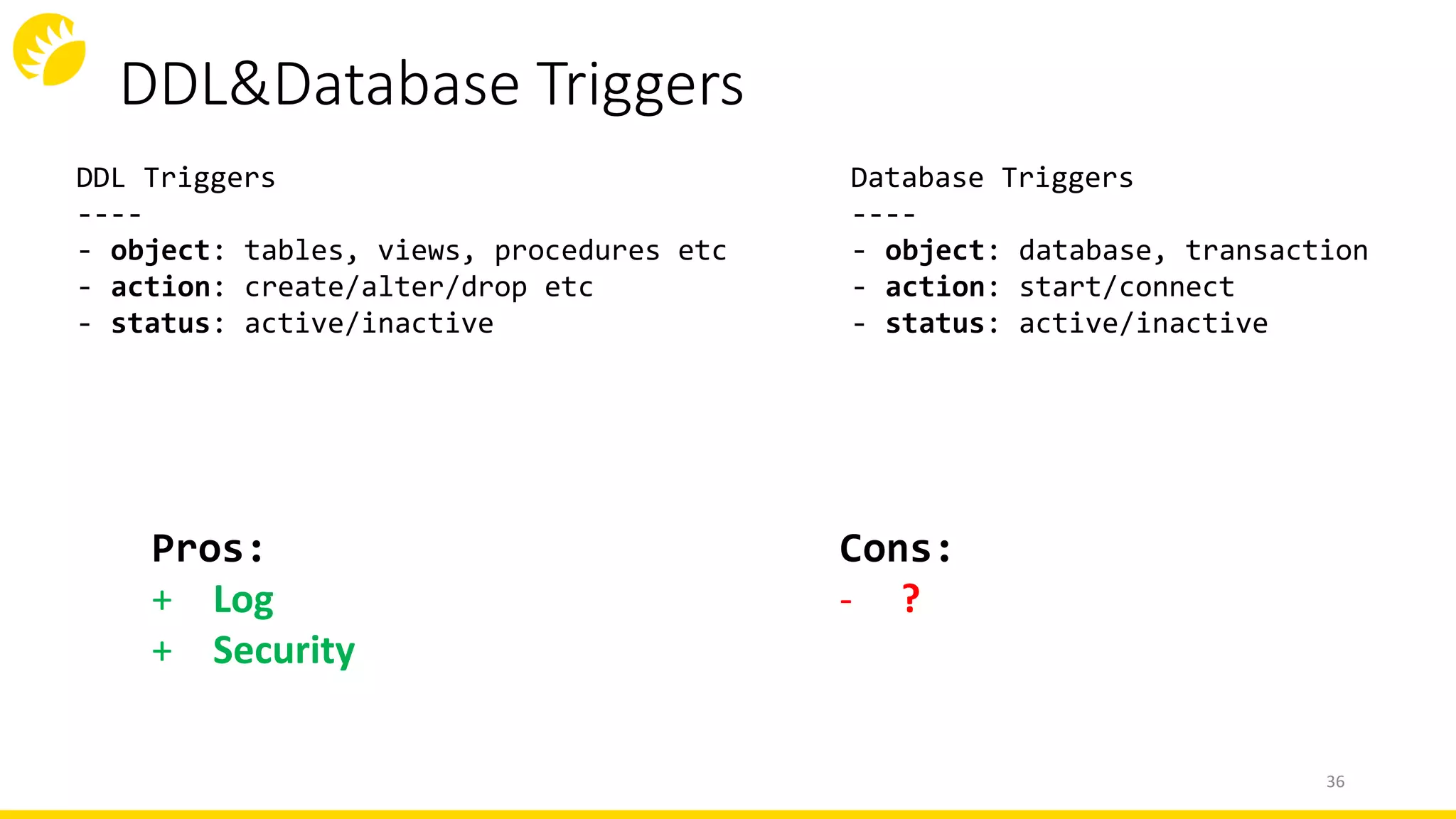
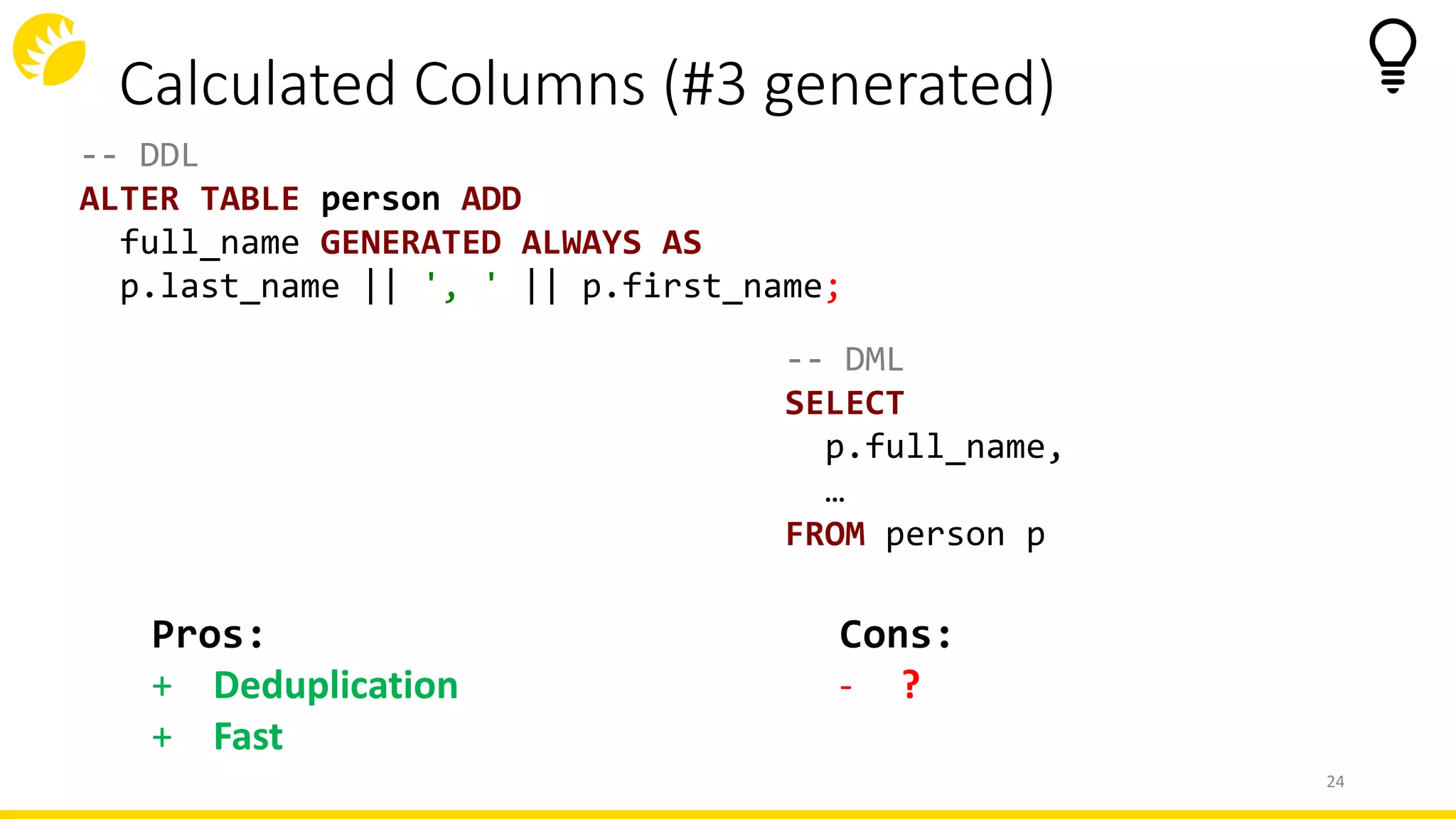
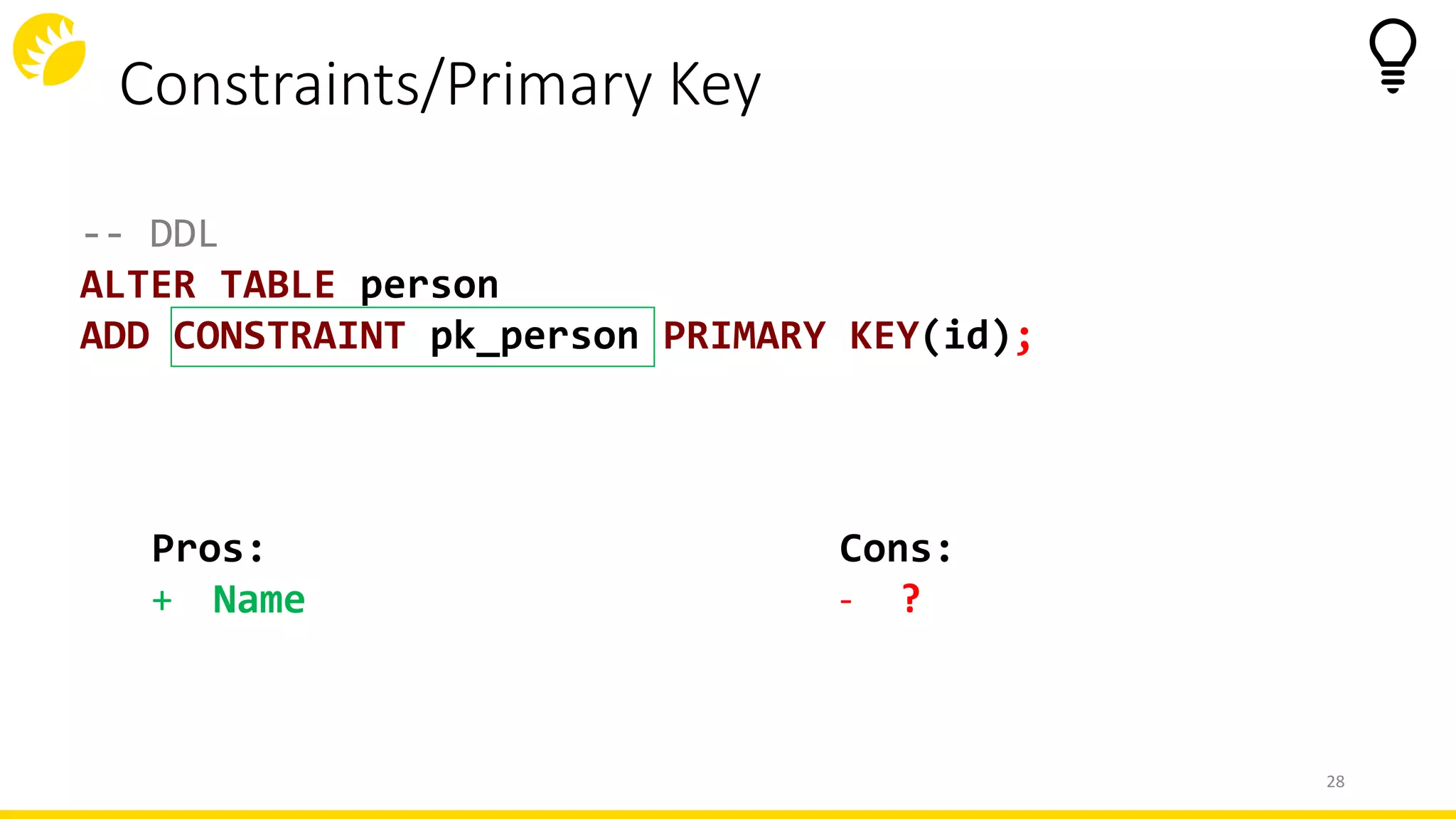
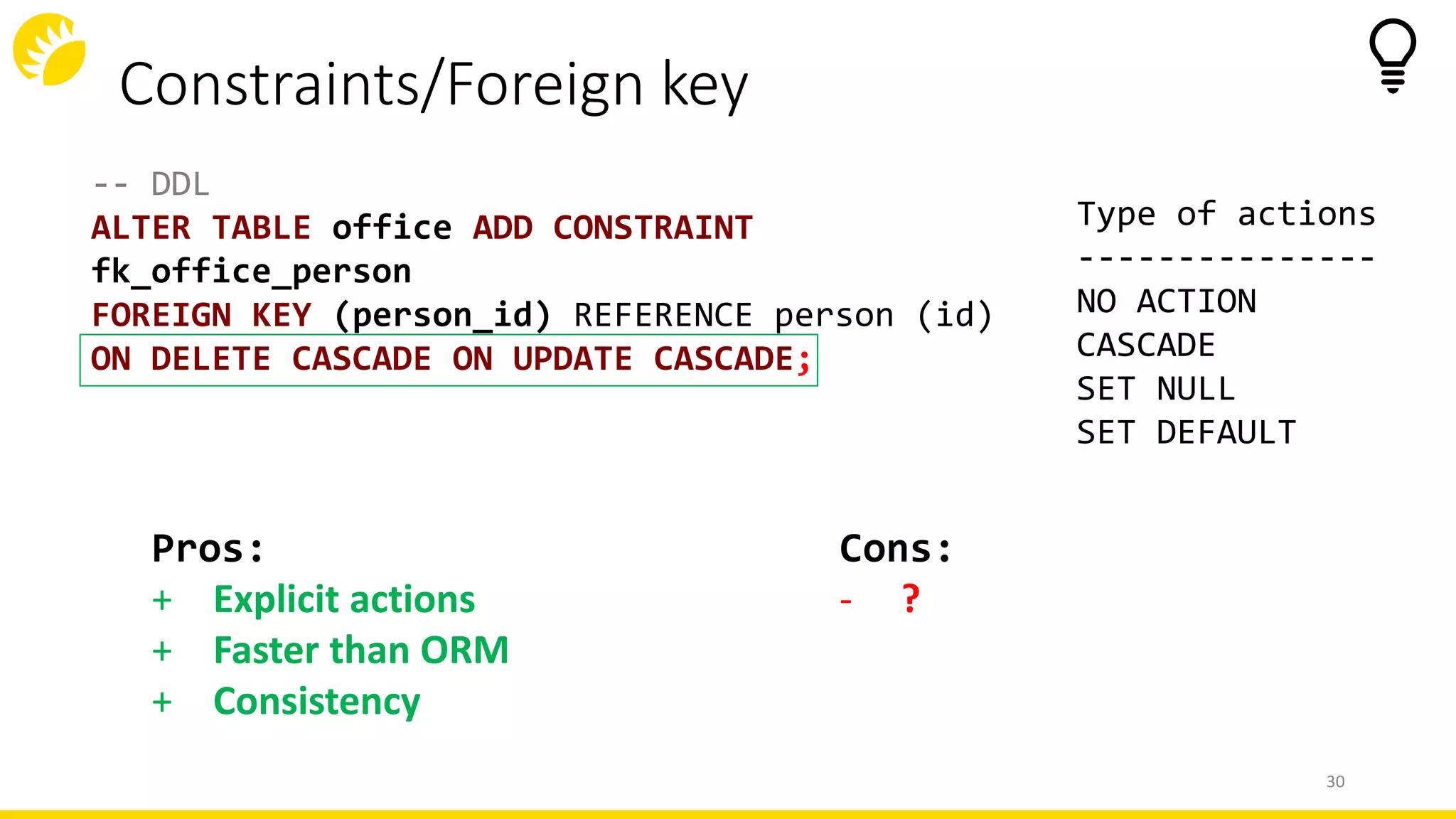
This document summarizes an SQL DDL presentation covering IDs, domains, calculated columns, constraints, and triggers. It discusses various techniques for each topic, such as using sequences or auto-increment for IDs, domains for standardizing data types, views or generated columns for calculations, primary keys, foreign keys, unique constraints and checks for data integrity rules, and DML, DDL, and database triggers for logging and validation. The presentation provides pros and cons of each approach and concludes that thinking low-level and writing high-level code are important principles for working with SQL DDL.
















