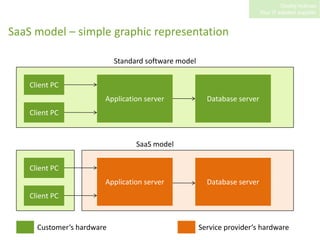
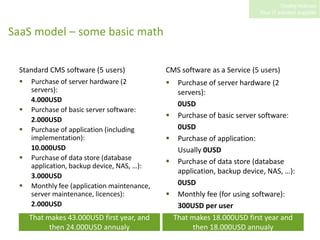
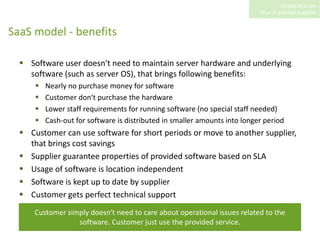
SaaS (Software as a Service) involves hosting applications online and providing access to customers via the internet on a pay-per-use basis. Some key benefits of SaaS include lower upfront costs than purchasing software licenses, reduced IT requirements as maintenance is handled by the provider, and the ability to access applications from anywhere. However, SaaS also presents security and availability risks if the provider's systems go down. Service level agreements are used to define the service quality customers can expect.