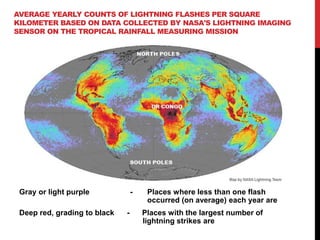
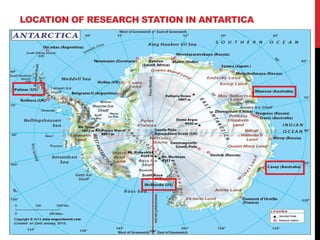
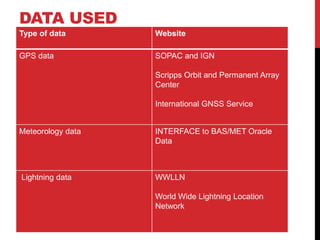
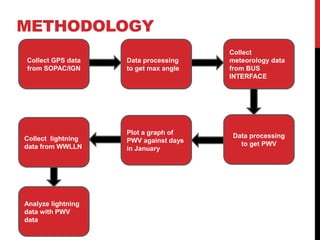
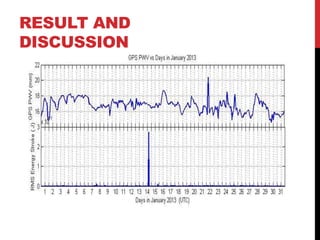
This document summarizes a student's research comparing lightning data from the World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN) in Antarctica to GPS precipitable water vapor (PWV) data. The student analyzed GPS PWV and lightning data from four Antarctic research stations between January 2013. On some days, GPS PWV increased before lightning occurred and decreased after, while on other days high GPS PWV did not coincide with lightning. The student concludes there is no direct correlation between GPS PWV and lightning in Antarctica and plans to further review literature and write a final report.