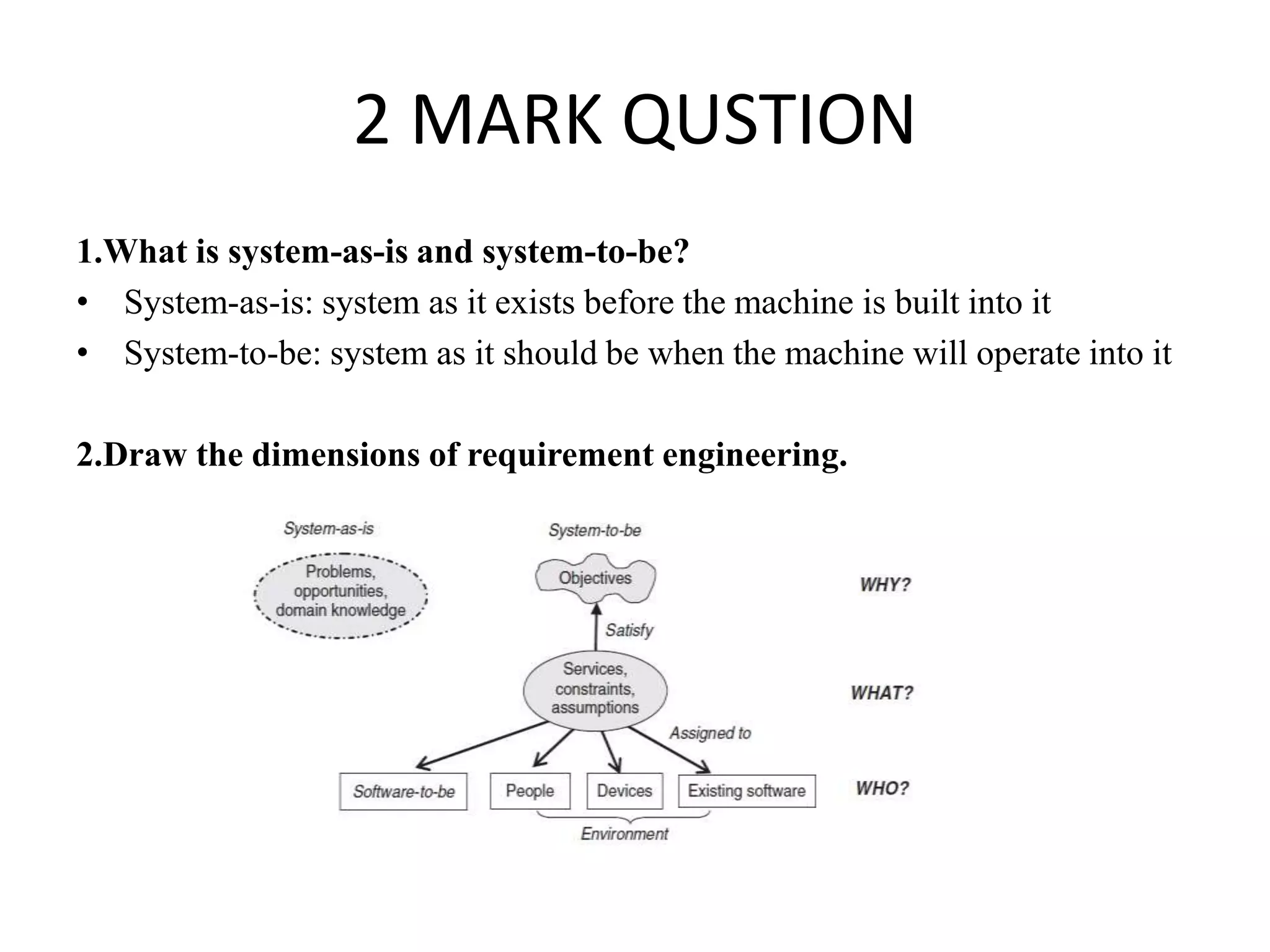
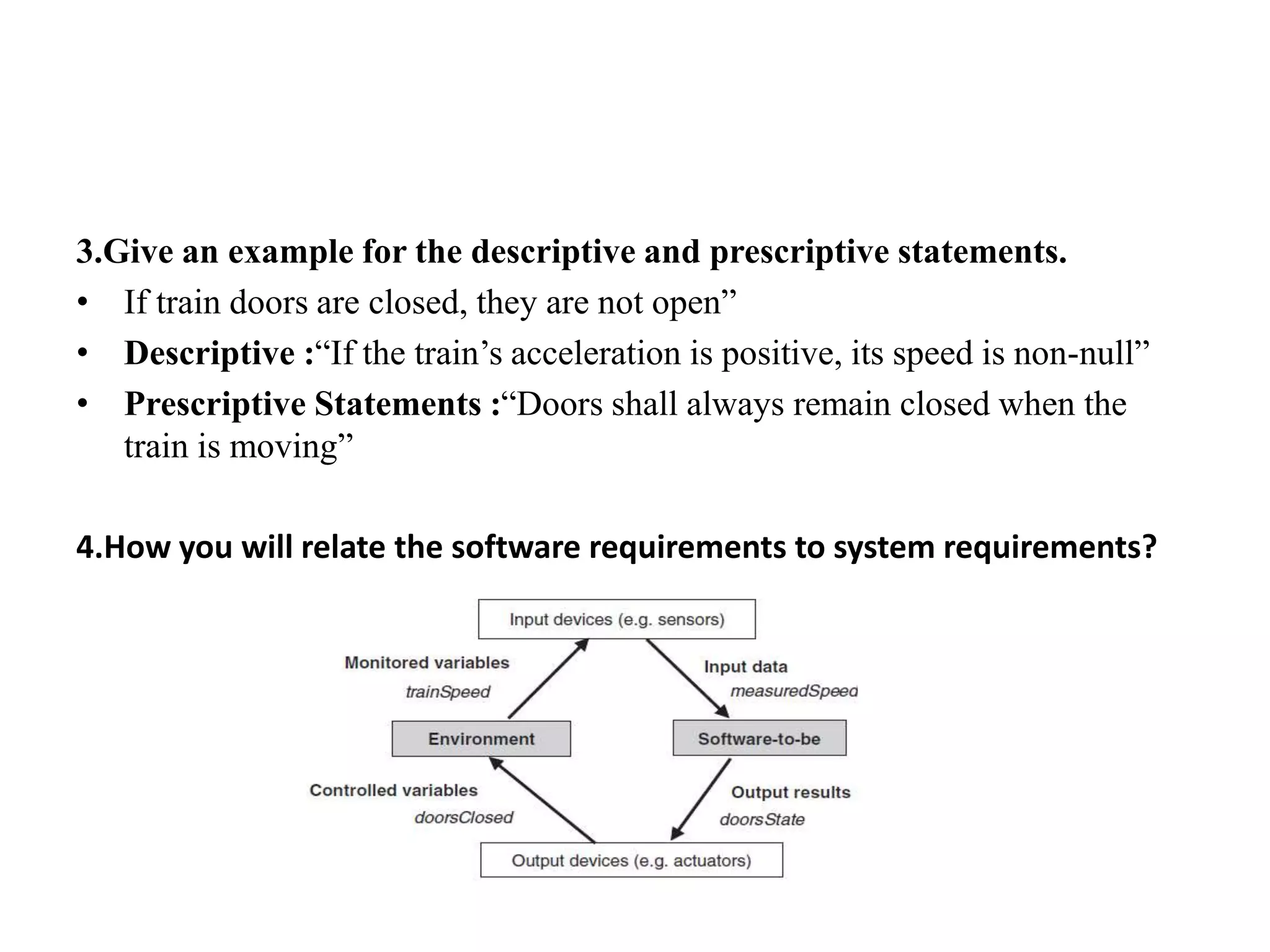
This document contains a presentation on software requirements engineering. It lists 10 multiple choice questions covering topics such as the difference between the system-as-is and system-to-be, examples of descriptive and prescriptive statements, how to relate software requirements to system requirements, the benefits of requirements taxonomies, and the aim of domain understanding. Interview techniques are also discussed such as identifying the right interview sample and appearing trustworthy. Other questions define fault trees, frame diagrams, and the difference between causal and biddable components.