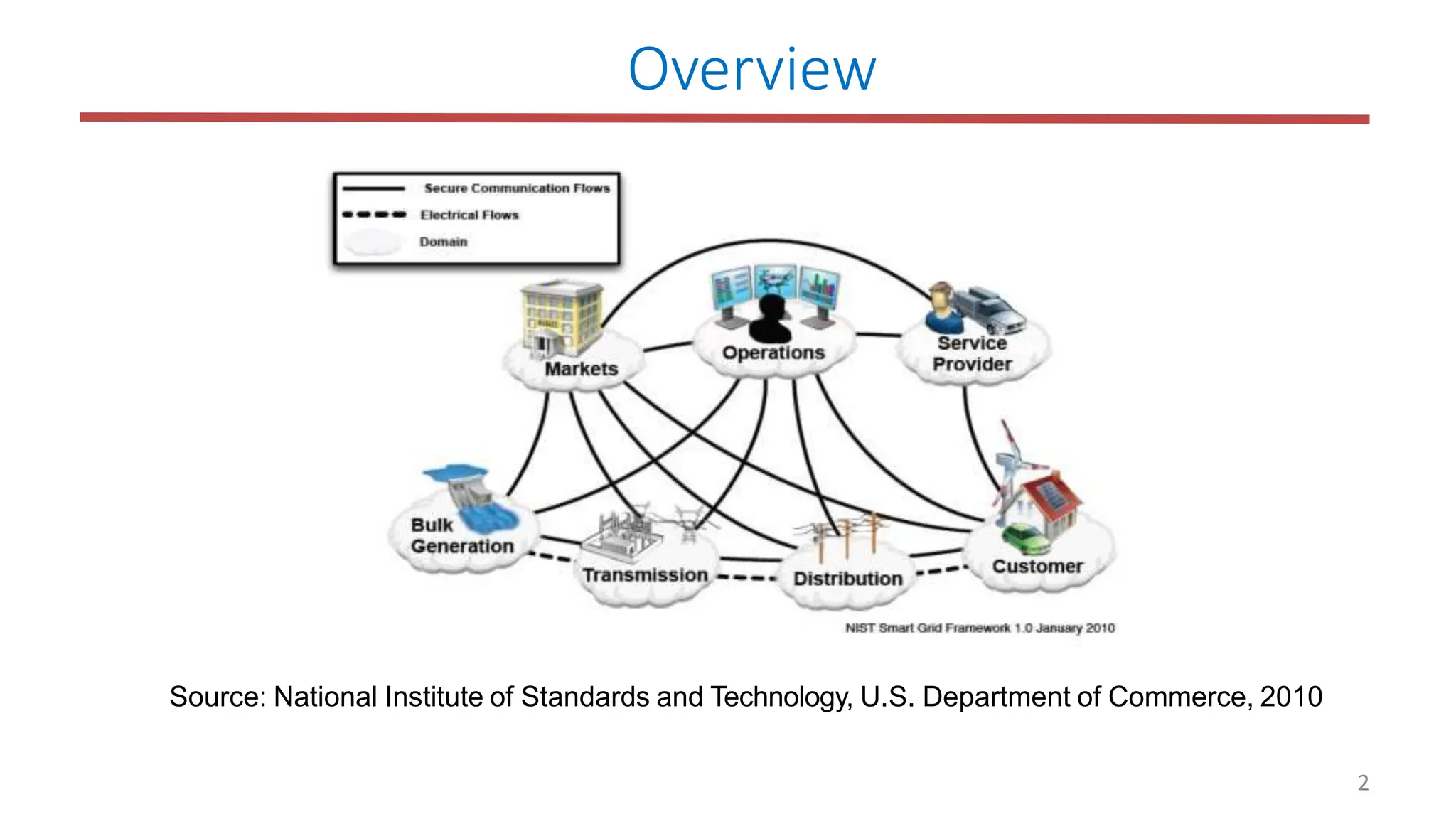
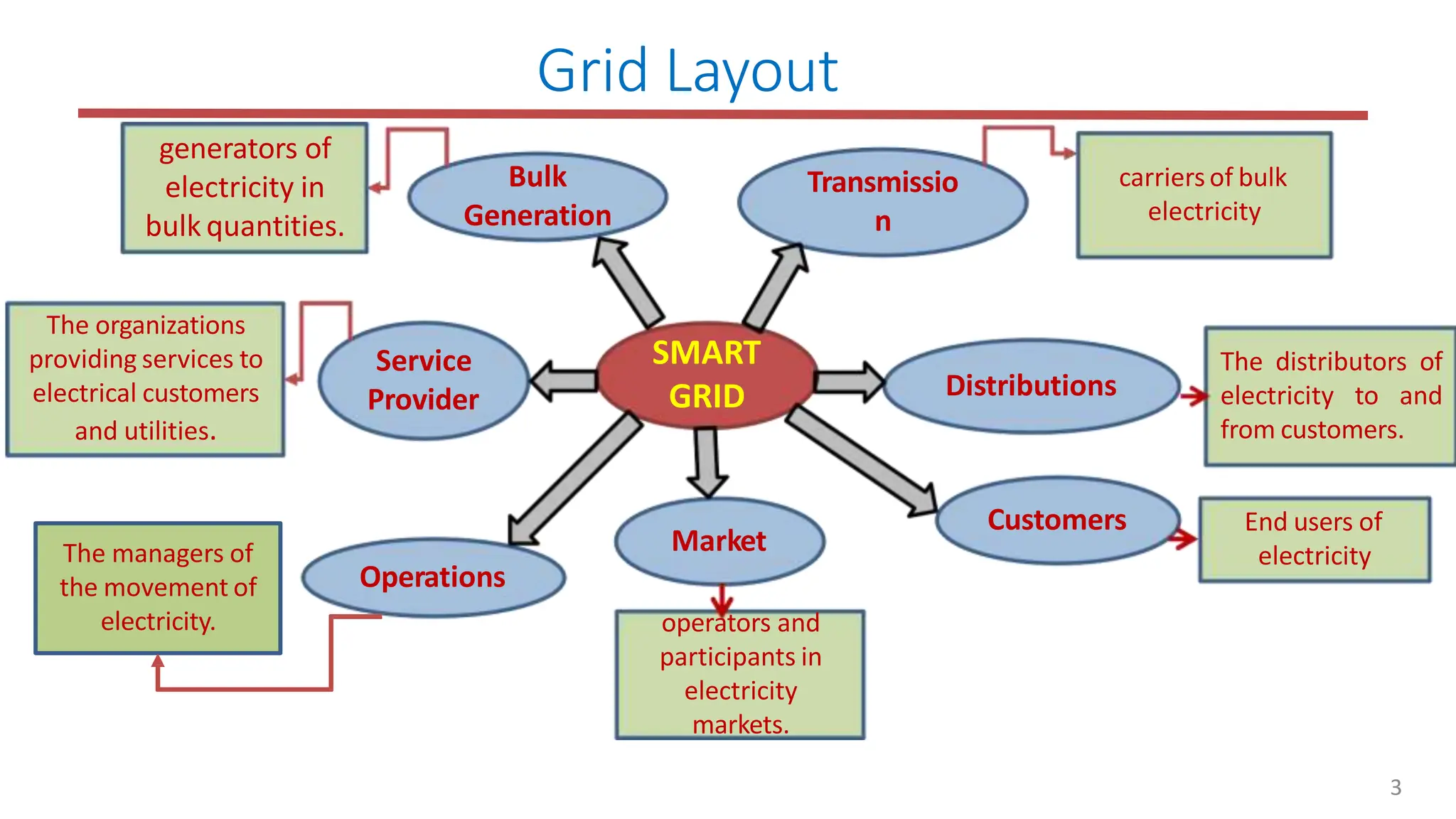
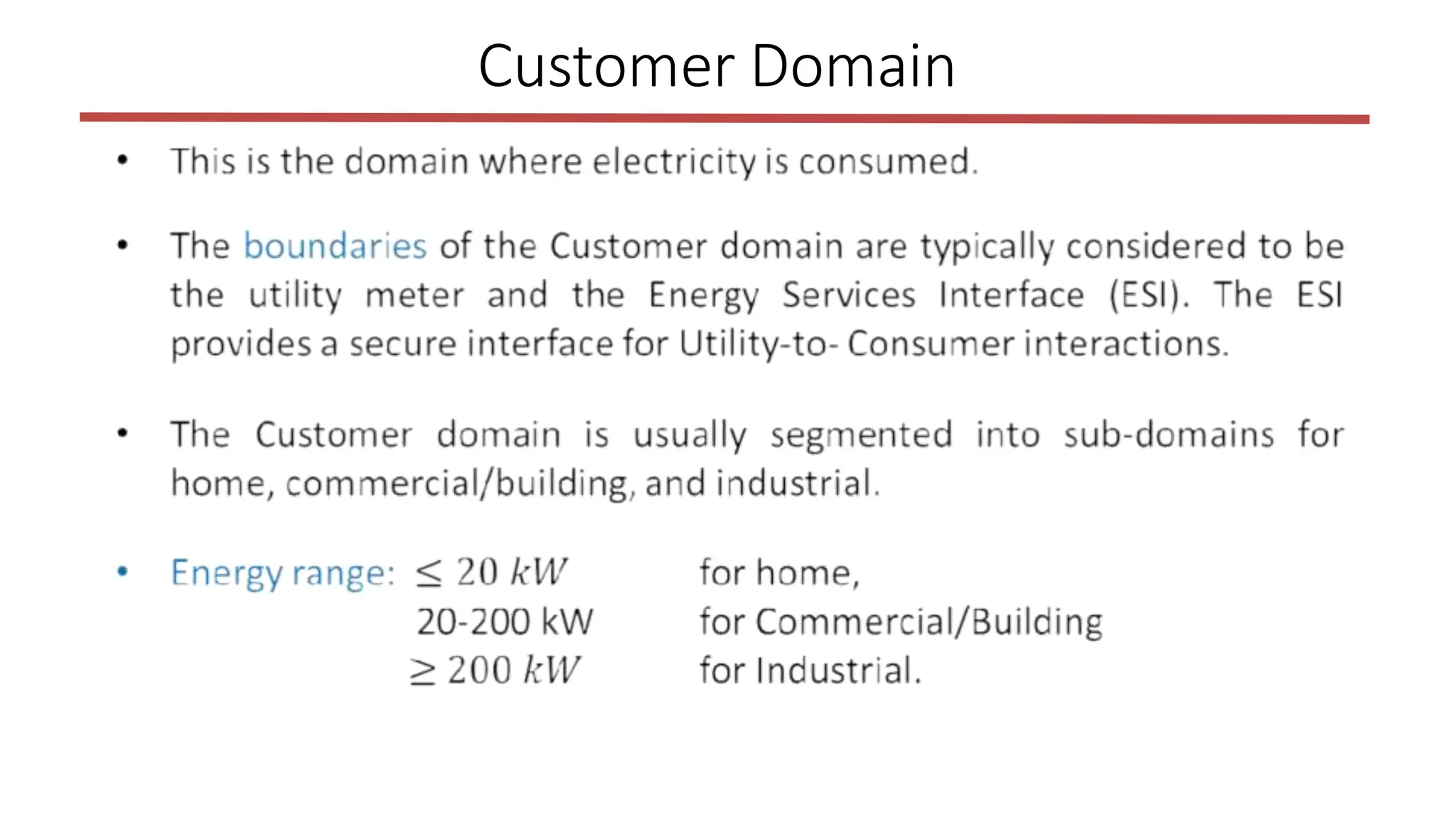
