Soils of telangana and water management
- 2. PROF.JAYASHANKAR TELANGANA STATE AGRICULTURE UNIVERSITY TERM PAPER ON SOILS OF TELANGANA AND WATER MANAGEMENT Sudha Rani.J.S RAD /2016-04 Dept.of Agronomy
- 3. The nature and properties of soils vary greatly depending on the variation in Soil forming factors and processes like… Physiography Geology Climate Soil moisture and temperature regimes.etc. Why different types of Soils are formed?
- 4. Major Soils Area(m. ha.) India has geographical area of 329 M.ha Alluvial soils 75 Black soils 72 Red soils 70 Laterite or Lateritic soils 25 Saline and Alkali soils 7.5 Desert soils 29 Forest and Hill Soils Peaty and Marshy soils Soil types in India
- 5. Telangana State: Mean Annual Rainfall of Telangana : 906.6mm Gross Cropped Area : 62.88 lakh ha Net Cropped Area : 49.61 lakh ha Gross Irrigated Area : 31.64 lakh ha Net Irrigated area : 22.55 lakh ha Cropping Intesity : 127 % Irrigation Intensity : 138 % Percent Area Under Rainfed Agriculture : 63.6 % Percent Area under ground water : 84 % source: Directorate of Economics and Statistics: Statstical year book 2016 5
- 6. S.No Crop Gross cropped area Gross Irrigated area Percent Irrigated area (%) 1 Rice 20.09 19.56 97.37 2 Maize 7.52 2.65 35.16 3 Ground nut 2.10 1.91 90.80 4 Cotton 17.13 2.16 12.62 5 Other crops 16.04 5.37 33.46 Total 62.88 31.64 50.32 Table 1: Crop wise irrigated area (lakh ha) of Telangana (2014-15) source: Directorate of Economics and Statistics: Statstical year book 2016 6
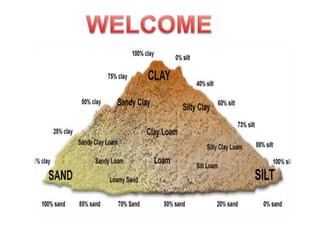
- 7. Major Soil types in Telangana 1.Red loamy sands (Dubba soils) 2. Red sandy loams (Chalaka Soils) 3. Lateritic soils 4. Shallow to Medium black soils 5. Deep black soils 6. Salt affected soils 7. Alluvial soils Soils of Andhra pradesh, 1976
- 8. Dominantly develop in the hot, semi- arid to sub-humid, sub-tropical climatic conditions Major Parent material: Acidic crystalline rocks such as granite and gneiss. Dominant pedogenic process was illuviation of clay. Red to yellowish in colour which is the result of coatings of ferric oxides on ped surfaces.
- 9. Occupy relatively higher topographic positions. In general they vary from loam to clay loam in texture. They are acidic to neutral in reaction. Translocated clay form characteristic Bt horizon which is called as argillic. They are deficient in nitrogen, phosphorus, micro-nutrients and organic matter. Dominant by presence of illite, chlorite and kaolinite type of secondary minerals.
- 11. Alluvial soils The name alluvial is given to soils that have developed on alluvium, irrespective of their place of occurrence and degree of profile development. Parent material: Of recent origin brought and laid down by various river system. They represent most fertile land for agricultural production.
- 12. They mostly occur in coastal and deltaic regions. Depending on the climate they may be alkaline in nature ( Contain calcid layer in sub surface- aridic conditions). Fluvial (stratified) in nature which reflects variation in their texture. Inherently rich in plant nutrients, fairer in phosphorus and potassium but are deficient in nitrogen and organic matter. Classification: In genetic system they were classified as Azonal. Taxanomically as Entisols Inceptisols Alfisols Aridisols
- 13. The word Laterite is derived from latin word which means brick. Laterites are typically formed in tropical and sub-tropical climates having alternate wet and dry seasons. Siliceous materials leach completely during weathering and sesquioxides left behind. It is compact to vescicular rock, which is composed of oxides iron and aluminium. It is highly weathered rock. They are rich in kaolinite. They are classified as Oxisols. Lateritic soils
- 15. BLACK COTTON SOILS The soils are dark in colour, rich in clay content which is >30%. They developed on basaltic material with marked alternating wet and dry conditions. The weathered product of the parent rocks are basic and rich in clays, that is dominantly of smectite type. Also develop from granite, gneisses containing lime or soda.
- 16. They have characteristic property of swell and shrink. Shrink upon drying and swell on wetting, this expansion causes pressure on soil particles and lead to Churning process. The slippage of one block over other forms slicken slides Expansion and contraction leads to formation of micro- topographic features, known as gilgai.
- 17. Classification: These soils, as per genetic system are classified in the orders of Intrazonal & Azonal (alluvial soils). According to soil taxonomy the black soils are in the orders: Vertisols, Inceptisols, Entisols.
