The document discusses soft tissue infections, including:
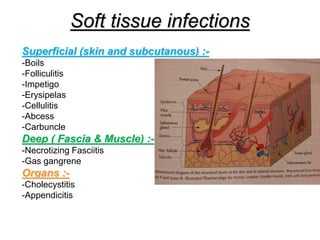
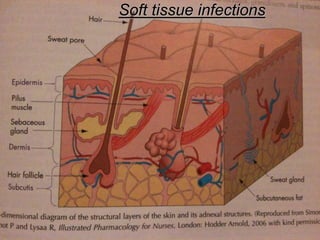
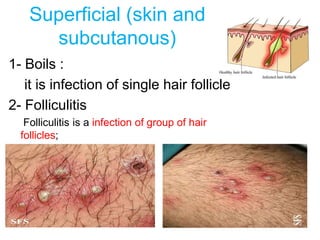
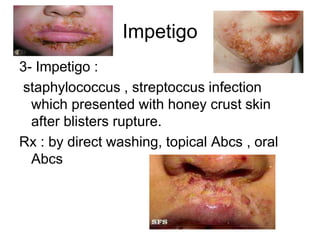
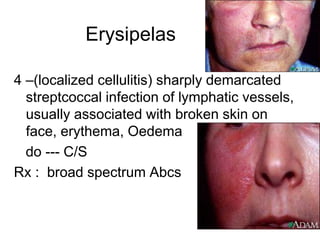
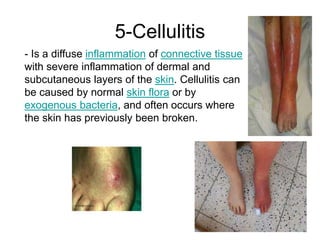
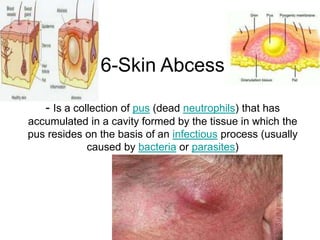
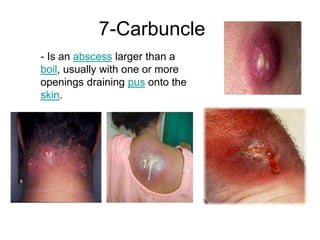
- Superficial infections like boils, folliculitis, impetigo, erysipelas, cellulitis, abscesses, and carbuncles.
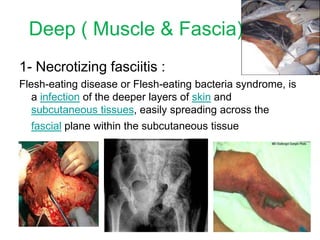
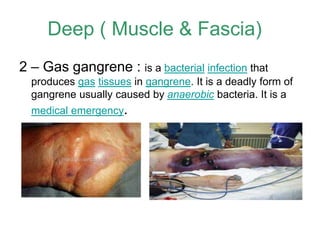
- Deep infections of the fascia and muscle like necrotizing fasciitis and gas gangrene.
- Organ infections like appendicitis and cholecystitis.
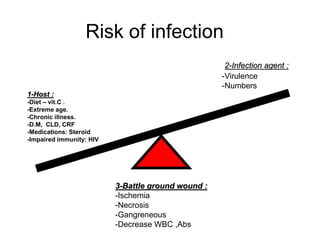
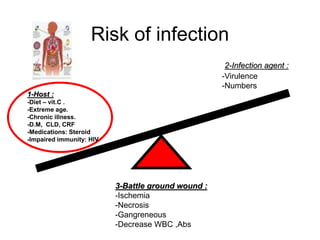
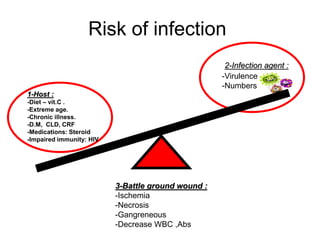
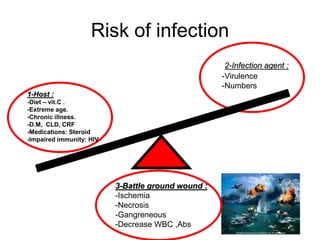
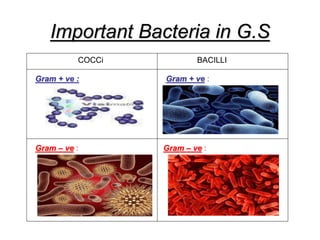
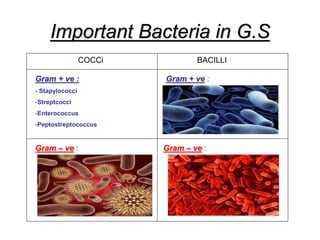
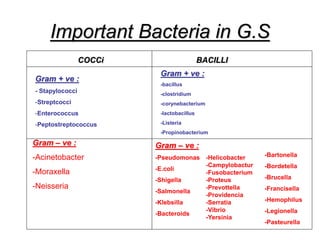
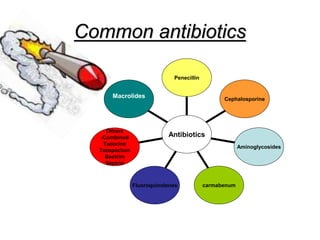
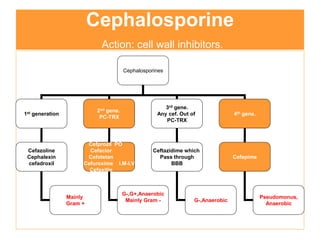
It also covers risk factors for infection, common bacteria in general surgery, antibiotic classes and examples.