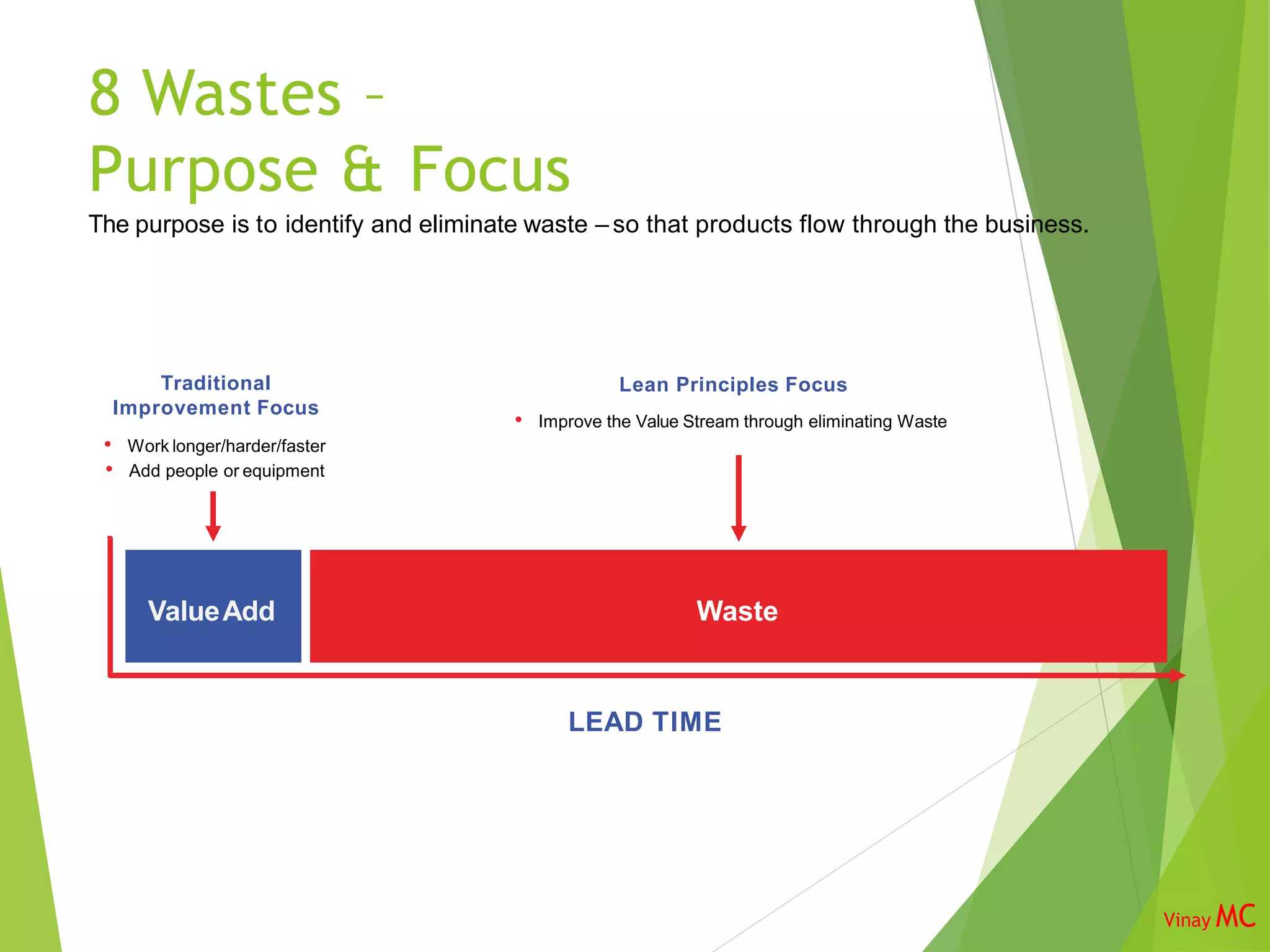
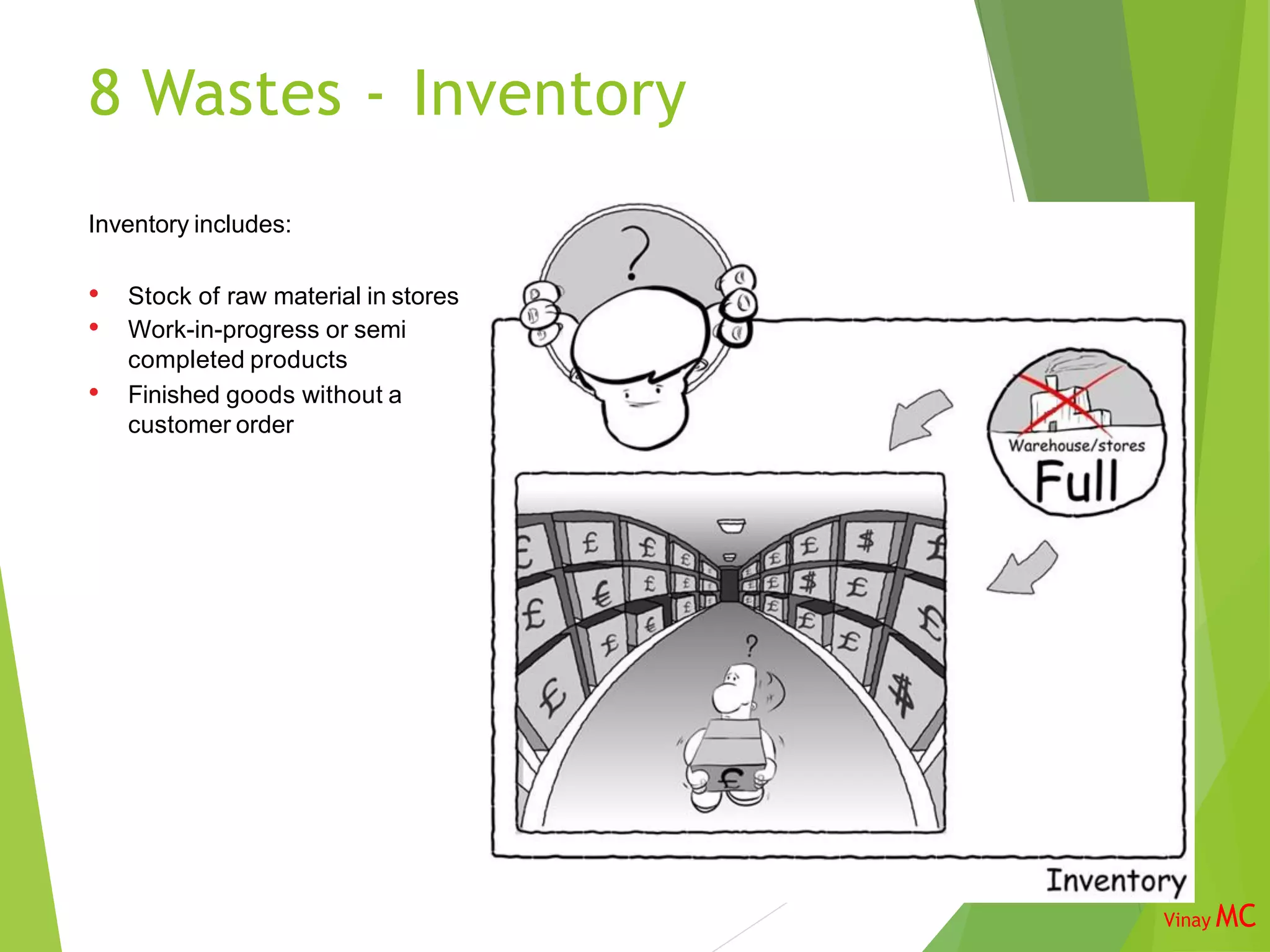
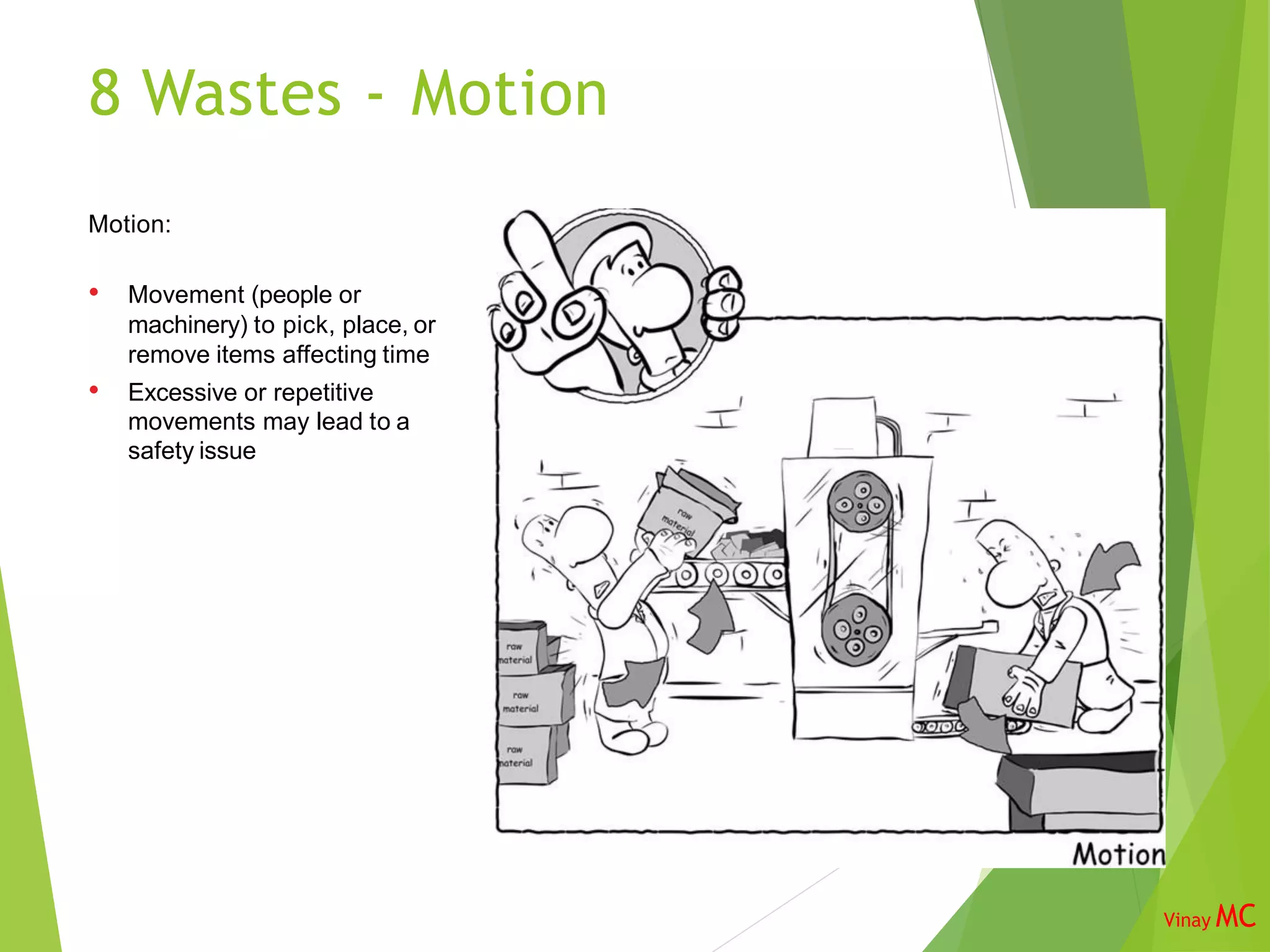