![Constraints/Checks
31
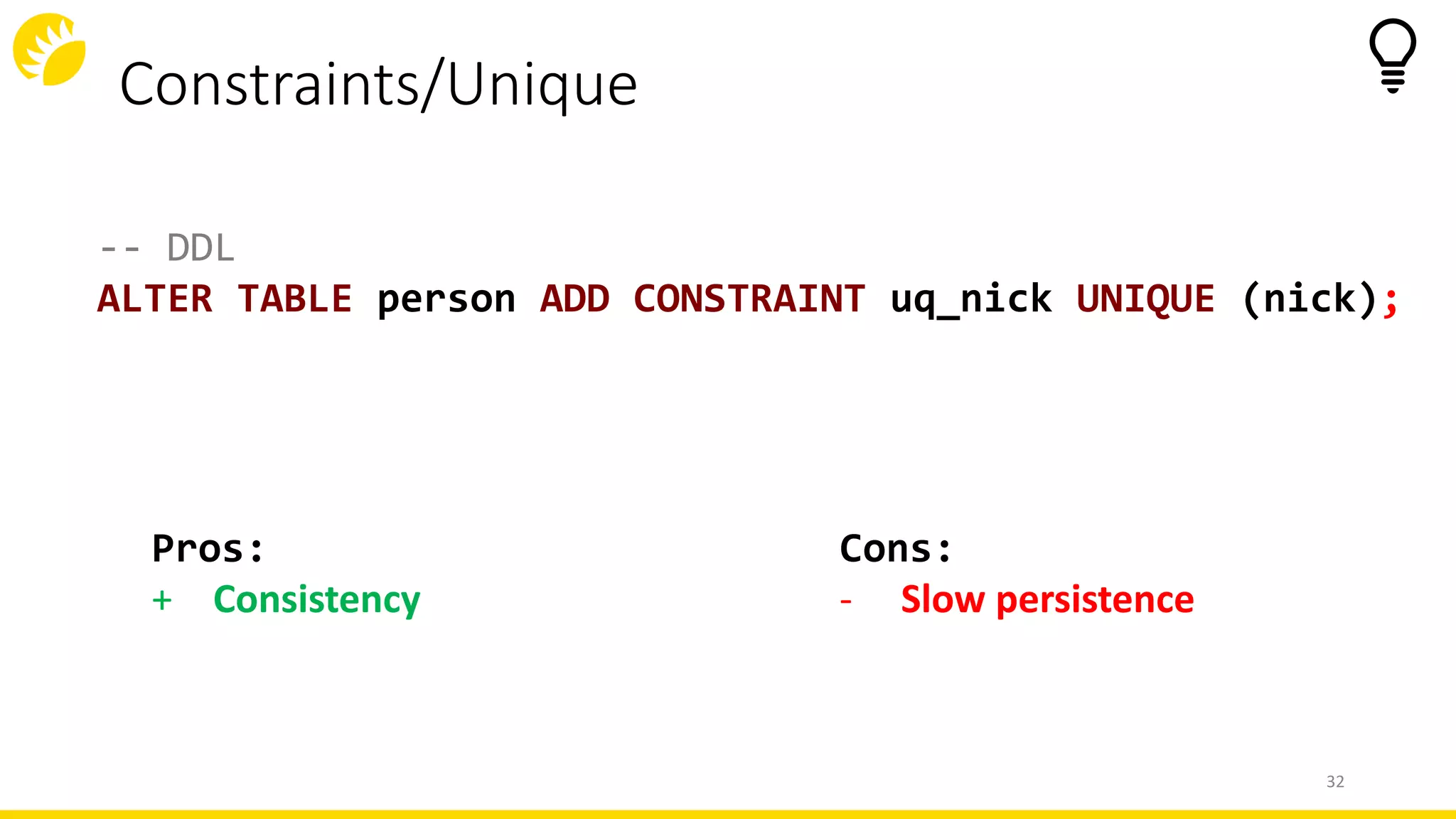
-- DDL
ALTER TABLE person
ADD CONSTRAINT chk_nick
CHECK(nick SIMILAR TO '[[:ALPHA:]]');
Cons:
- Slow persistence
Pros:
+ Consistency](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20190924sqlddltricksandtipsjprof-191002062738/75/SQL-DDL-tricks-and-tips-JProf-27-Minsk-24th-September-31-2048.jpg)