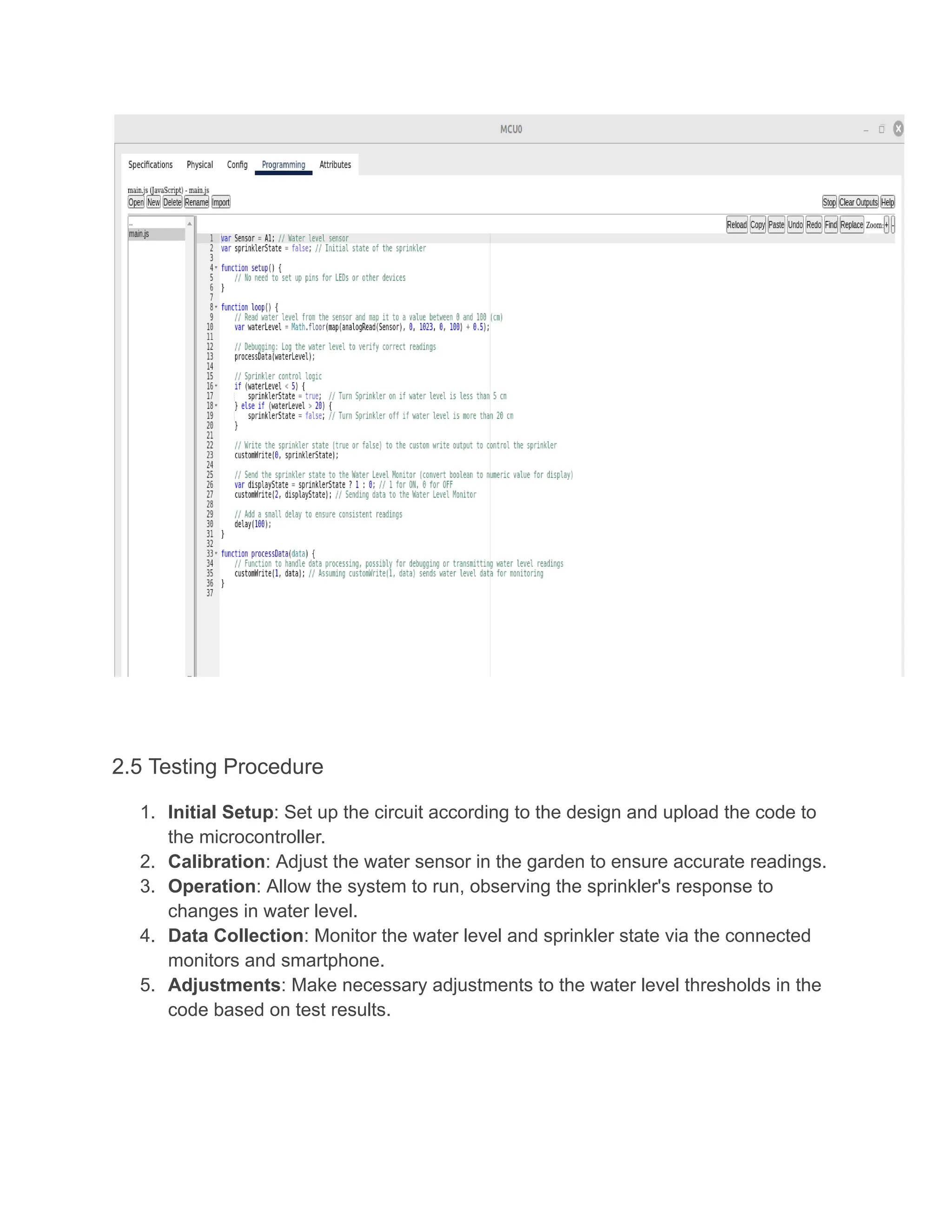
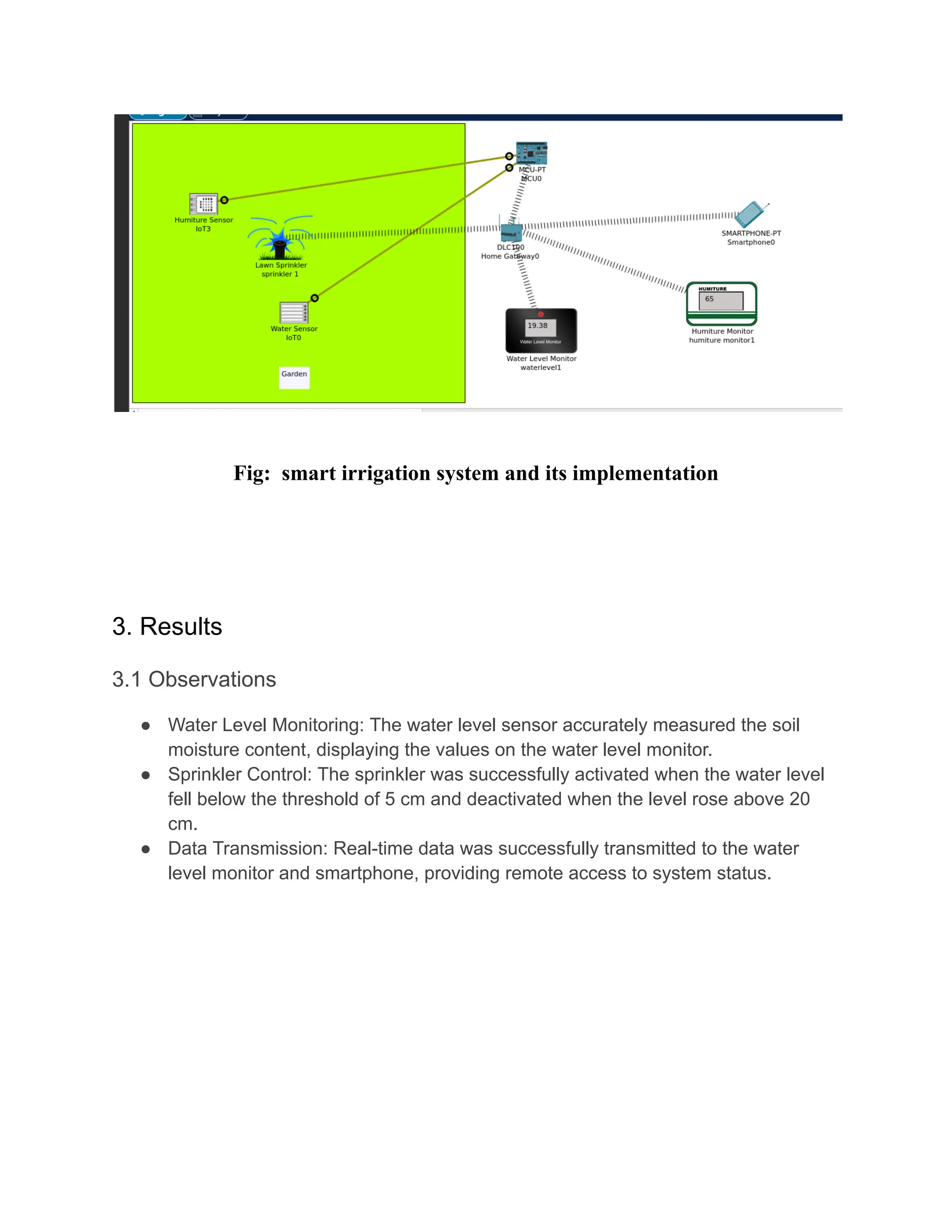
The document outlines a lab report on a smart irrigation system designed by Bikash Banjara at Kathmandu University, focusing on automating lawn sprinkling based on real-time water level data. The system utilizes IoT devices to monitor soil moisture and activates sprinklers when necessary, aiming to reduce water waste in gardening and agricultural contexts. The report details the materials, methods, and results, demonstrating the effectiveness of the system in optimizing water usage.