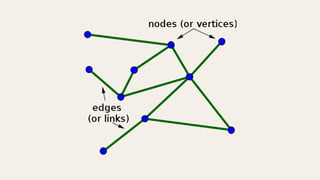
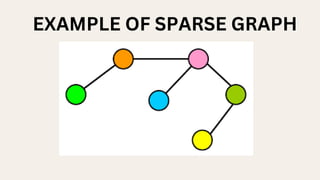
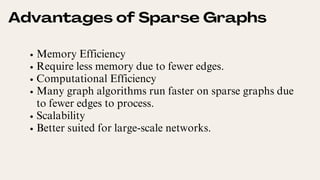
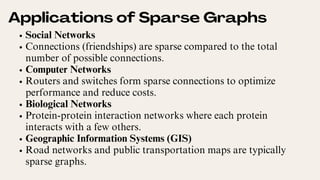
Sparse graphs have relatively few edges compared to vertices and are characterized by their efficiency in memory and computation. Algorithms such as BFS, DFS, Dijkstra's, and Kruskal's are effective for analyzing sparse graphs, making them suitable for large-scale applications in social networks, computer networks, and biological systems. Their advantages stem from reduced memory usage and optimized processing for scalability.