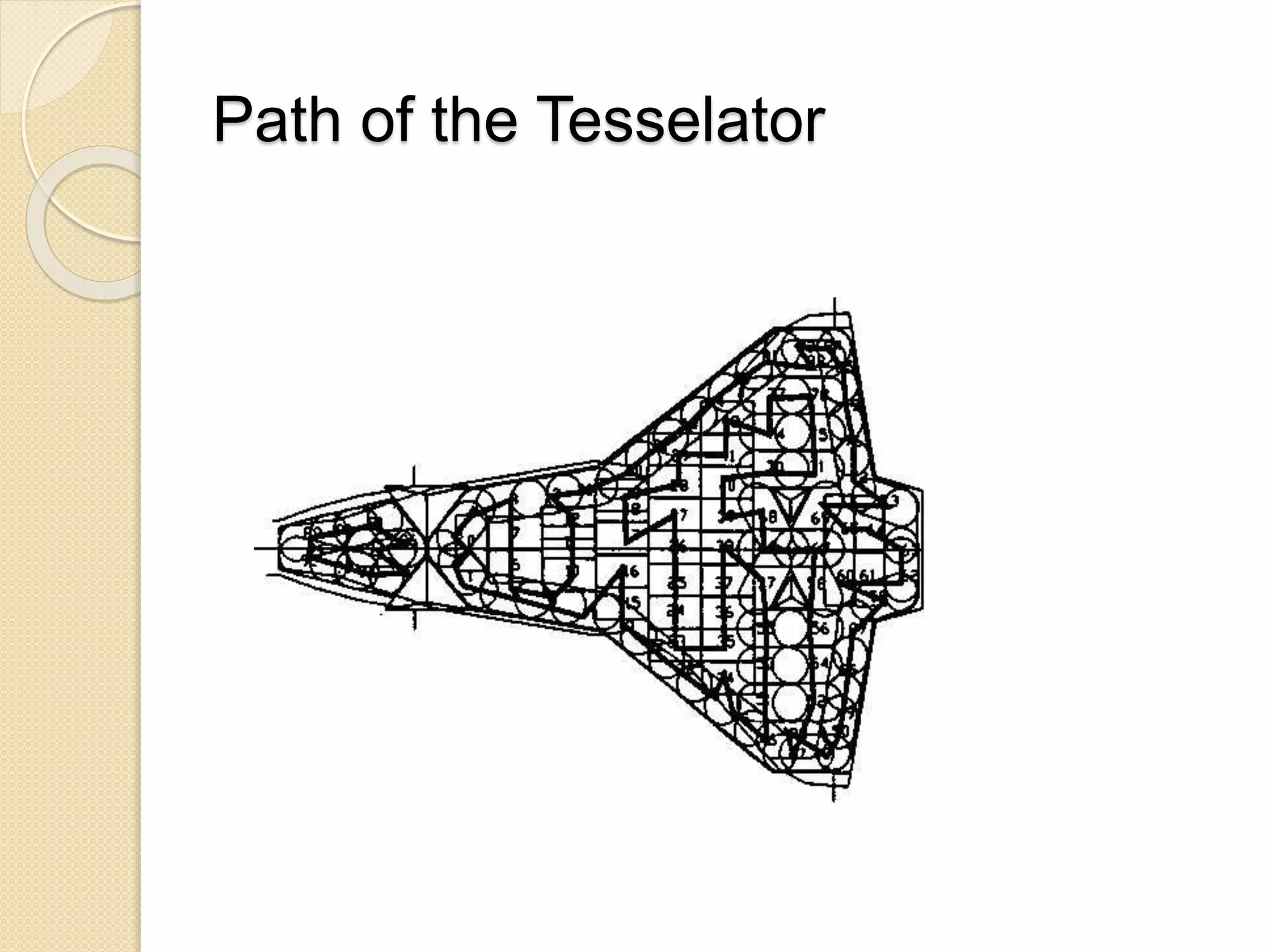
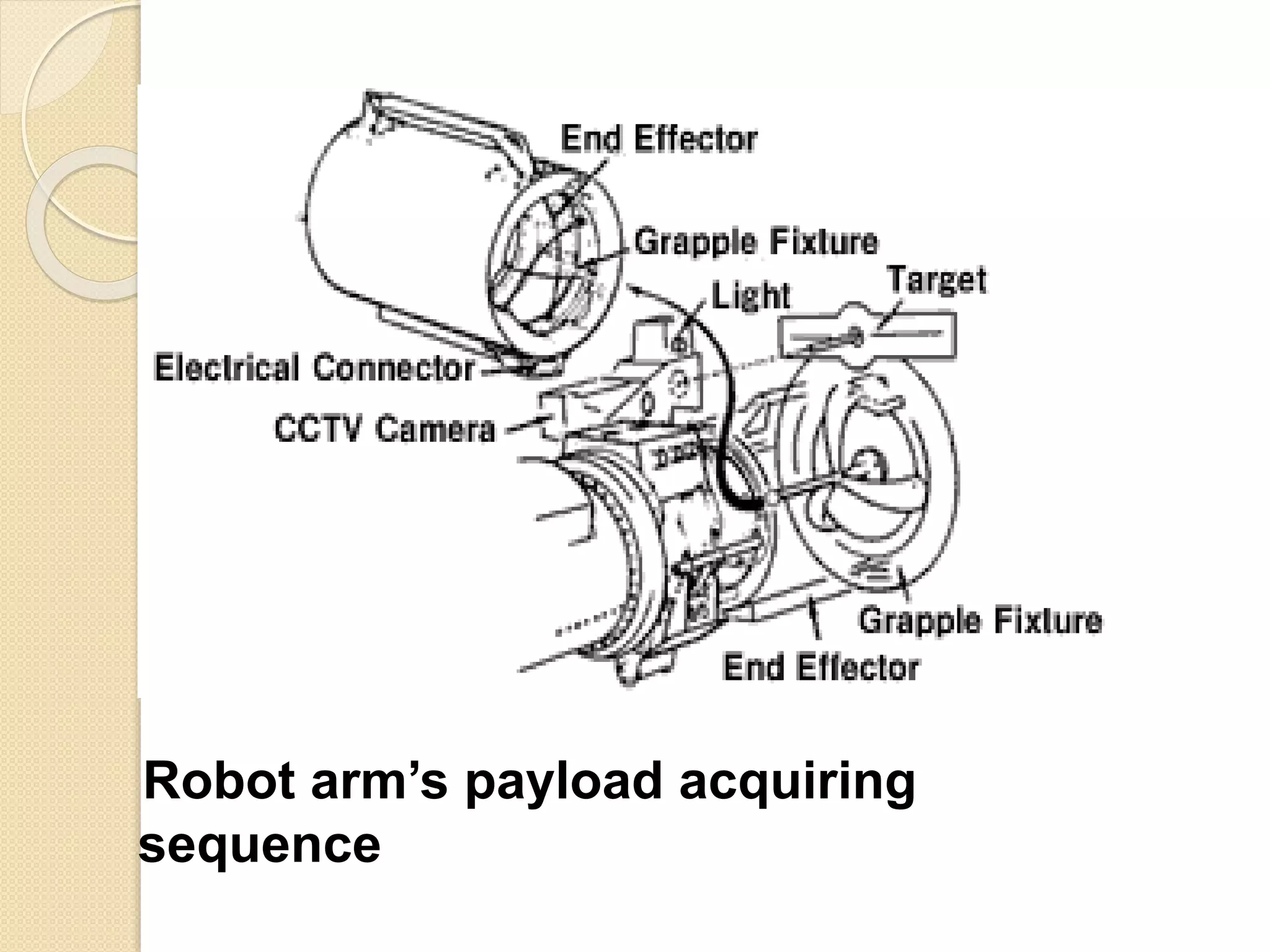
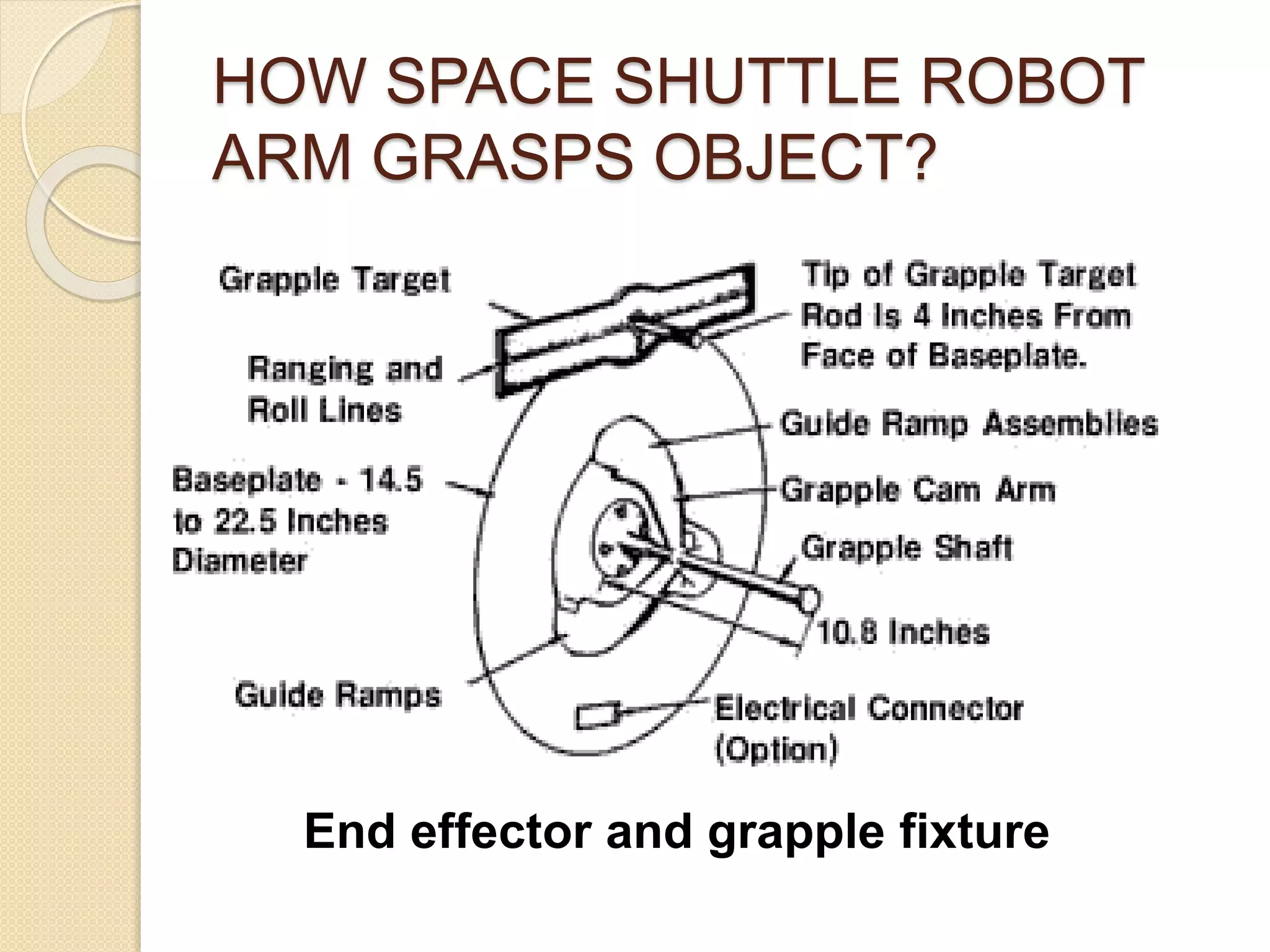
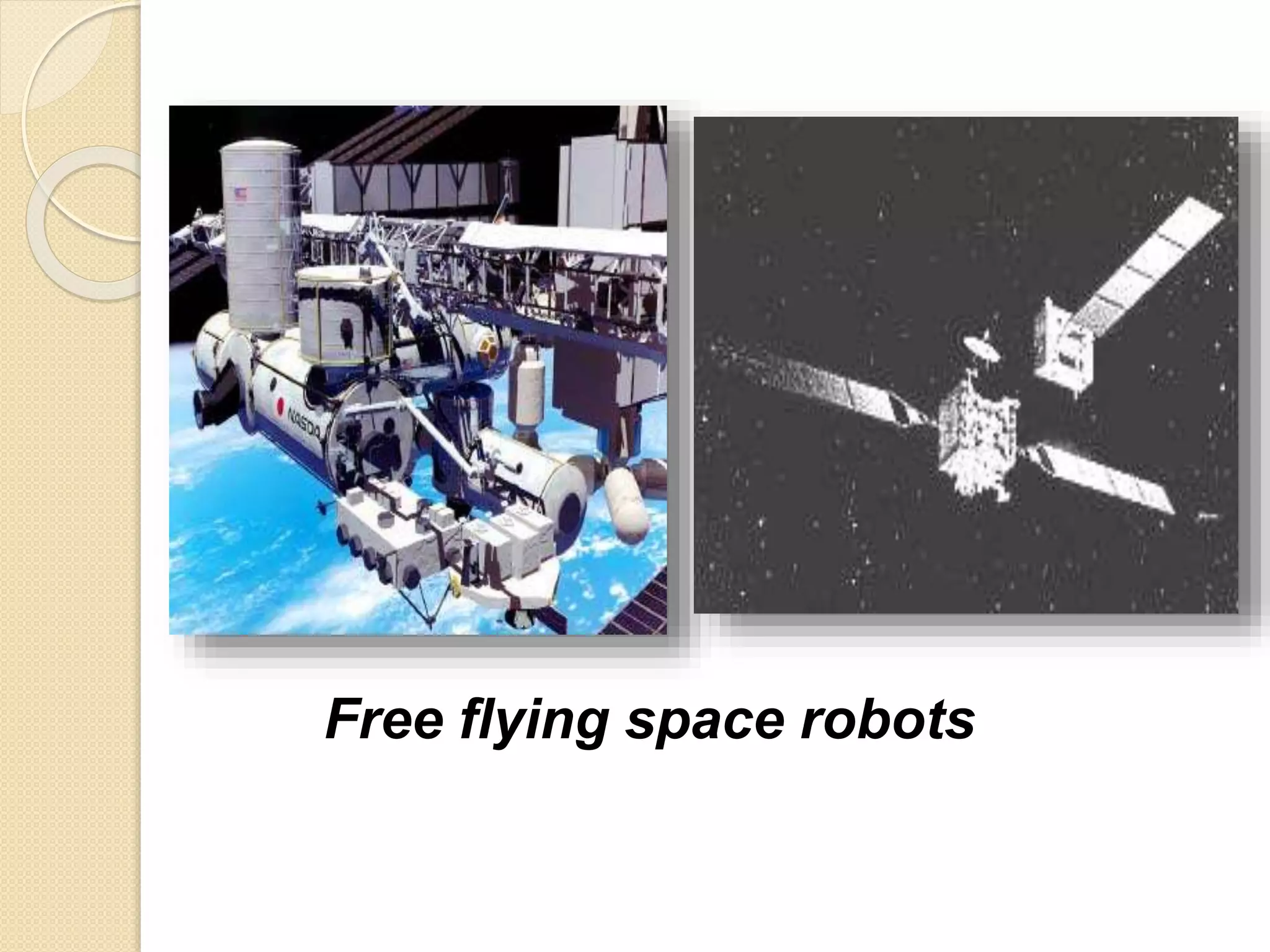
