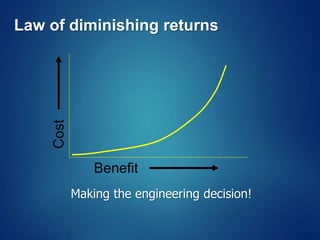
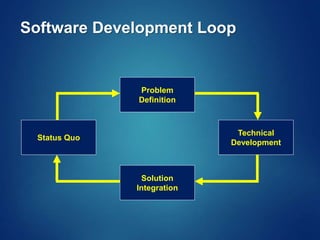
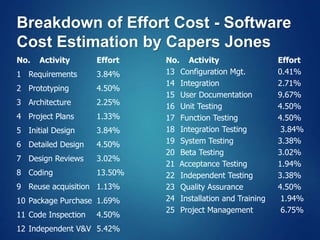
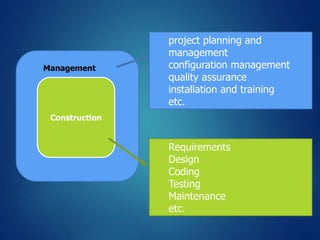
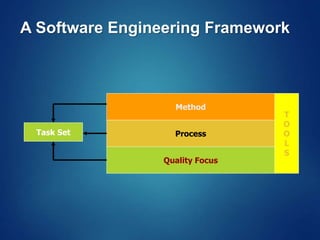
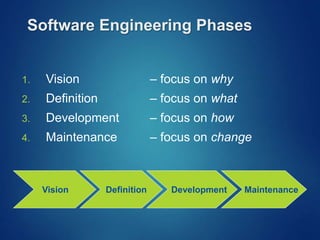
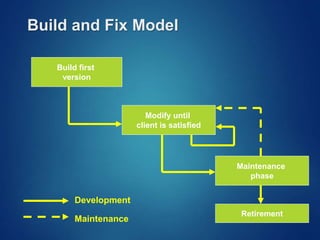
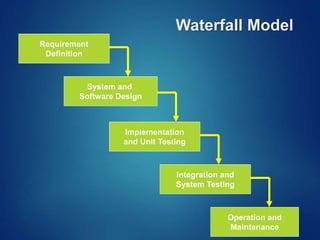
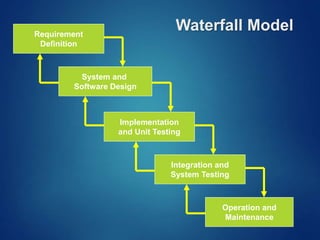
The document provides an overview of software engineering, covering traditional and agile process models, requirement engineering, software design, testing, project management, risk analysis, and software quality assurance. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach to software development, balancing conflicting requirements such as cost, efficiency, and reliability. Additionally, it outlines various software engineering phases and lifecycle models while addressing cost estimation and effort breakdown in software engineering practices.