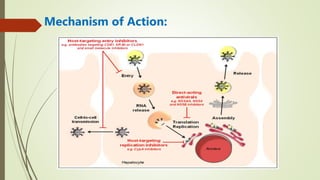
The document provides an overview of hepatitis C, detailing its causes, treatment options for both acute and chronic forms, and the mechanism of action of the antiviral drug Sovaldi (sofosbuvir). Sovaldi is a nucleotide analog that inhibits the hepatitis C virus's viral protein, aiding in virus elimination with high effectiveness when used in combination with other antivirals. Egypt has a particularly high prevalence of hepatitis C, underscoring its public health significance.