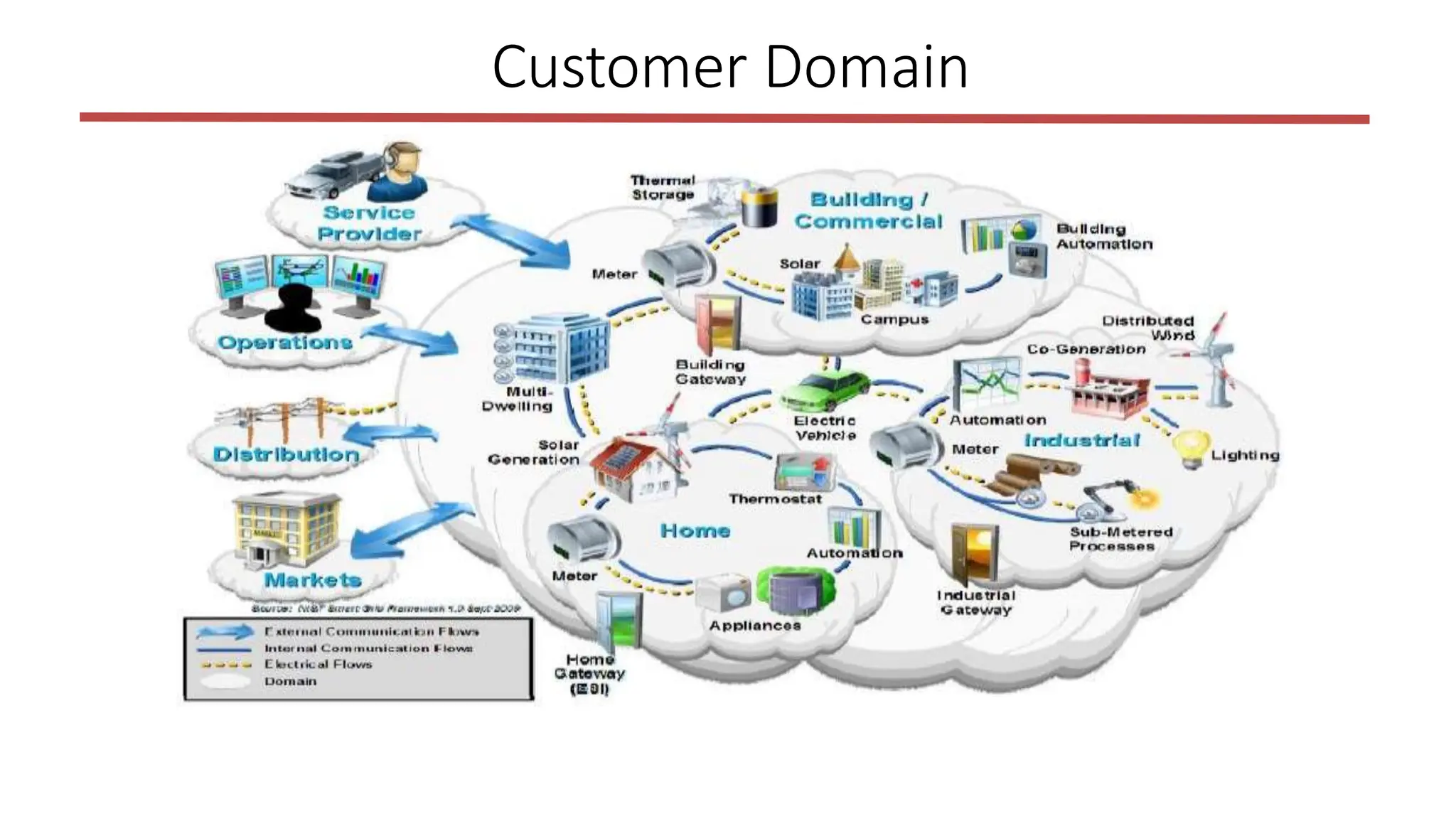
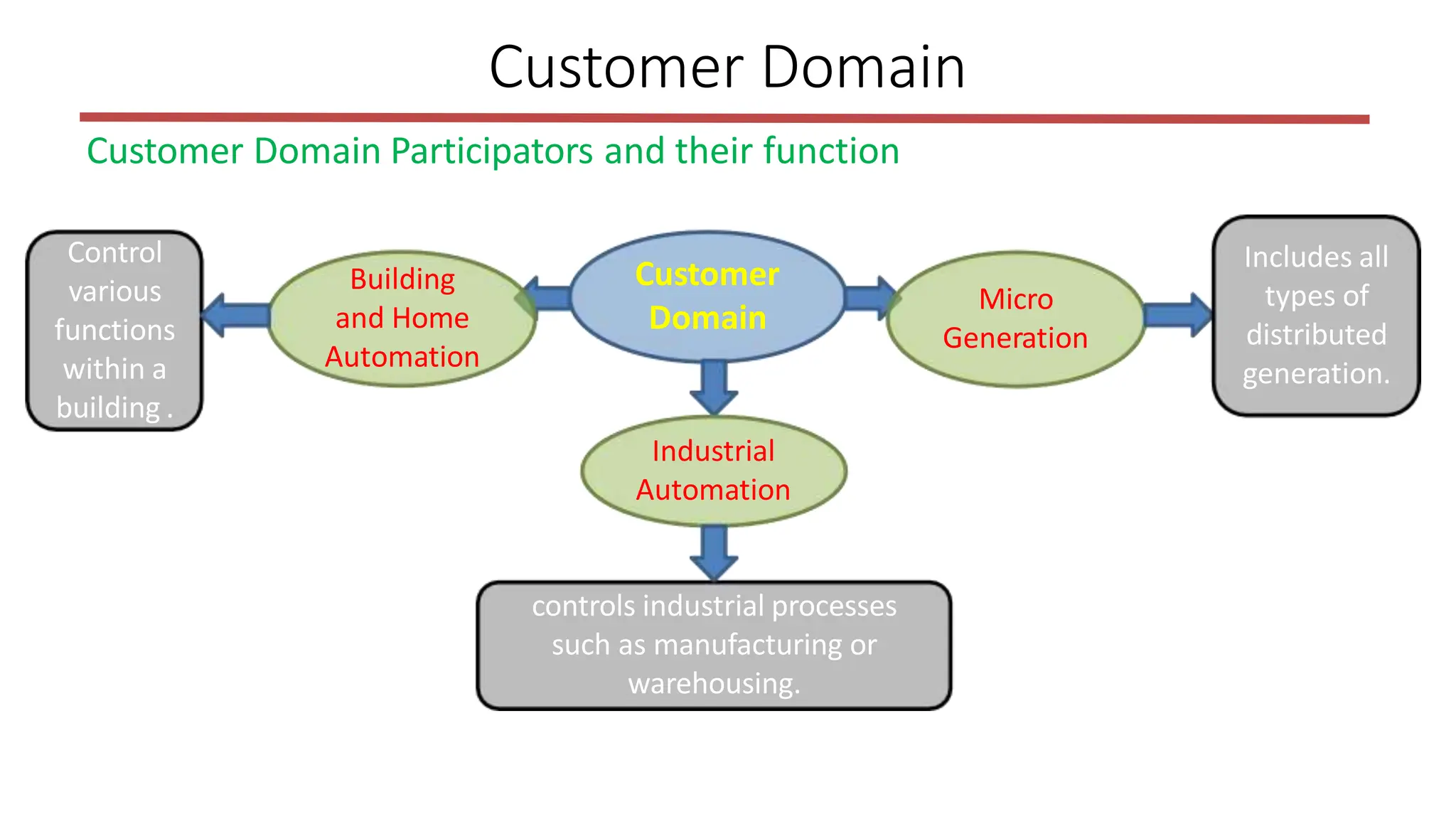
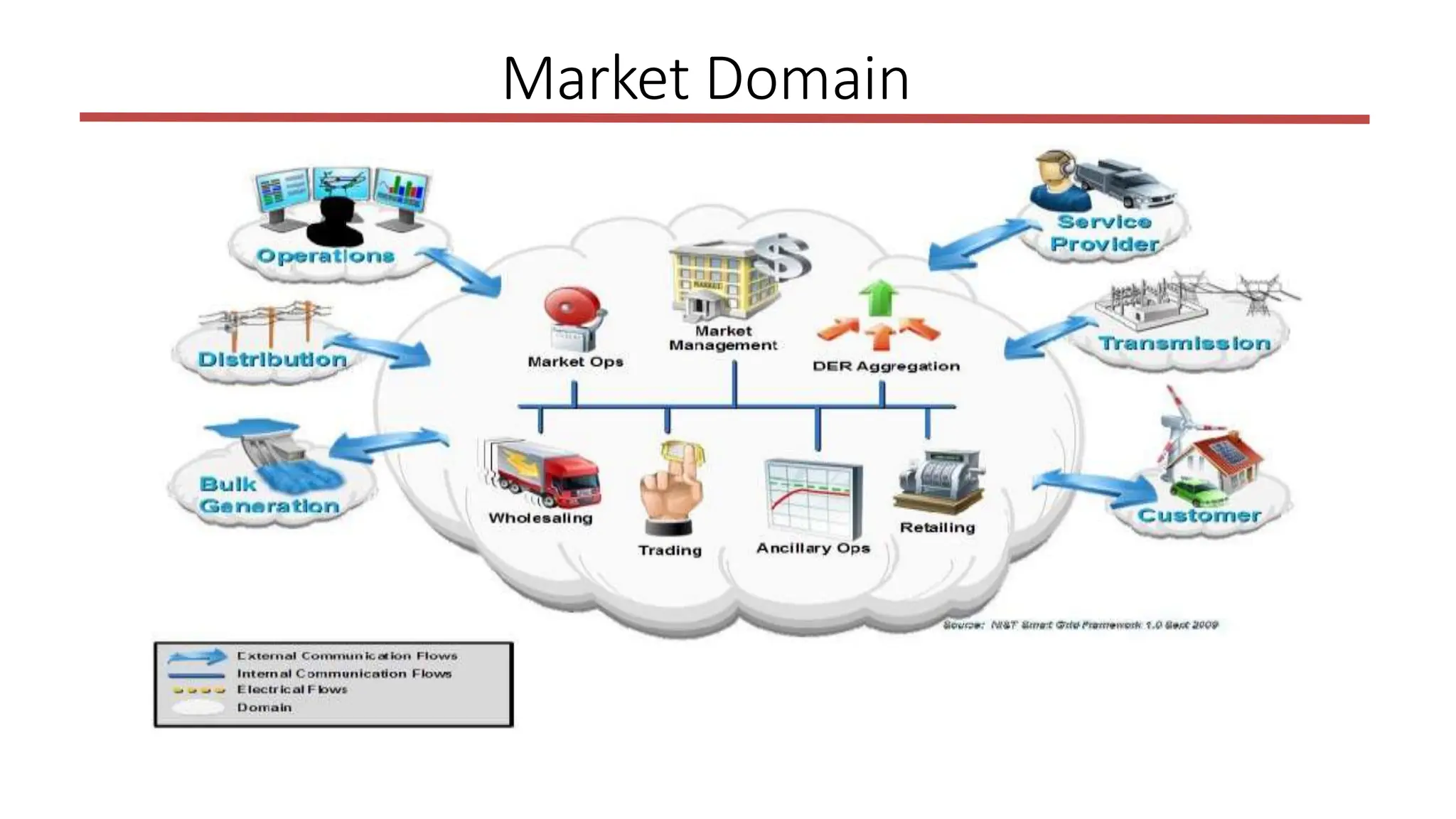
