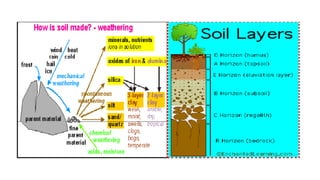
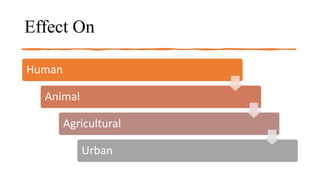
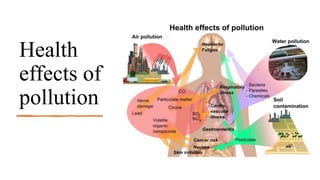
This document provides information about Muskaan Verma's course details and a summary of soil pollution. It defines soil pollution as the contamination of soil that reduces its productive capacity. The main causes of soil pollution are listed as acid rain, excess application of fertilizers and pesticides, disposal of urban solid wastes and industrial wastes. The effects of soil pollution on humans, animals, agriculture and urban areas are outlined. Control methods discussed include banning plastic bags, recycling plastic waste, banning deforestation, and optimizing fertilizer and pesticide use.