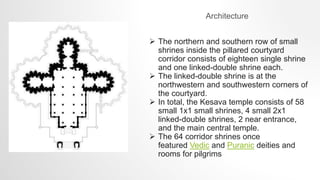
The document provides information about the Chennakesava Temple located in Somanathapura, Karnataka, India. It was consecrated in 1258 CE by general Somanatha Dandanayaka. The temple was destroyed during Muslim attacks but was later restored. It has an architecture consisting of 58 small shrines, 4 linked-double shrines, and a central temple. The document also discusses the history of the town of Somanathapura and the founding of the temple in the 13th century.