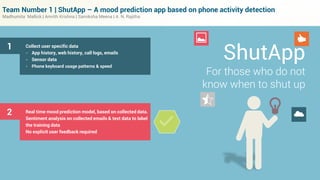
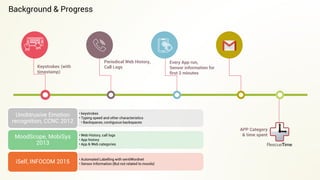
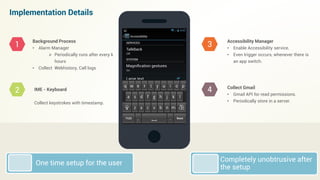
This document describes an app called ShutApp that predicts a user's mood based on their phone activity and data collected from the phone without explicit user feedback. It collects data like app usage, call logs, keyboard usage patterns, and analyzes emails to label training data. It then builds a real-time mood prediction model using this collected data and sentiment analysis. The summary is:
1. ShutApp is a mood prediction app that collects phone usage data like app history, call logs, keyboard patterns without explicit user input to label training data.
2. It uses this collected data to build a real-time mood prediction model using sentiment analysis of emails and texts.
3. The app aims to predict a user