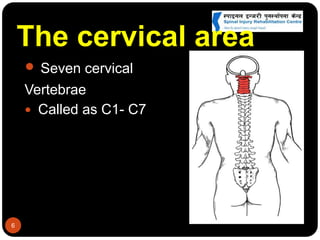
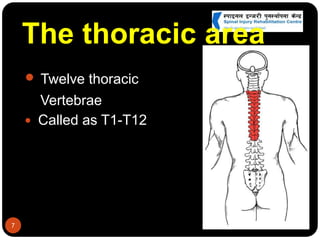
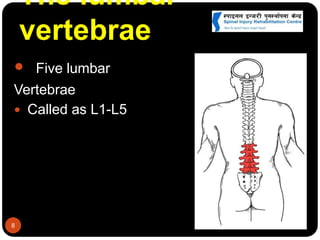
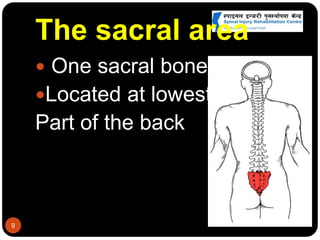
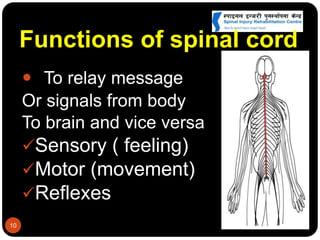
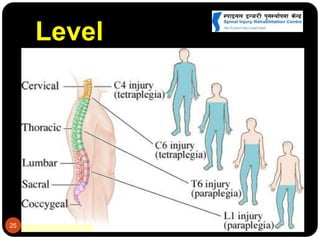
This document discusses spinal cord injury (SCI) management in Nepal. It defines SCI and notes resource limitations in developing countries. The aim of treatment is to prevent further injury and complications. The spinal column consists of vertebrae in the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions. The spinal cord relays sensory, motor, and reflex signals. SCI is an insult to the spinal cord that changes motor, sensory or autonomic function. Management requires a multidisciplinary approach including aggressive initial care, transport care, clinical evaluation, definitive acute care, comprehensive rehabilitation, and lifelong follow-up to minimize complications.