The document provides an introduction to software engineering, covering the software development life cycle, various methods including waterfall, iterative, agile, and scrum, as well as programming concepts in C++ and object-oriented programming. It emphasizes the importance of requirements gathering, system design, and testing, detailing programming languages and fundamental OOP principles. Additionally, it acknowledges resources and contributors to the author's learning experience.


![Introduction
• In my point of view, Software Engineering is planning, designing,
implementing, maintaining and supporting of software systems for
specific work given. It pivots around areas on requirement gathering
and analysis, system design, prototyping, system implementation,
system integrating, system testing, system deployment and system
support.
• Different Types of Software:
l
Embedded Software (Running on Devices)
l
System Software (Like Operating Systems)
l
Application Software (Database Programs, Web based software, Word Processors
etc) [1]
l
Specific Application Software:
l
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
l
Content Management Systems (CMS)
l
Human Resource Management (HRM) Systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-3-320.jpg)
![Software/System Development Life Cycle
• All about gathering requirement, planning, designing, developing and
maintaining a software system. [2, 3]
• Many professionals involved in different phases.
l
Project Managers
l
Business System Analysts
l
Software Architects
l
Software Developers
l
Software Testers
l
Implementation Engineers
l
Customer Support Teams](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-4-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• There are a lot methods but here I am giving you a few of the most common.
•
• Waterfall Method
Step by Step Mechanism which involves different phases of the life
cycle [4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-5-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• Waterfall Method [4]:
l
Advantages:
l
Simple
l
Clearly defined steps
l
Targets are clearly defined
l
Disadvantages:
l
No delivery until all phases are finished
l
Not good for OOP and complex projects
l
Not good for long and ongoing projects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-6-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• Iterative Method [5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-7-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• Agile Methods [6, 7]:
• Caters different projects differently.
• Small time frames with well defined outcomes.
• Working software is delivered after each iteration.
• More interactive.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-8-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• Scrum Methodology [7, 8]:
• Key Stakeholders:
• Product Owner – Gathers requirements, Discusses with the S/W
architects, Writes use-cases, Deals with major stakeholders of the
project, Release Management.
• Scrum Master – Makes sure the team is adhering to the scrum
principles, Coaches the scrum team, Ensures proper communication
between the product owner and the team
• Scrum Team - The team that performs the defined goals;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-9-320.jpg)
![Software Development Methods
• Scrum Methodology [7, 8]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-10-320.jpg)

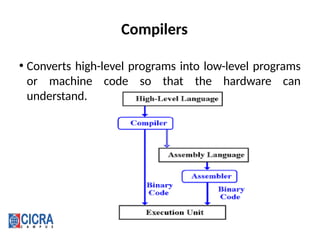
![Assemblers
• Converts assembly code into machine code.
Sample Assembly Code [9]:
Start: .org $8020
SEI
LDA #$80
STA $0315
LDA #$2D
STA $0314
CLI
RTS
INC $D020
JMP $EA31
l
In machine code:
8020 78
8021 A9 80
8023 8D 15 03
8026 A9 2D
8028 8D 14 03
802B 58
802C 60
802D EE 20 D0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-13-320.jpg)









![References – Mentioned with Thanks
[1] http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/A/application.html
[2]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Systems_development_life_cycle
[3] https://www.techopedia.com/definition/22193/software-development-life-cycle-sdlc
[4]https://www.tutorialspoint.com/sdlc/sdlc_waterfall_model.htm
[5]https://www.tutorialspoint.com/sdlc/sdlc_iterative_model.htm
[6]https://www.tutorialspoint.com/sdlc/sdlc_agile_model.htm
[7]https://www.versionone.com/agile-101/agile-methodologies/
[8] http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/d9c992/the-agile-scrum-framework/
[9] http://wiki.c2.com/?MachineCode
[10] http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/program_structure/
[11]http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/variables/
[12]http://www.rapidtables.com/convert/temperature/how-celsius-to-fahrenheit.htm
[13]http://www.studytonight.com/cpp/cpp-and-oops-concepts.php
[14]http://tx.english-ch.com/teacher/aisa/level-a/animal-classes/
[15] http://magizbox.com/training/object_oriented_programming/site/overview/
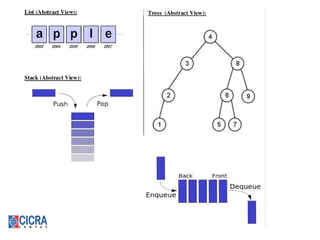
[16]http://www.studytonight.com/data-structures/introduction-to-data-structures
Special Thanks: Seebo Networks Lanka (Pvt) Ltd. And IFS R&D International (Pvt) Ltd for all the
things I learned there and also knowledge, tips and hints taken from their training materials;
specially IFS and also internet resources that I referred apart from above specially for images for
DS which I could not mention the URLs here; they were take from my Articles to Vidusara
Magazine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/softwareengineering-181009101332/85/Software-Engineering-27-320.jpg)