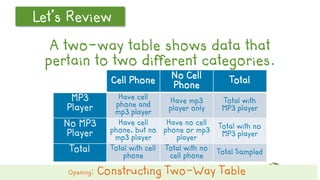
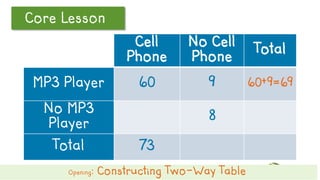
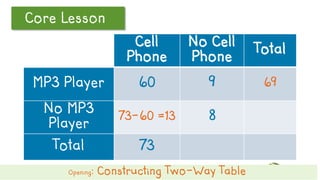
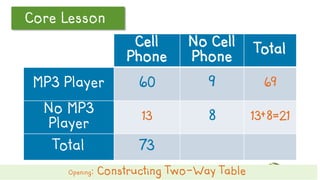
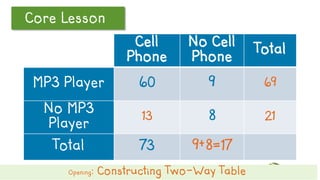
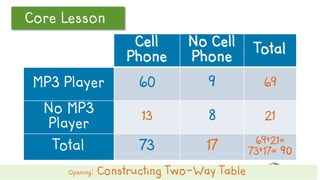
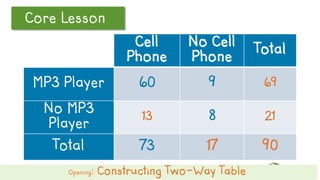
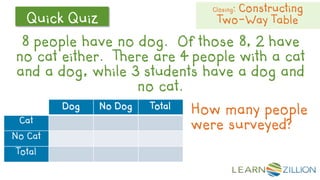
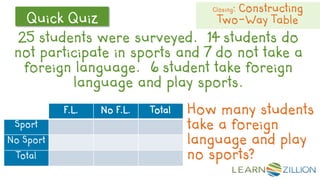
This document discusses how to construct and interpret a two-way table to organize categorical data about two variables. It explains that a two-way table shows the relationship between two categories of data and can be used to summarize survey results. An example is provided of constructing a two-way table from data about students' cell phone and MP3 player ownership. The document also includes a guided practice example and quiz questions to help understand two-way tables.