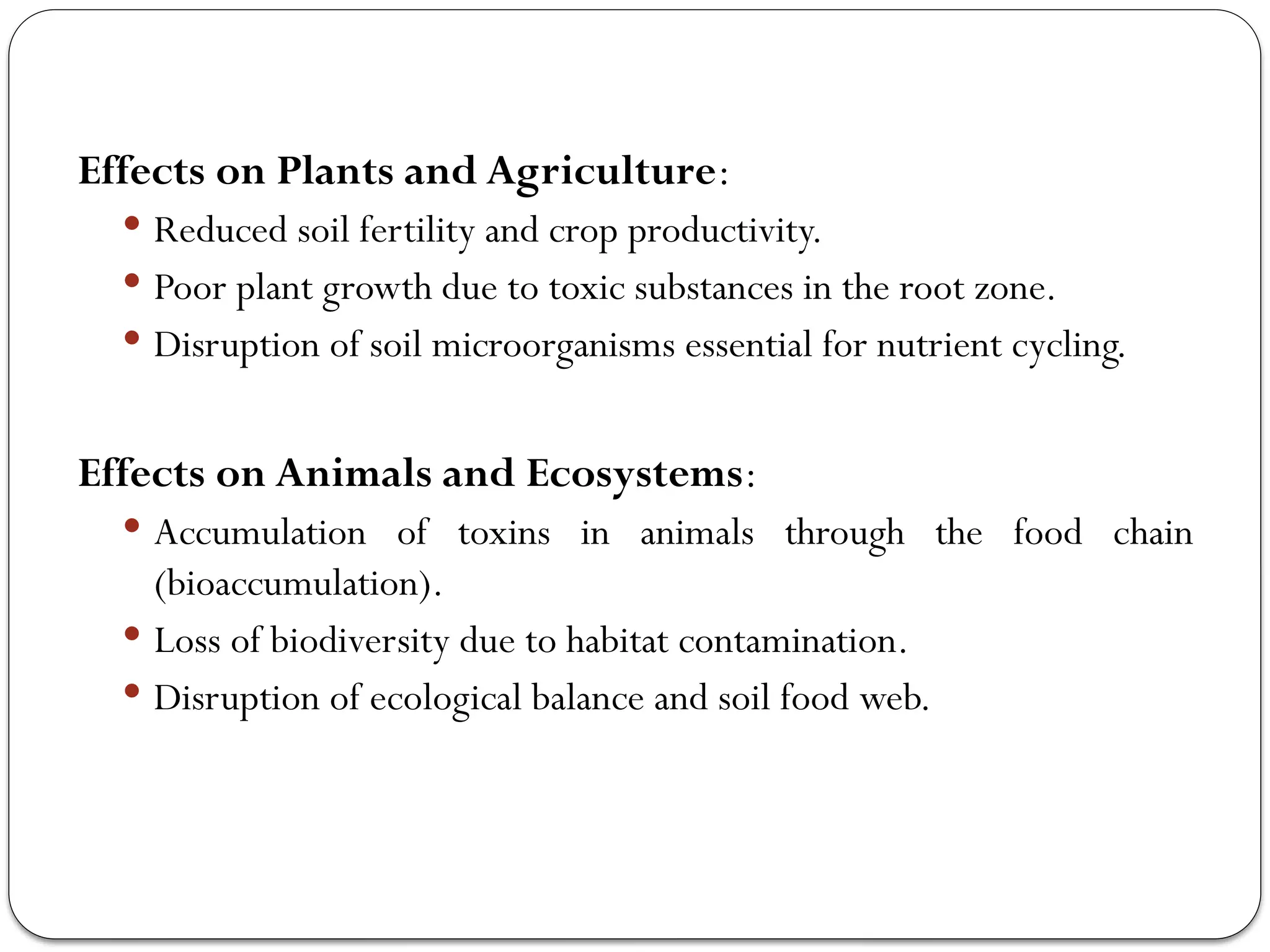
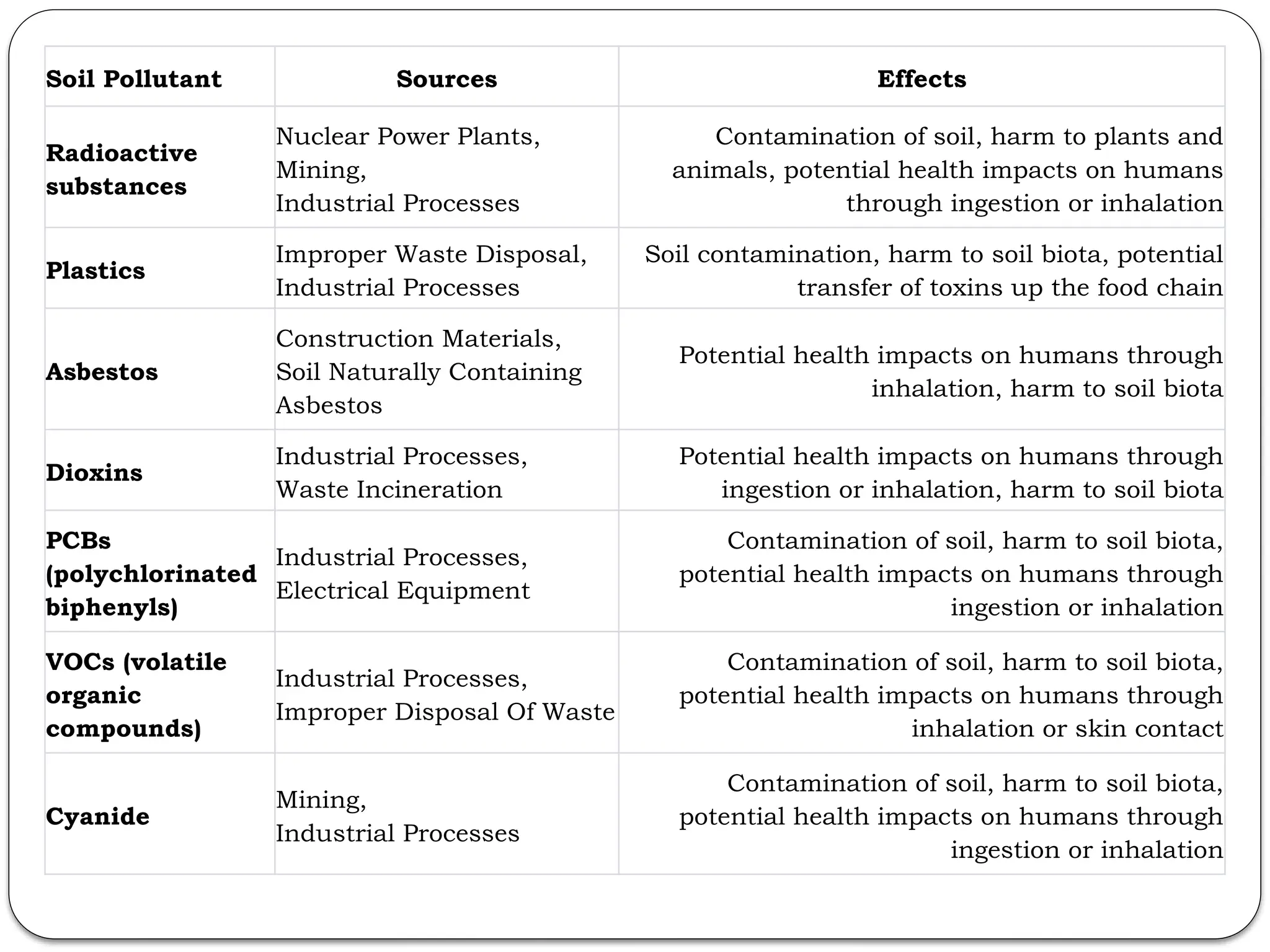
Soil Pollutant: Reason: Pollutant Name: Their Effects:
Heavy metals (e.g. lead, cadmium)
Industrial Discharge,
Mining,
Waste Incineration:
Pesticides and herbicides Agricultural Use,
Industrial Discharge,
Residential Use
Petroleum products: Oil Spills, Industrial Discharge, Improper Disposal Of Waste
Salts and other inorganic compounds: Agricultural Practices,
Irrigation With Saline Water, Industrial Discharge
Acids and alkalis: Industrial Discharge,
Mining:
Radioactive substances Nuclear Power Plants,
Mining,
Industrial Processes
Plastics: Improper Waste Disposal,
Industrial Processes:
Asbestos Construction Materials,
Soil Naturally Containing Asbestos
Dioxins Industrial Processes, Waste Incineration:
PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls) Industrial Processes,
Electrical Equipment
VOCs (volatile organic compounds): Industrial Processes,
Improper Disposal Of Waste
Cyanide: Mining,
Industrial Processes