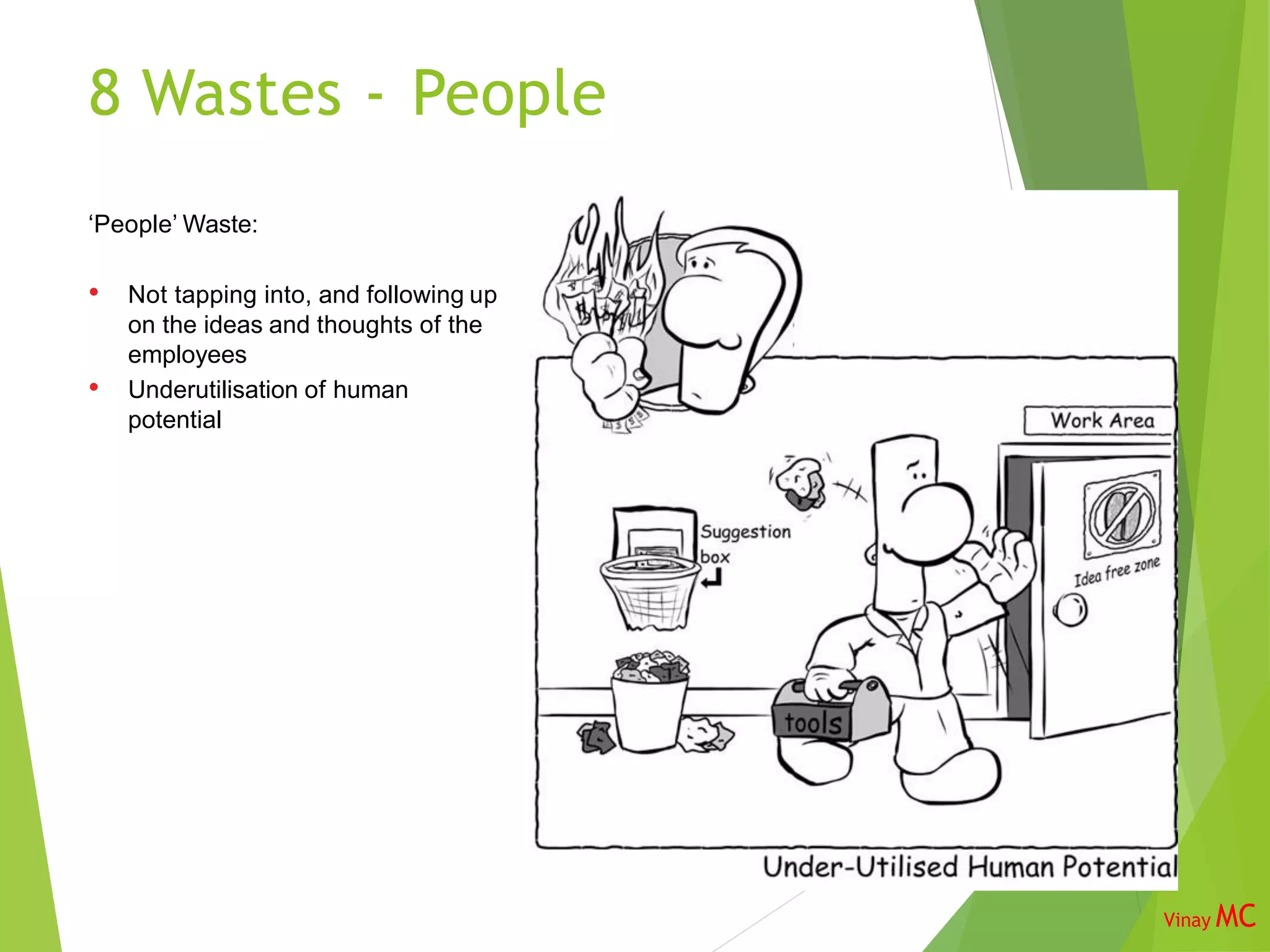
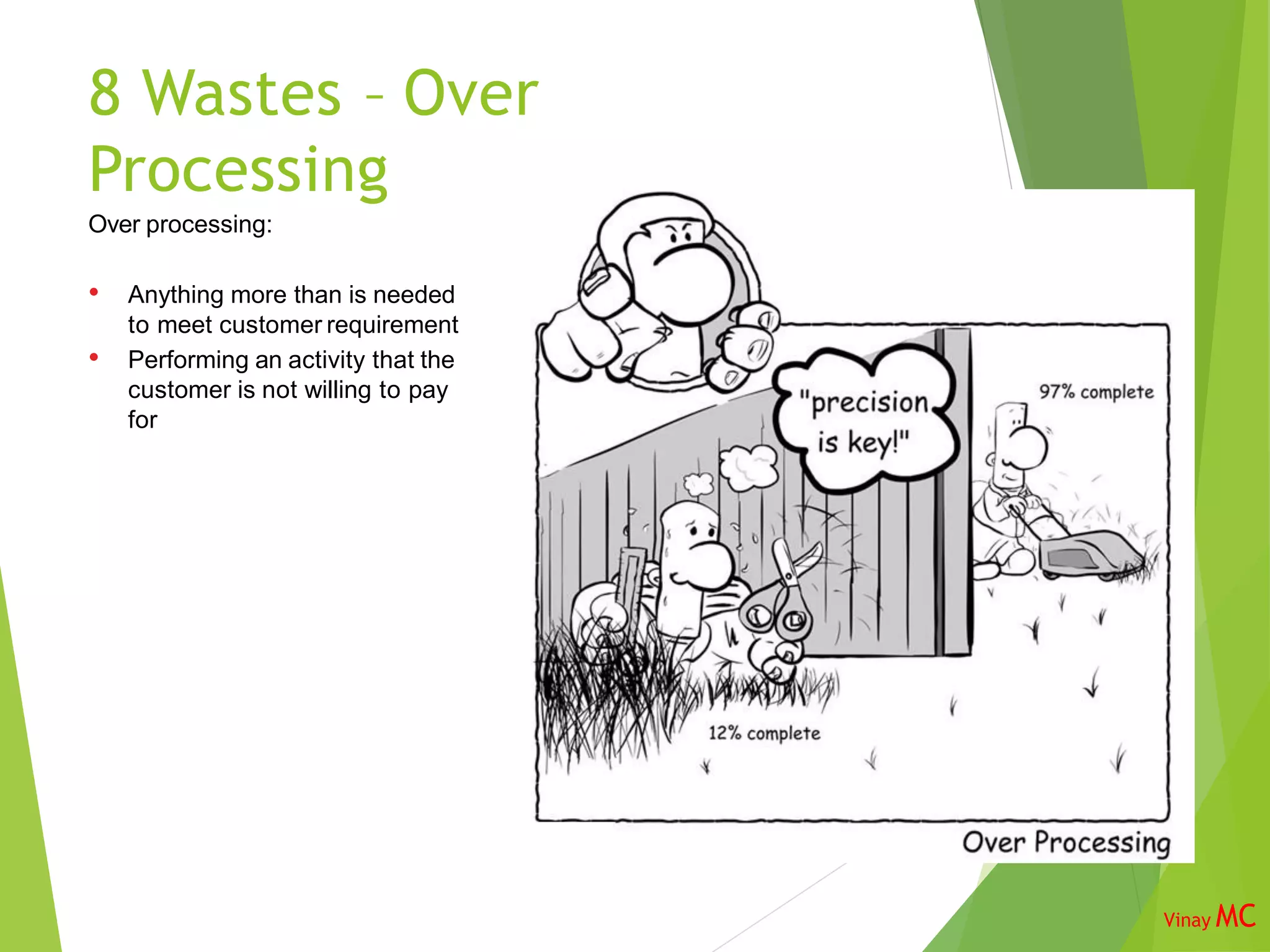
The document discusses the 8 wastes framework in Lean Six Sigma. It identifies the 8 categories of waste as transportation, inventory, motion, unused talent of employees, waiting, overproduction, overprocessing, and defects. The purpose is to identify and eliminate non-value adding activities to improve flow through the business and optimize costs, quality, safety, and employee utilization. Implementing the 8 wastes approach requires involvement from various roles across the organization.