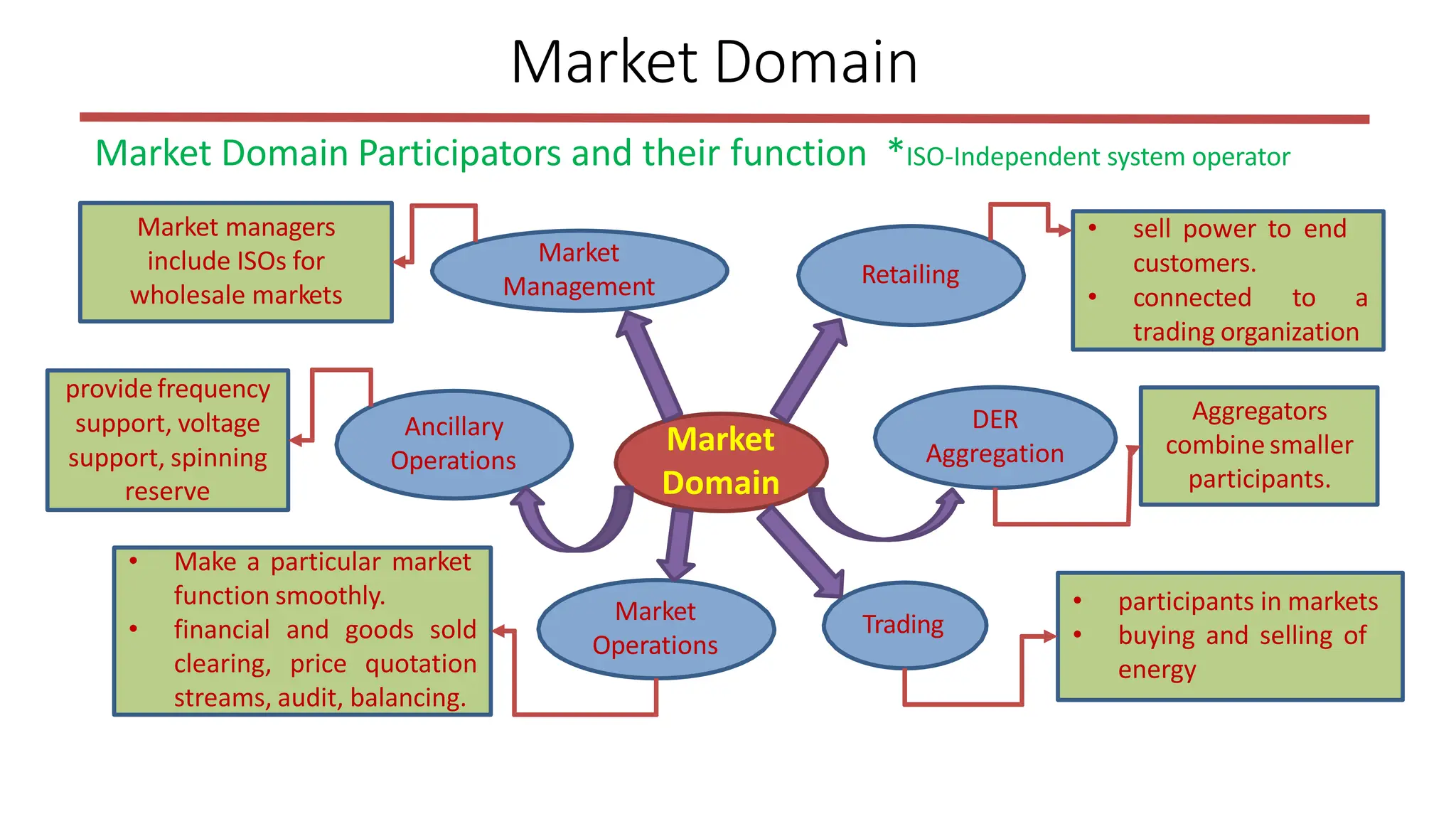
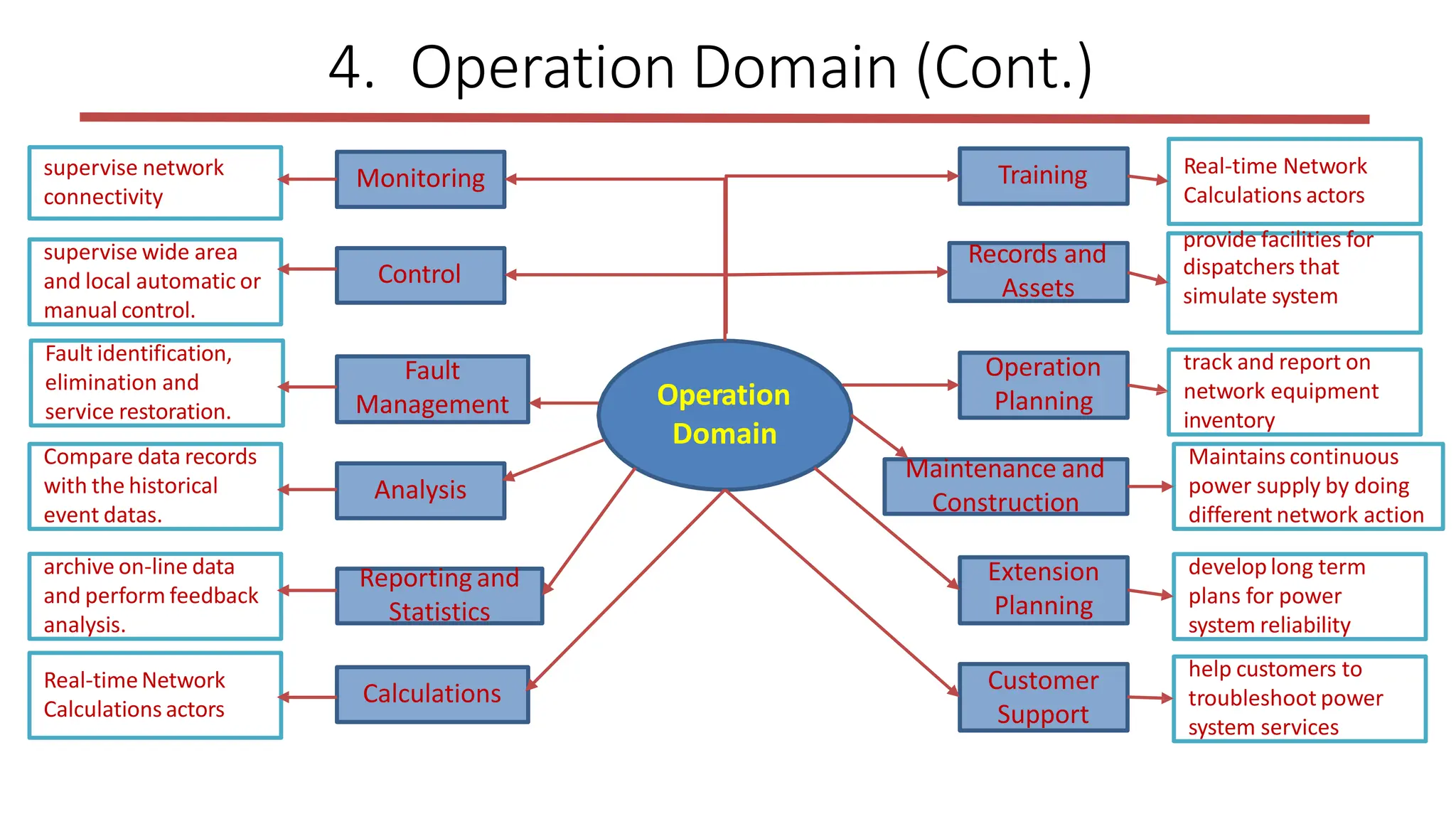
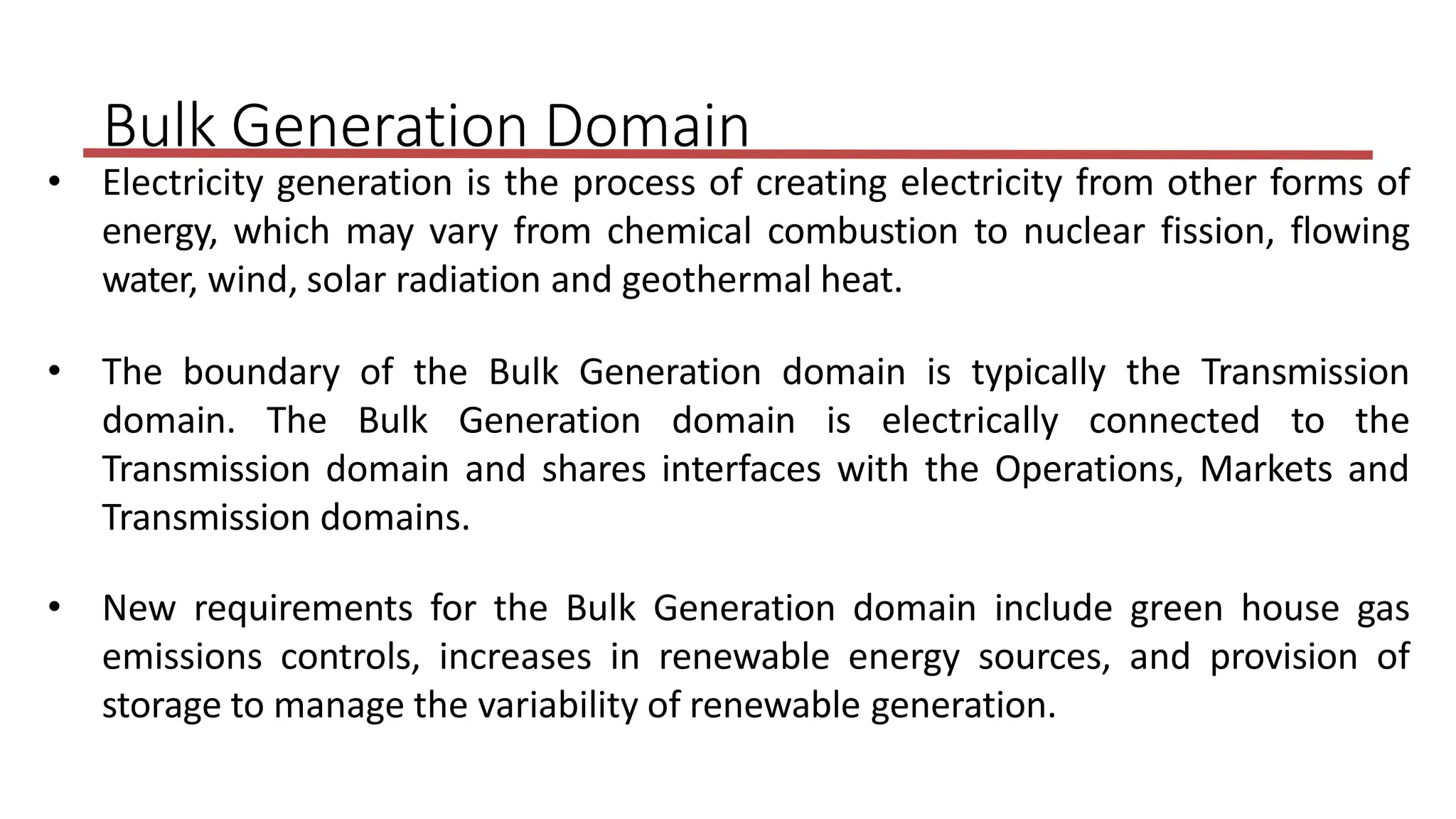
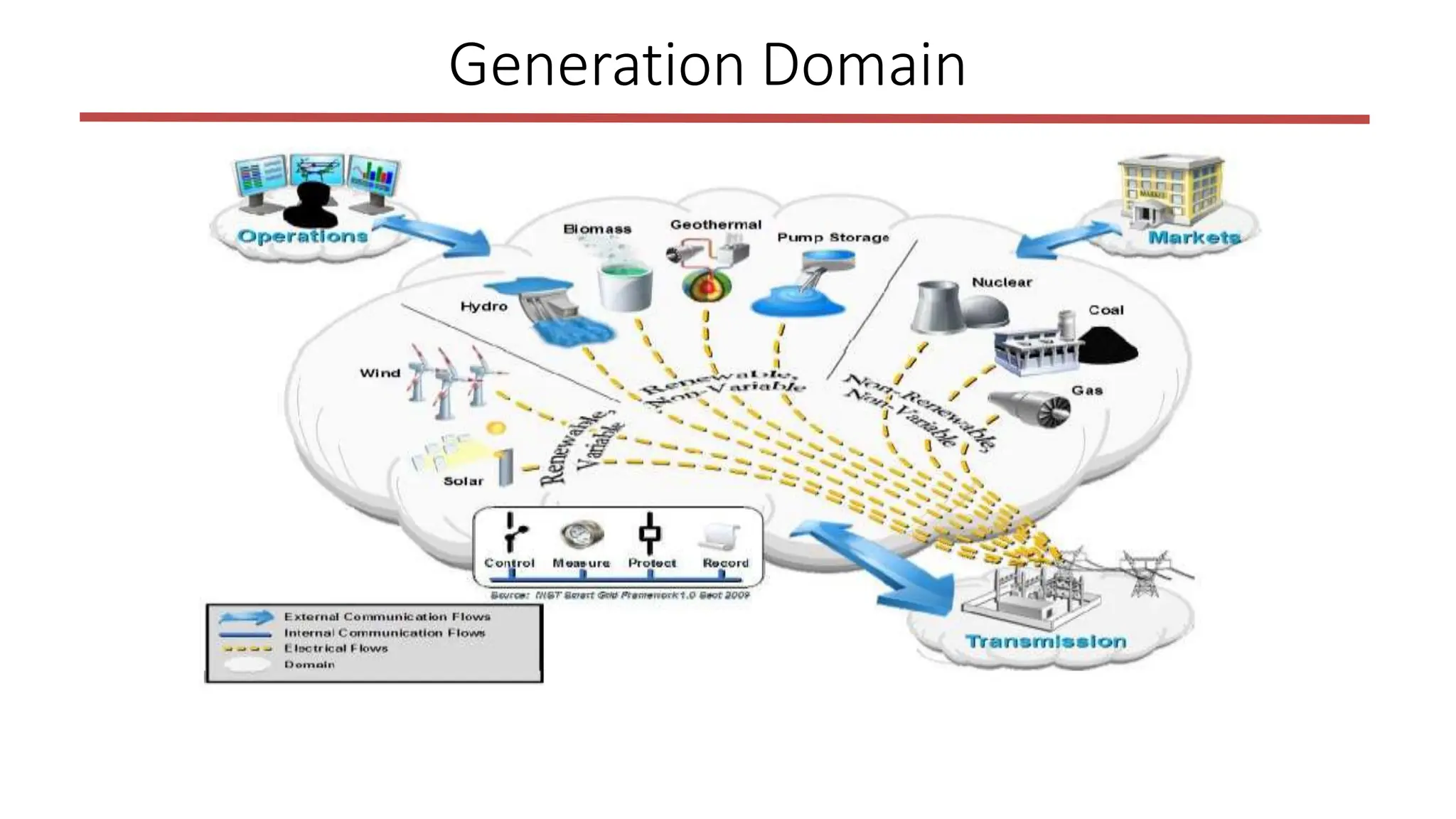
