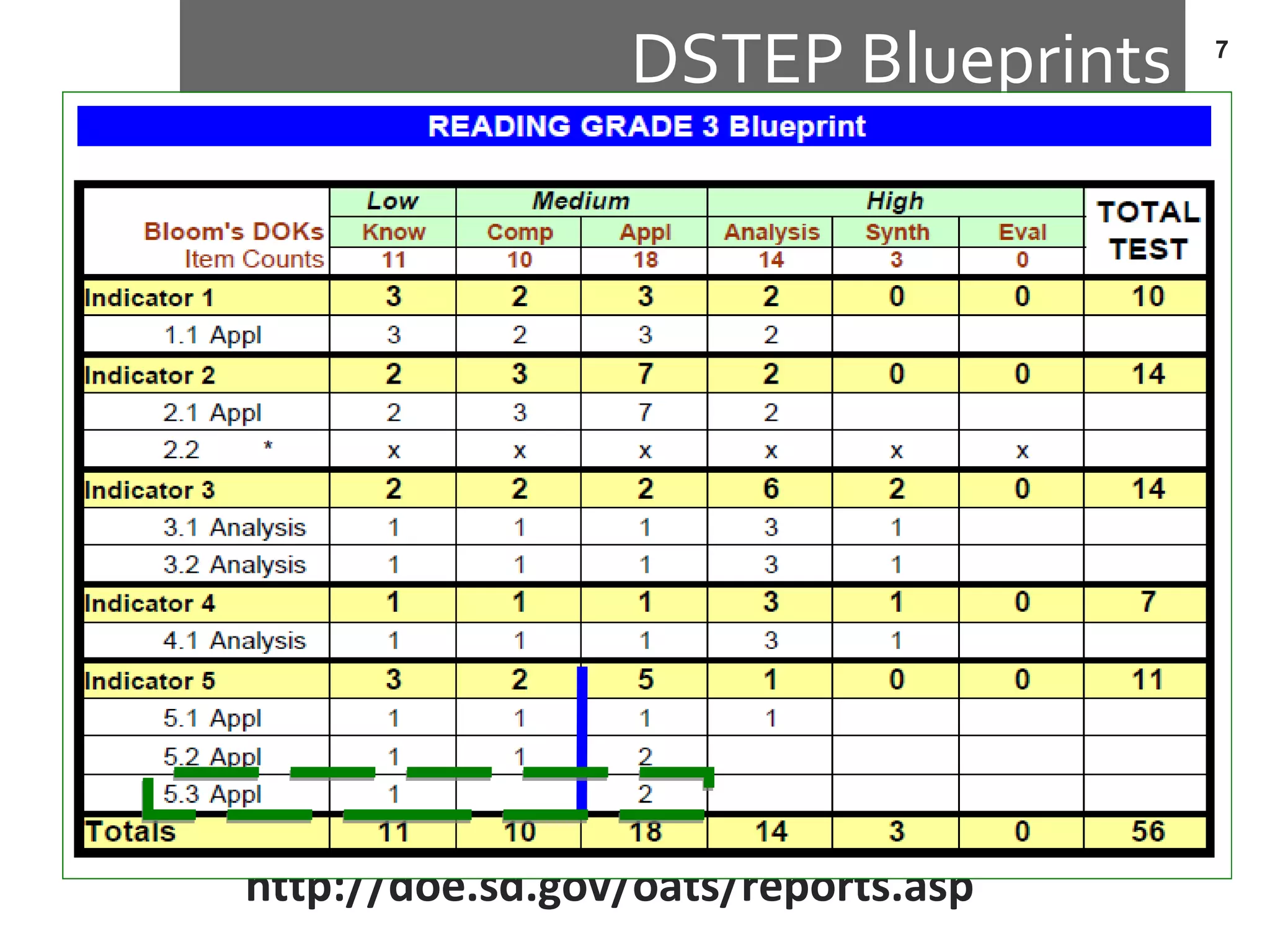
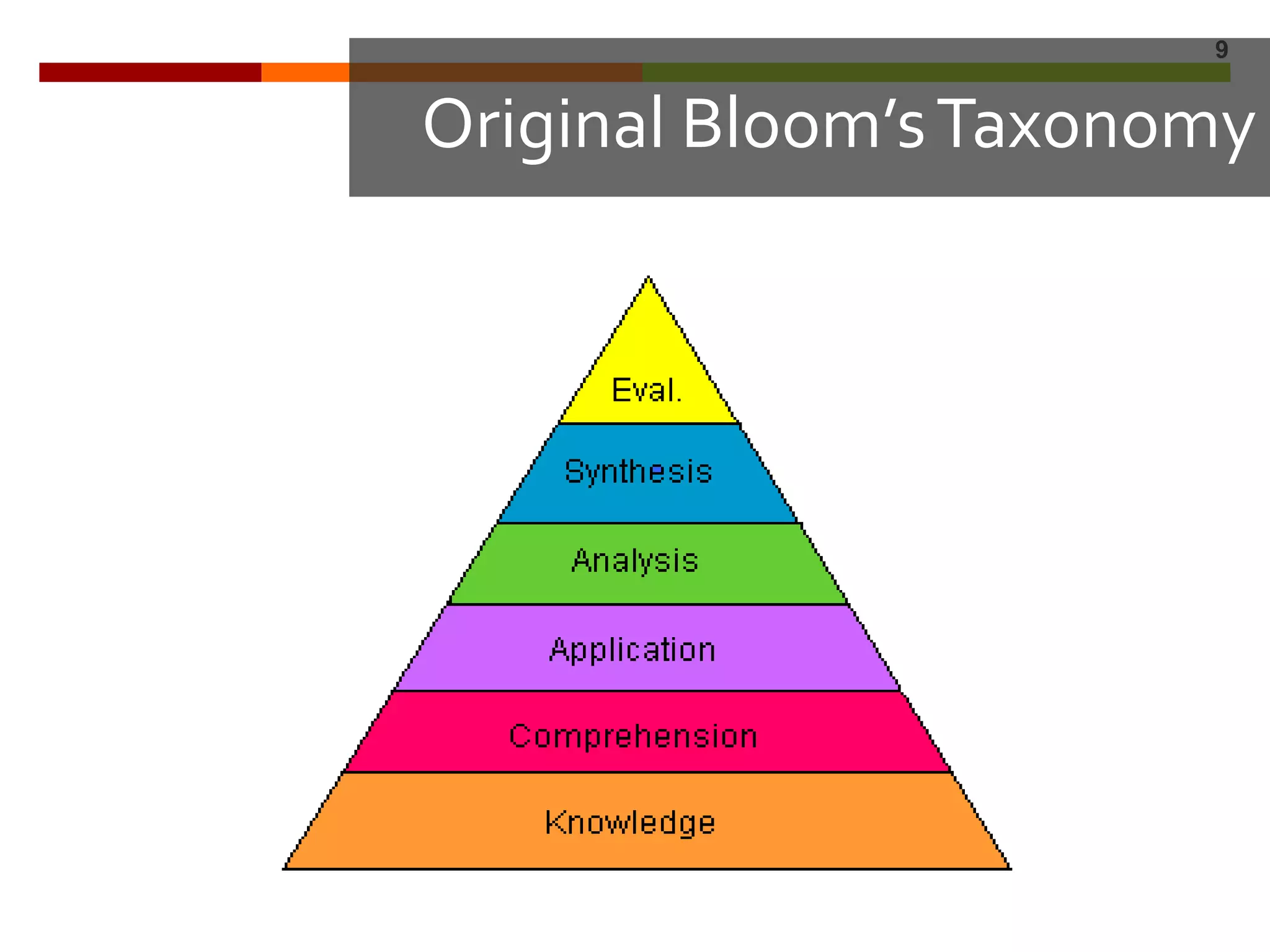
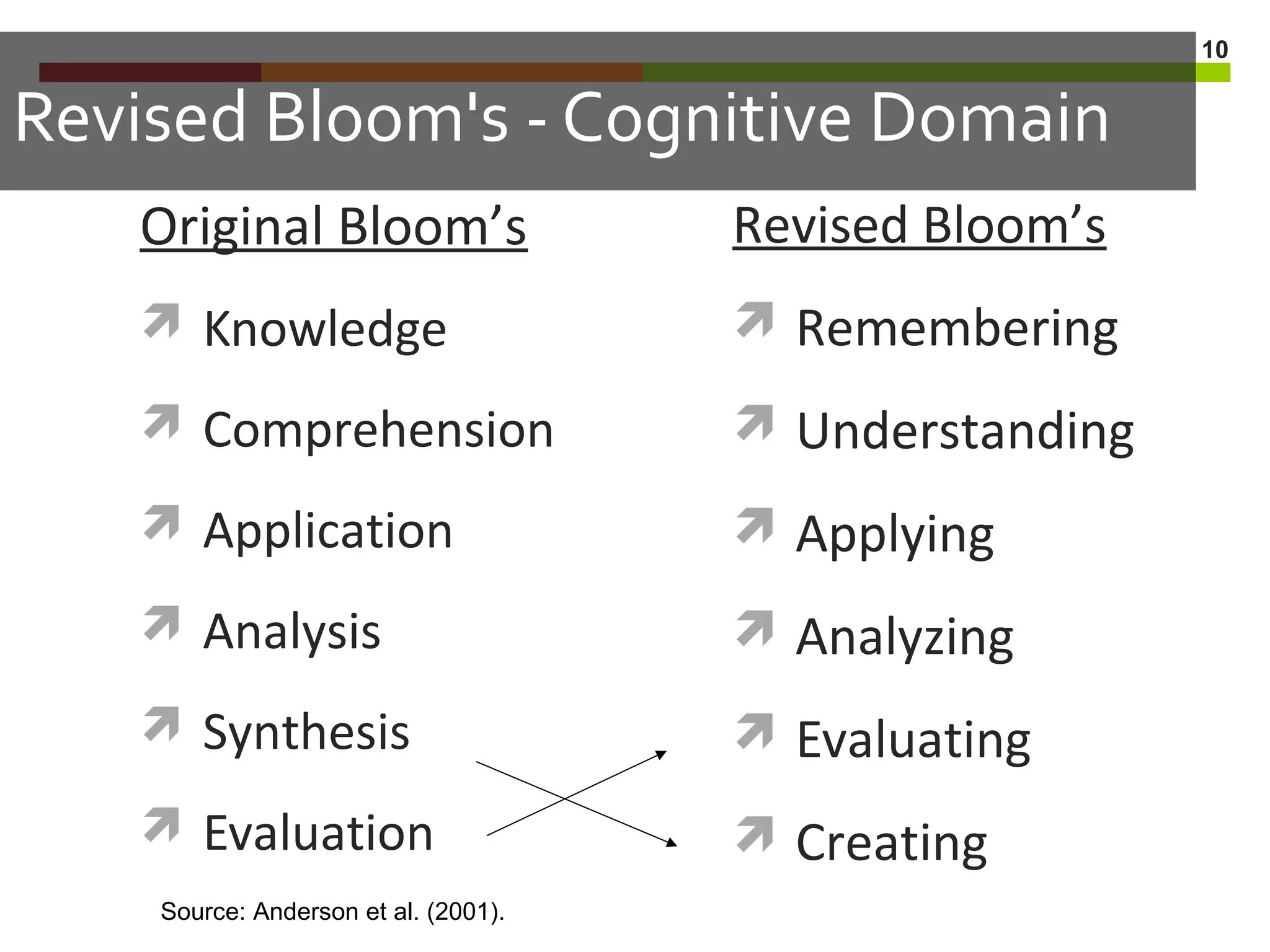
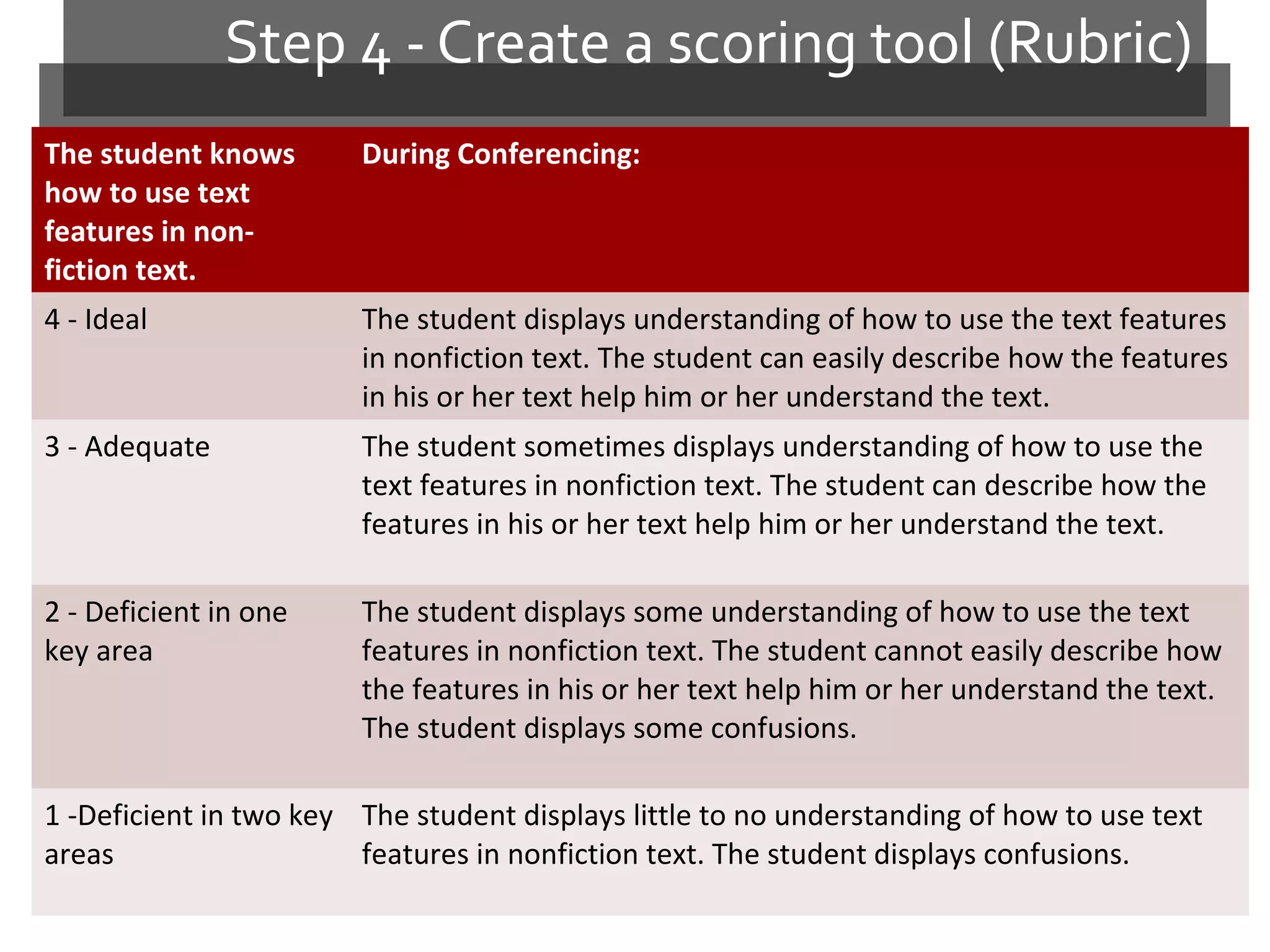
This document discusses standards-based instructional practices. It notes that scores on South Dakota reading assessments have been low in certain areas. It presents hypotheses for this, including that classroom rigor may not match assessment rigor. It introduces the Standards In Practice model, a 6-step process for ensuring classroom assignments demonstrate proficiency in content standards. Steps include completing assignments, analyzing task demands, identifying standards, creating rubrics, scoring student work, and revising instruction based on results. Bloom's Taxonomy and rigor are discussed in the context of aligning standards, instruction, and assessment.