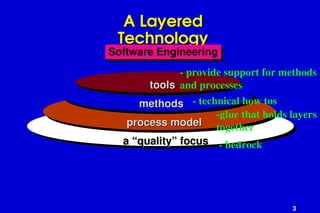
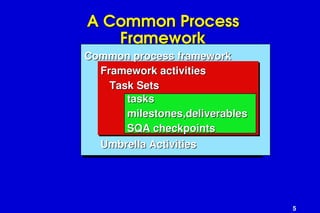
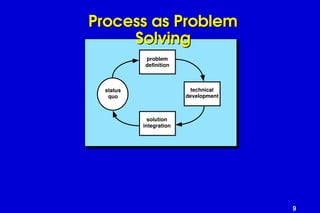
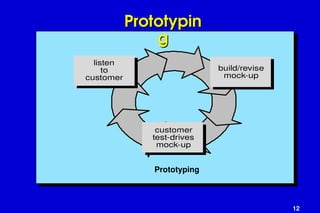
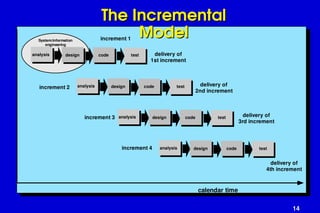
The document outlines software engineering as a systematic approach to software development, operation, and maintenance, defined by IEEE standards. It describes various software types, maintenance methods, and frameworks for managing software projects, including different process models such as the linear, incremental, and spiral models. Additionally, it mentions various umbrella activities and emphasizes adaptability based on project characteristics.