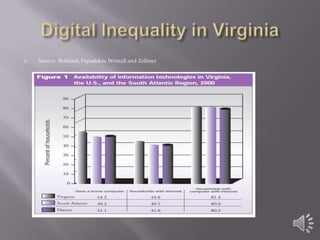
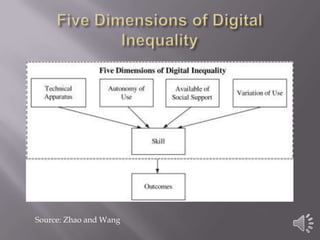
The document discusses solutions to address digital inequality in Virginia. It defines digital inequality as going beyond just differences in access to the internet and involving five dimensions: technical apparatus, autonomy of use, availability of social support, variation of use, and skill. The best solutions proposed include installing computers and expanding hours at public libraries, expanding access to public schools after hours, and providing information literacy courses to enhance computer skills. Simply providing computers and access may not be enough and could widen achievement gaps without proper support and training.