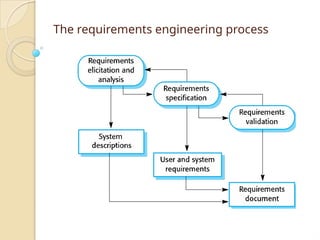
The document discusses the software development life cycle (SDLC), emphasizing the interleaved activities of specification, development, validation, and evolution. It details the requirements engineering process, software design, implementation, and the importance of validation through various testing stages. Additionally, it highlights the need for software evolution to adapt to changing business requirements.