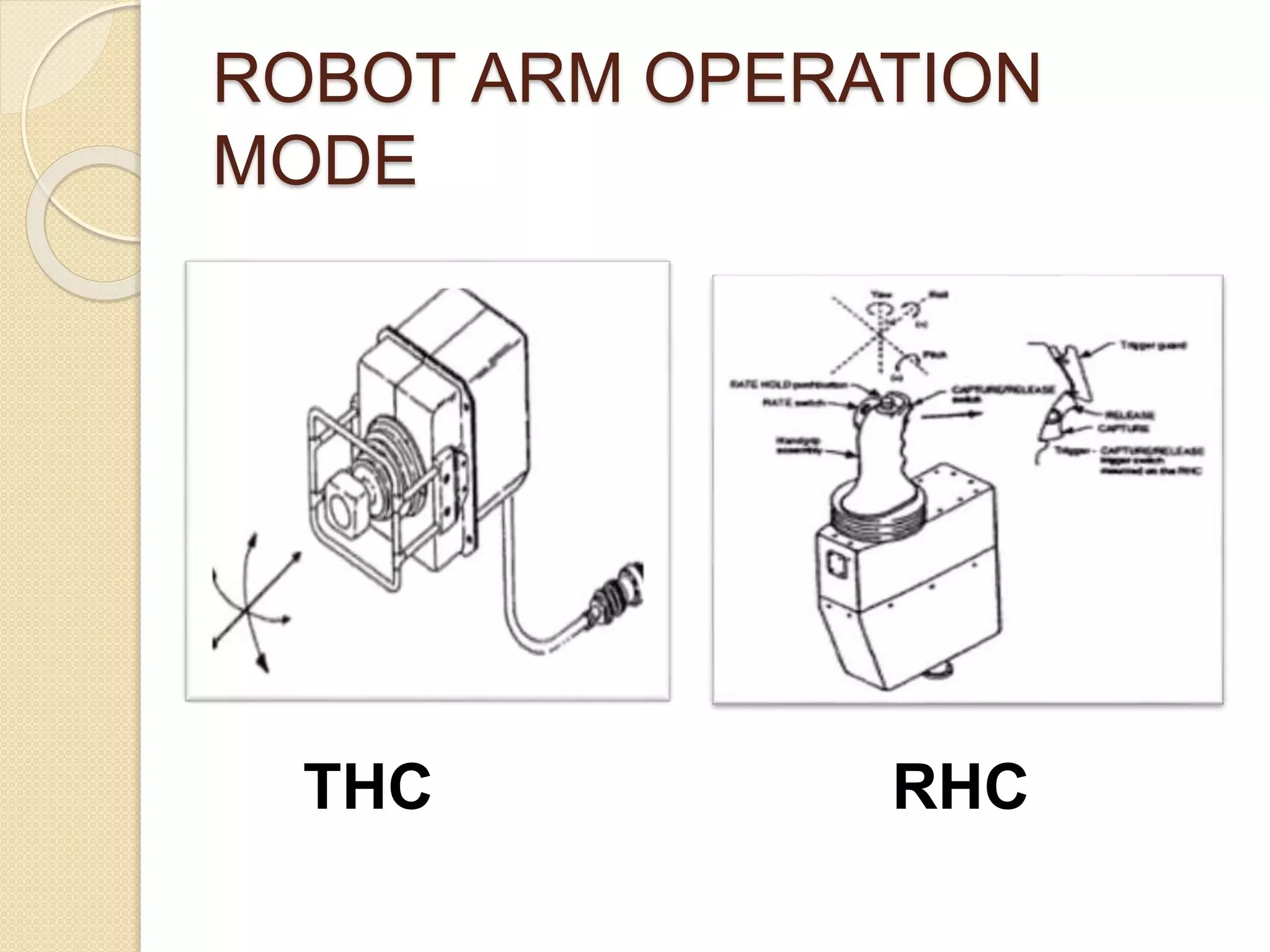
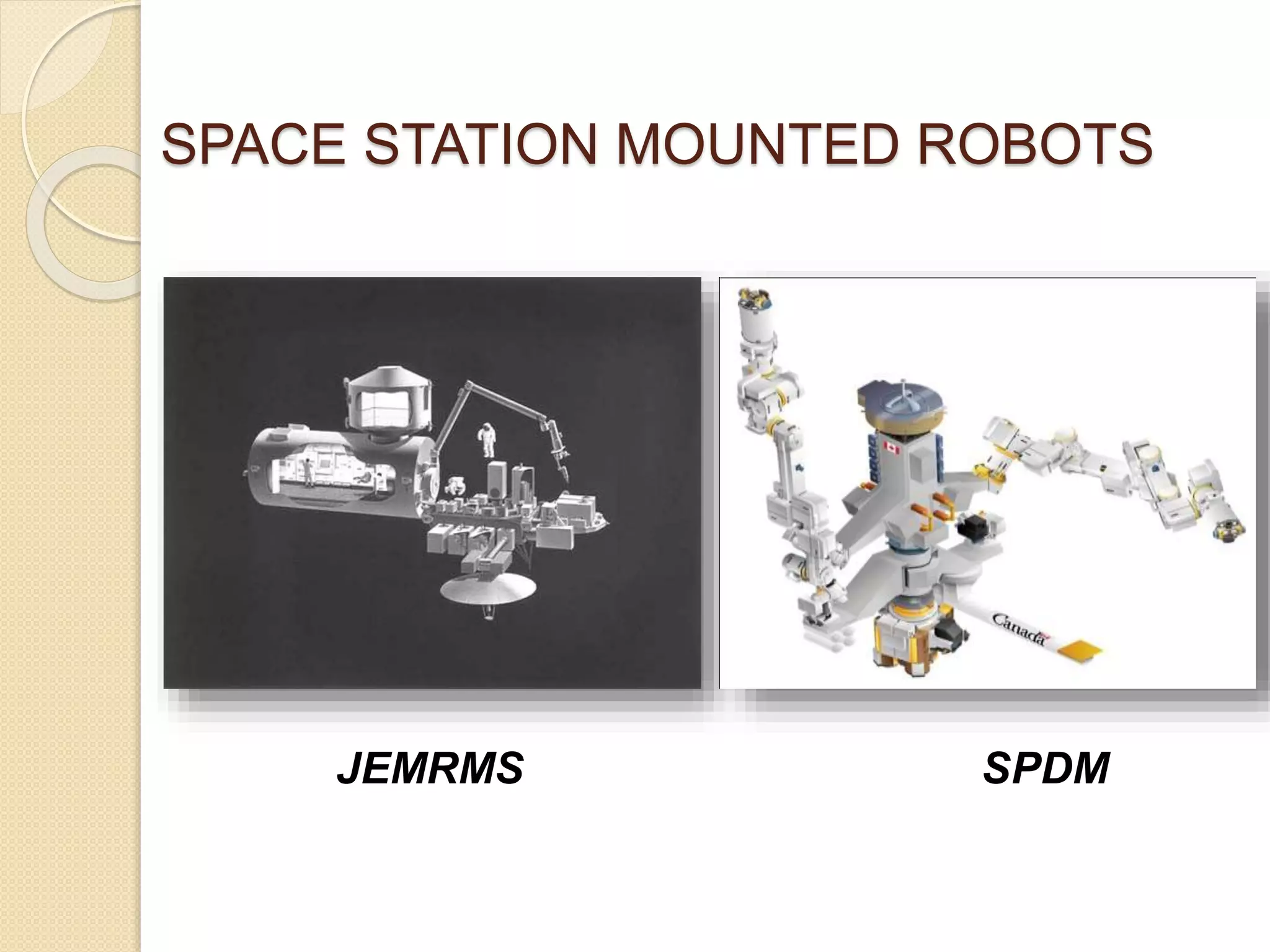
This document discusses space robotics. It begins by defining robots and their uses. Space robotics involves developing machines that can operate in the space environment, usually under human control. Some key applications are in-orbit assembly, maintenance, and resupply. Designing robots for space presents challenges due to zero gravity, vacuum conditions, and thermal extremes. Space robots have specific structures involving joints, arms, wrists and grippers. The document discusses examples like the space shuttle robot arm which was used to survey and transport during spacewalks. It concludes that space robotics will enable more people to explore space indirectly.