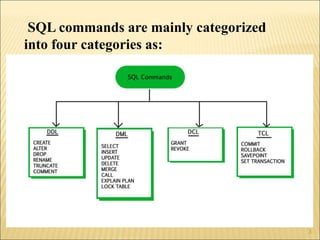
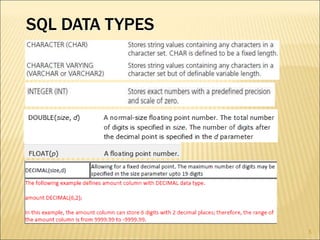
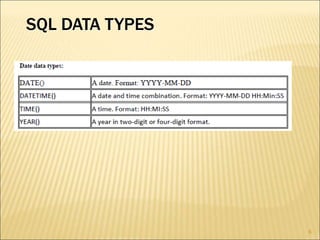
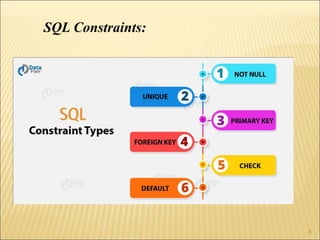
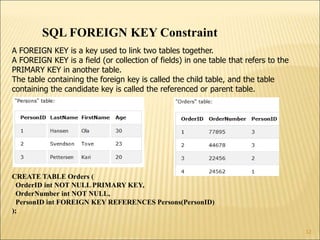
SQL is a standard language for creating and manipulating relational databases. It allows users to define schemas through commands like CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, and DROP TABLE. SQL also supports various data types for columns and includes constraints like PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, CHECK, DEFAULT and others to manage data integrity. Common SQL commands are categorized into DDL, DML, DQL and DCL groups for database definition, manipulation, queries, and control functions.