- 18. Salt-affected soils often occur on irrigated lands, especially in arid and semiarid regions, where annual precipitation is insufficient to meet the evaporation needs of plants. These soils contain considerable amounts of soluble salts and/or sodium on the exchangeable complex. In arid and semi-arid regions due to high evaporative demand, the dissolved salts move upwards by capillary action. Salt-affected soils
- 19. Classification of Salt-affected soils Class EC(dS/m) pH ESP Saline >4 <8.5 >15 Saline-sodic >4 >8.5 >15 Sodic <4 >8.5 >15 Saline soils will develop due to high evaporative demand dissolved salts in parent material or ground water will come to surface. Sodic soils form by byproducts of weathering accumulate by surface runoff in lower topographies, and during post-monsoon SAR ratio is increased in the soil.
- 20. • Ranga Reddy 2.0 • Nizamabad 5.0 • Medak 16.0 • Mahabubnagar 51.0 • Nalgonda 23.6 • Warangal 8.1 • Khammam 6.0 • Karimnagar 4.1 • Adilabad 3.5 • TOTAL 119.3 Extent of salt effected soils in different districts of Telangana District Area (‘000 ha)
- 21. Adilabad District is located in Northern Telangana Zone . Area : 16,105 km2 Majorparent materials: Granite, Gneiss, basalt, sandstone, limestone. It has annual rainfall of 1051mm The district is largely occupied by blacksoils of about 72% Dominant crops: Jowar, Paddy, Maize, pulses, Cotton, Soybean etc. Adilabad Ground water brochure, Adilabad-2013
- 22. KARIMNAGAR Area: 11,823 sq. km Rainfall: 950mm. Dominant soil types: Sandy loams and red chalkas with interspread black soils.Alkaline soils are present along chandragiri vagu project, siricilla, gagillapur, dacharam, thotapally and parts of husnabad. Parent materials: Granite, gneisses, sandstone, limestone, shale, quartzite. Karimnagar CDAP
- 23. NIZAMABAD It is one of the Northern district of Telangana, extending over an area of 7,956 sq. km. Physiographically the district is located in the table land of the Deccan plateau. Average Rainfall is 999 to 1101.0 mm. Temperature: 14oC to 40oC Soils of Nizamabad district showed mostly Red Sandy clay loam to Sandy loam . Few pedons show clayey soils.
- 24. It is part of Southern deccan plateau. Climate is Semi-arid, with mean annual rainfall of 890mm (NBSS & LUP)The total area is 9,71,086 ha. The dominant parent material is Granite-gneiss formed during archean period of evolution. Soils in Medak are mainly effected by physiography, climate and parent material.Major soils types are Red loamy soil, Black soils & Laterites. Medak
- 25. Distribution of soils in Medak dist Soil Type Area Slope Parent material Location Classification Red Loamy 70.57% 6,86,979 ha 3-8% Hills, Hill summits, isolated hills, rolling lands etc. Granite & Granite- Gneiss Mutyapalli, Medak, Siddipet, Narayankhed , Narsapur etc. Alfisols Inceptisols Entisols Black 14.56% 1,40,467 ha. 1-3% Plateaus and gently sloping landforms Basalt Sadasivapet, Nyalkal, Manur, Kalher, Kohir etc. Vertisols Laterites 8.7% 82,869 ha. 3-8% Upper plateau, broad valleys Laterite Zaheerabad, Jerasangam, Nyalkal, Kohir etc. Alfisols Alluvial soils also present in medak along the coast of Manjira, Haldi, Peddavadu, Nakkavagu etc. They areclassified inti Entisolsand Inceptisols. Reddy et al., 2005
- 26. Area: 12,834 km2 Rain fall: 994mm Temperature: 13oC to 50oC . Main Crops: Paddy,Cotton, Maize, Chilli, Greengram, Groundnut. Soil types: Red earths, Black soils, Forest soils. WARANGAL
- 27. Area: 16,029 sq. km. Rainfall: 1124mm Main crops: Paddy, Jowar, Pulses, Groundnut, Chilli, Cotton and Tobacco KHAMMAM
- 28. RANGAREDDY It is located in Deccan plateau region of Telangana Rainfall: 781mm Soil types: Red soils: 125000 ha – 51% Red Chalka : Medchal, Shameerpet, Quitubullapur, Hayathnagar, Saroornagar, Rajendranagar etc. Dubba soil: Ibrahim patnam, Yacharam, Maheswaram, Kandukur etc. Black cotton soil: 98000 ha – 40% Chevella, Shahbad, Vikarabad, Nawabpet, Dharur, Pudur, Tandur, Peddemul, Yalal, Basheerabad, Marpally, Mominpet and Bantaram. Agriculture Contingency Plan for Rangareddy distict,2014
- 29. NALGONDA It covers an area of 14,240 Sq. Kms. The average rainfall in the district is 772 mm. On an average there are 46 rainy days. (i.e days with rainfall of over 2.5mm or more). Soil Type: The soils of the district are mainly 'red earth's' comprising loamy sands, sandy loams and sandy clay loams.
- 30. • Granite, Gneiss, Limestone and alluvium • Drainage: Krishna along with tributaries like alair, dindi, halia, peddavagu etc. • In the areas of flat topography and along sides of river Krishna and its tributaries, regur or black cotton soil is found. • Red soils: 85% • Black soils: Limestone • Alluvial soils: 1% along coasts of Alair, kargal etc.
- 31. Soil types: Loamy Sands(Dubba): 13% Red Sandy loams (Chalka): 67% Black soils: 20%