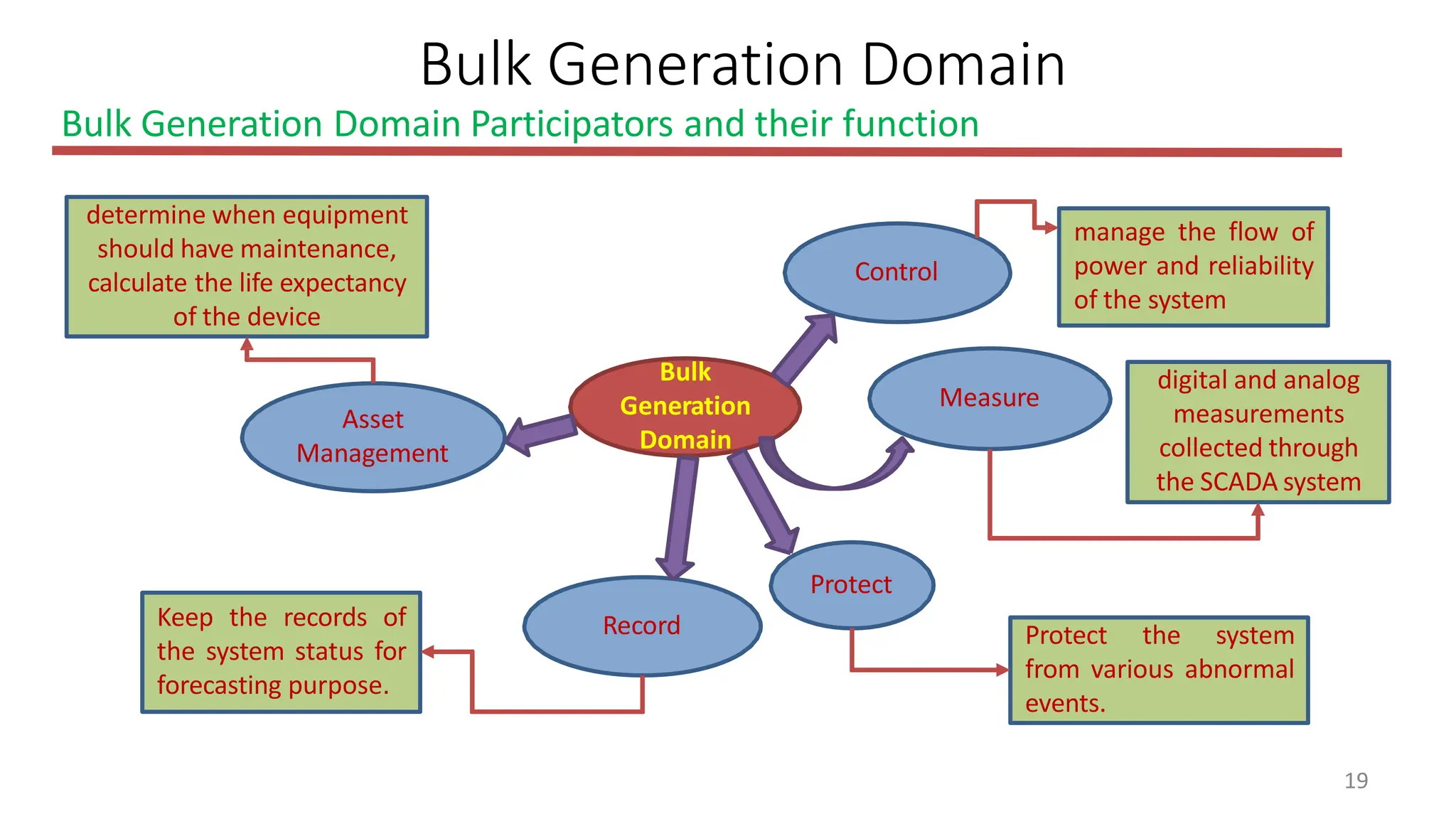
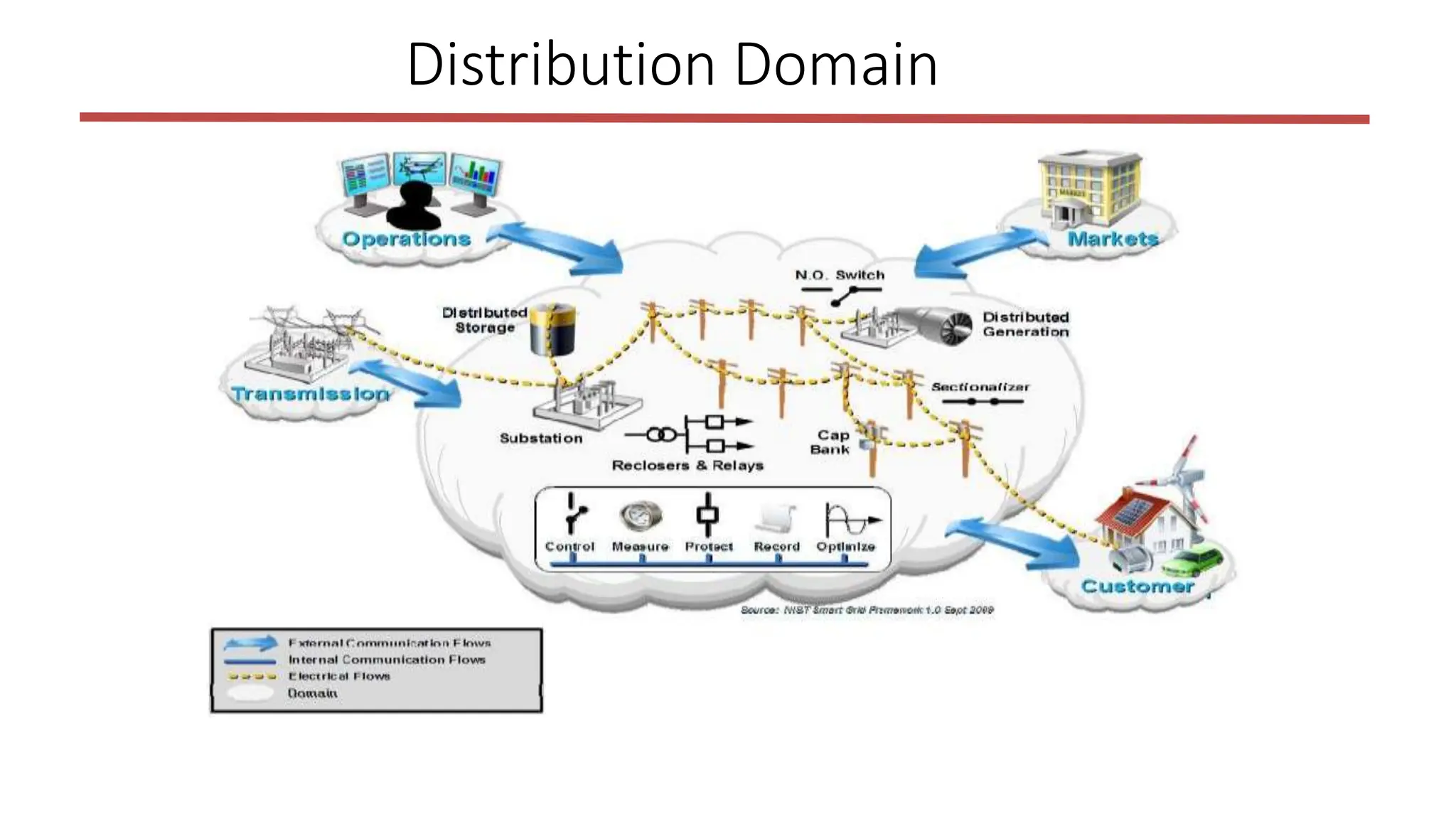
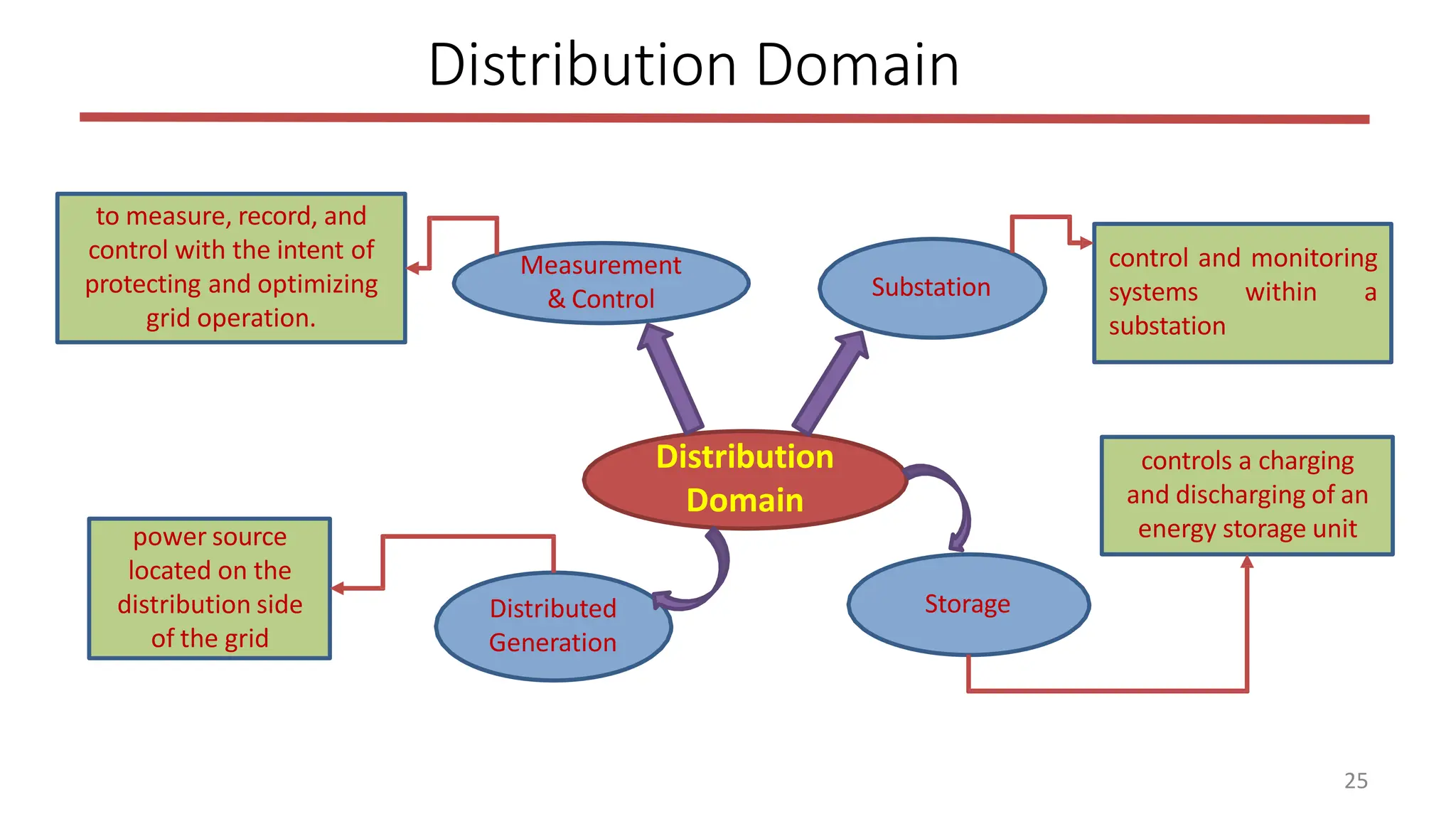
The document outlines the structure and functions of the smart grid, detailing various domains including customer, market, service provider, operations, bulk generation, transmission, and distribution. Each domain includes specific participants, their roles, and challenges associated with interoperability, energy management, and market operations. The emphasis is placed on the integration of advanced technologies for efficient energy distribution and management while addressing environmental factors and customer interactions.