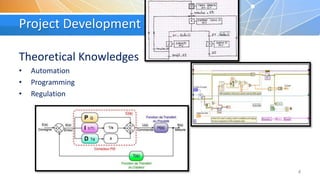
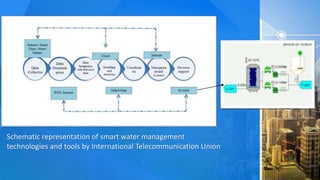
The document summarizes a proposed water regulation system project that aims to:
1) Regulate water supply according to season, time of day, and type of day.
2) Enable users to monitor water consumption in real-time.
3) Prevent excessive water use and detect leaks.
The system would use sensors like the Waspmote Smarwater sensor to measure water quality parameters and the Rosemount flow meter to monitor flow rates and consumption. It seeks to more efficiently manage water supply and help address increasing global water demands.