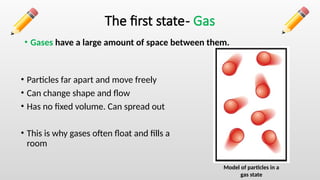
The document describes the states of matter, including solids, liquids, and gases, and their characteristics, focusing on particle arrangement and movement. It also differentiates between physical changes, where no new products are formed, and chemical changes, where new substances are created. The lesson includes examples like water's different states and practice questions for reinforcement.